Open Datasets for AI-Enabled Radio Resource Control in Non-Terrestrial Networks

0
⛏️
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Strategies for resource allocation can enhance the capabilities and reliability of non-terrestrial networks (NTN)
- This leads to improved spectrum utilization, meeting quality of service (QoS) requirements, and overall system optimization
- Allocating resources in a multi-constellation system with heterogeneous satellite links and dynamic user traffic is challenging
- Artificial intelligence (AI) can help mitigate these complexities and minimize overhead
- Real-world open datasets are crucial for developing AI models to address radio control optimization problems
Plain English Explanation
Non-terrestrial networks (NTNs), such as satellite systems, have the potential to provide a wide range of applications and services across various domains. However, effectively managing the resources in these complex, multi-constellation systems with diverse satellite links and dynamic user demand can be challenging. By implementing effective resource allocation strategies, the capabilities and reliability of NTNs can be enhanced, leading to better spectrum utilization, meeting quality of service (QoS) requirements, and overall system optimization.
To address these challenges, there is a growing shift towards utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) for intelligent decision-making and resource management. AI has the ability to handle the complexities and dynamics of these systems more effectively, minimizing the overhead and ensuring fair resource distribution.
Real-world open datasets play a pivotal role in the development of these AI models. Datasets representing realistic traffic patterns, network performances, and demand for fixed and dynamic user terminals can enable the creation of advanced resource management solutions. However, acquiring suitable datasets can be a significant challenge. This paper aims to identify and publish pertinent real-world open datasets to inspire and assist the research community in developing innovative solutions to the resource allocation optimization problems in NTNs.
Technical Explanation
The paper emphasizes the importance of effective resource allocation strategies in enhancing the capabilities and reliability of non-terrestrial networks (NTNs). By optimizing resource utilization, the authors aim to improve spectrum utilization, meet quality of service (QoS) requirements, and achieve overall system optimization.
Allocating resources in a multi-constellation system with heterogeneous satellite links and highly dynamic user traffic demand poses significant challenges. To mitigate these complexities and minimize the overhead, the paper highlights the growing trend of utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) for intelligent decision-making and resource management.
The researchers recognize the pivotal role of real-world open datasets in the development of AI models addressing radio control optimization problems. Datasets representing realistic traffic patterns, network performances, and demand for fixed and dynamic user terminals can enable the creation of advanced resource management solutions.
However, the authors acknowledge that acquiring suitable datasets can be arduous. Therefore, this paper aims to identify and publish pertinent real-world open datasets to inspire and assist the research community in crafting innovative solutions to the resource allocation optimization challenges in NTNs.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a well-structured and comprehensive approach to addressing the resource allocation challenges in non-terrestrial networks (NTNs). The authors recognize the importance of effective resource management strategies and the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to mitigate the complexities involved.
One potential limitation of the research is the availability and quality of the real-world open datasets. The authors highlight the difficulties in acquiring suitable datasets, which could pose a barrier to the development of robust AI models. While the paper identifies several relevant datasets, the representation of realistic traffic patterns, network performances, and user demand across diverse scenarios may still be limited.
Additionally, the paper does not delve into the specific AI techniques or algorithms that could be employed for resource management optimization. Further research and experimentation may be necessary to determine the most effective AI-based approaches for this complex problem domain.
Despite these potential limitations, the paper establishes a solid foundation for the research community to build upon. The identification and publication of pertinent open datasets can serve as a valuable resource, enabling researchers to develop and benchmark innovative solutions for resource allocation optimization in NTNs.
Conclusion
This paper highlights the critical importance of effective resource allocation strategies in enhancing the capabilities and reliability of non-terrestrial networks (NTNs). By optimizing resource utilization, NTNs can achieve improved spectrum usage, meet quality of service (QoS) requirements, and achieve overall system optimization.
The paper emphasizes the growing trend of utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) to mitigate the complexities and dynamics involved in resource management within multi-constellation NTN systems. Real-world open datasets play a pivotal role in the development of these AI-based solutions, enabling researchers to create innovative approaches to address the resource allocation optimization challenges.
By identifying and publishing pertinent open datasets, the authors aim to inspire and assist the research community in crafting advanced resource management solutions for NTNs. This work lays the foundation for further research and development, ultimately driving the advancement of NTN technologies and their widespread adoption across various domains.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
⛏️

0
Open Datasets for AI-Enabled Radio Resource Control in Non-Terrestrial Networks
Husnain Shahid, Miguel Angel Vazquez, Laurent Reynaud, Fanny Parzysz, Musbah Shaat
By effectively implementing the strategies for resource allocation, the capabilities, and reliability of non-terrestrial networks (NTN) can be enhanced. This leads to enhance spectrum utilization performance while minimizing the unmet system capacity, meeting quality of service (QoS) requirements and overall system optimization. In turn, a wide range of applications and services in various domains can be supported. However, allocating resources in a multi-constellation system with heterogeneous satellite links and highly dynamic user traffic demand pose challenges in ensuring sufficient and fair resource distribution. To mitigate these complexities and minimize the overhead, there is a growing shift towards utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) for its ability to handle such problems effectively. This calls for the development of an intelligent decision-making controller using AI to efficiently manage resources in this complex environment. In this context, real-world open datasets play a pivotal role in the development of AI models addressing radio control optimization problems. As a matter of fact, acquiring suitable datasets can be arduous. Therefore, this paper identifies pertinent real-world open datasets representing realistic traffic pattern, network performances and demand for fixed and dynamic user terminals, enabling a variety of uses cases. The aim of gathering and publishing the information of these datasets are to inspire and assist the research community in crafting the advance resource management solutions. In a nutshell, this paper establishes a solid foundation of commercially accessible data, with the potential to set benchmarks and accelerate the resolution of resource allocation optimization challenges.
Read more4/22/2024

0
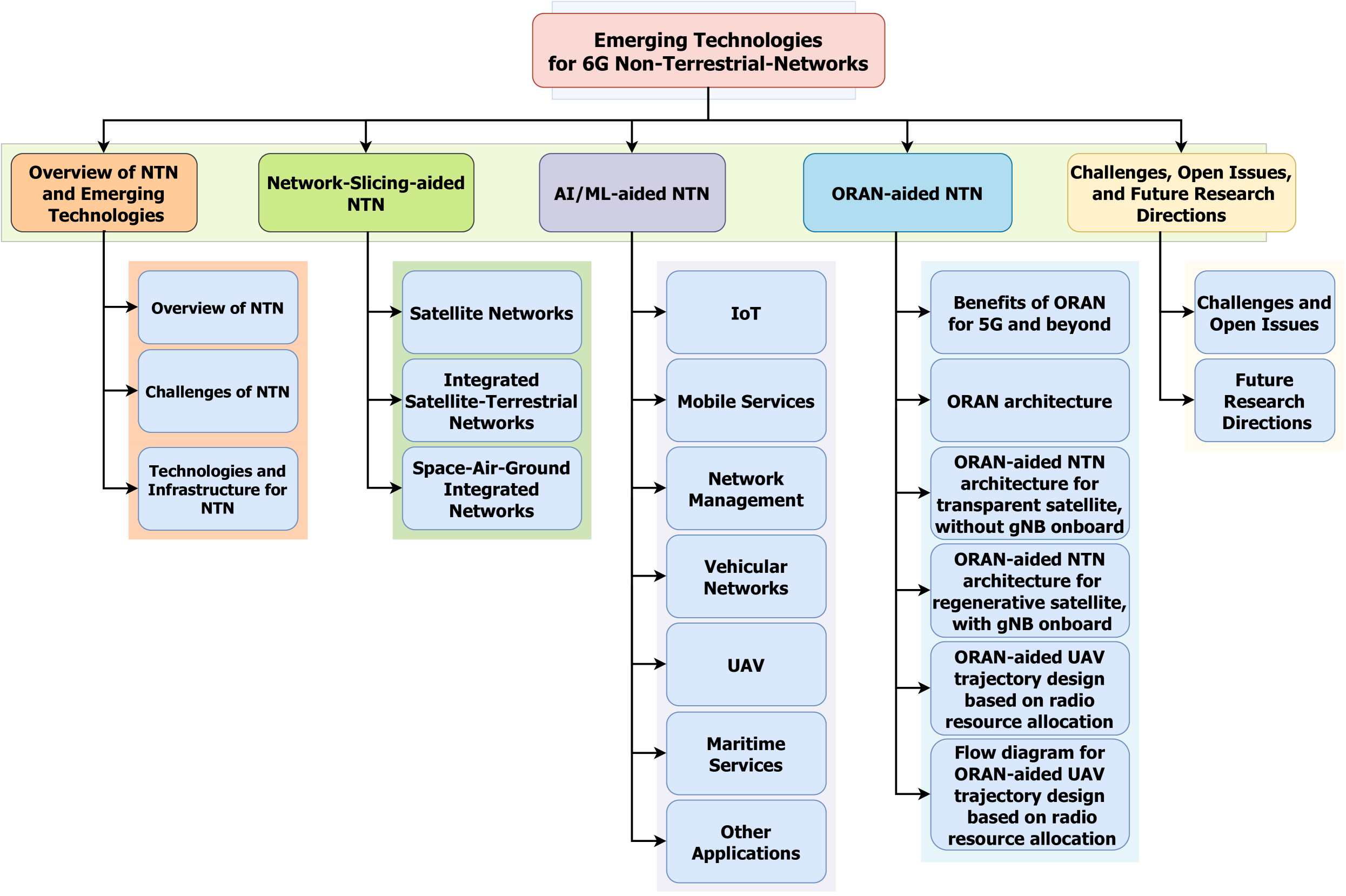
Emerging Technologies for 6G Non-Terrestrial-Networks: From Academia to Industrial Applications
Cong T. Nguyen, Yuris Mulya Saputra, Nguyen Van Huynh, Tan N. Nguyen, Dinh Thai Hoang, Diep N Nguyen, Van-Quan Pham, Miroslav Voznak, Symeon Chatzinotas, Dinh-Hieu Tran
Terrestrial networks form the fundamental infrastructure of modern communication systems, serving more than 4 billion users globally. However, terrestrial networks are facing a wide range of challenges, from coverage and reliability to interference and congestion. As the demands of the 6G era are expected to be much higher, it is crucial to address these challenges to ensure a robust and efficient communication infrastructure for the future. To address these problems, Non-terrestrial Network (NTN) has emerged to be a promising solution. NTNs are communication networks that leverage airborne (e.g., unmanned aerial vehicles) and spaceborne vehicles (e.g., satellites) to facilitate ultra-reliable communications and connectivity with high data rates and low latency over expansive regions. This article aims to provide a comprehensive survey on the utilization of network slicing, Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML), and Open Radio Access Network (ORAN) to address diverse challenges of NTNs from the perspectives of both academia and industry. Particularly, we first provide an in-depth tutorial on NTN and the key enabling technologies including network slicing, AI/ML, and ORAN. Then, we provide a comprehensive survey on how network slicing and AI/ML have been leveraged to overcome the challenges that NTNs are facing. Moreover, we present how ORAN can be utilized for NTNs. Finally, we highlight important challenges, open issues, and future research directions of NTN in the 6G era.
Read more7/4/2024


0
Energy-efficient Functional Split in Non-terrestrial Open Radio Access Networks
S. M. Mahdi Shahabi, Xiaonan Deng, Ahmad Qidan, Taisir Elgorashi, Jaafar Elmirghani
This paper investigates the integration of Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) within non-terrestrial networks (NTN), and optimizing the dynamic functional split between Centralized Units (CU) and Distributed Units (DU) for enhanced energy efficiency in the network. We introduce a novel framework utilizing a Deep Q-Network (DQN)-based reinforcement learning approach to dynamically find the optimal RAN functional split option and the best NTN-based RAN network out of the available NTN-platforms according to real-time conditions, traffic demands, and limited energy resources in NTN platforms. This approach supports capability of adapting to various NTN-based RANs across different platforms such as LEO satellites and high-altitude platform stations (HAPS), enabling adaptive network reconfiguration to ensure optimal service quality and energy utilization. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of our method, offering significant improvements in energy efficiency and sustainability under diverse NTN scenarios.
Read more9/4/2024


0
Data Service Maximization in Integrated Terrestrial-Non-Terrestrial 6G Networks: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach
Nway Nway Ei, Kitae Kim, Yan Kyaw Tun, Zhu Han, Choong Seon Hong
Integrating terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks has emerged as a promising paradigm to fulfill the constantly growing demand for connectivity, low transmission delay, and quality of services (QoS). This integration brings together the strengths of the reliability of terrestrial networks, broad coverage and service continuity of non-terrestrial networks like low earth orbit satellites (LEOSats), etc. In this work, we study a data service maximization problem in space-air-ground integrated network (SAGIN) where the ground base stations (GBSs) and LEOSats cooperatively serve the coexisting aerial users (AUs) and ground users (GUs). Then, by considering the spectrum scarcity, interference, and QoS requirements of the users, we jointly optimize the user association, AU's trajectory, and power allocation. To tackle the formulated mixed-integer non-convex problem, we disintegrate it into two subproblems: 1) user association problem and 2) trajectory and power allocation problem. We formulate the user association problem as a binary integer programming problem and solve it by using the Gurobi optimizer. Meanwhile, the trajectory and power allocation problem is solved by the deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) method to cope with the problem's non-convexity and dynamic network environments. Then, the two subproblems are alternately solved by the proposed block coordinate descent algorithm. By comparing with the baselines in the existing literature, extensive simulations are conducted to evaluate the performance of the proposed framework.
Read more7/22/2024