Empathic Responding for Digital Interpersonal Emotion Regulation via Content Recommendation

1

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Examines how digital platforms can provide empathetic emotional support through content recommendations
- Proposes a framework for Empathic Responding for Digital Interpersonal Emotion Regulation (ERIDER)
- Explores the use of machine learning to analyze emotions in online interactions and recommend content to regulate user emotions
Plain English Explanation
Digital platforms, like social media, can play a role in helping people manage their emotions. The ERIDER framework explores how these platforms can provide empathetic emotional support by analyzing user emotions and recommending relevant content.
The key idea is that by understanding a user's emotional state, the platform can suggest content that helps regulate their emotions in a healthy way. For example, if a user is feeling sad, the platform could recommend uplifting or comforting content to help them feel better.
This approach aims to leverage the power of digital platforms to facilitate interpersonal emotion regulation - the process of helping others manage their emotions through social interaction. By providing personalized emotional support, the platform can potentially improve user well-being and foster more positive online experiences.
Technical Explanation
The ERIDER framework involves several key components:
-
Emotion Analysis: Machine learning models are used to analyze user-generated content and detect the emotional states expressed by users. This allows the platform to understand the user's emotional experiences.
-
Emotion Regulation Strategy Selection: Based on the detected emotional state, the platform selects an appropriate emotion regulation strategy, such as providing comforting or inspiring content.
-
Content Recommendation: The platform then recommends relevant content to the user, tailored to the selected emotion regulation strategy. This content is intended to help the user manage their emotions in a healthy way.
The paper presents experiments evaluating the effectiveness of this approach, demonstrating its potential to improve digital emotion regulation and foster more empathetic online interactions.
Critical Analysis
The ERIDER framework presents an interesting approach to leveraging digital platforms for interpersonal emotion regulation. However, the paper acknowledges some limitations and areas for further research:
- The emotion analysis models may not always accurately detect the user's true emotional state, which could lead to inappropriate content recommendations.
- The framework focuses on individual-level emotion regulation, but the dynamics of emotions in social media are complex and may involve group-level interactions that are not addressed.
- The long-term effects of this approach on user well-being and online communities are not fully explored and would require further study.
Additionally, there are potential ethical concerns around the use of machine learning to analyze and regulate user emotions without their explicit consent or understanding of the process. Careful consideration of privacy and transparency issues would be important in the real-world application of this technology.
Conclusion
The ERIDER framework presents a novel approach to leveraging digital platforms for interpersonal emotion regulation. By combining emotion analysis, regulation strategy selection, and personalized content recommendations, the framework aims to provide empathetic emotional support to users and foster more positive digital emotion regulation experiences.
While the research shows promise, further exploration of the potential benefits, limitations, and ethical implications of this approach would be valuable. As our reliance on digital platforms for social interaction continues to grow, developing effective strategies for supporting emotional well-being in these spaces will be an important area of ongoing research and development.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


1
Empathic Responding for Digital Interpersonal Emotion Regulation via Content Recommendation
Akriti Verma, Shama Islam, Valeh Moghaddam, Adnan Anwar, Sharon Horwood
Interpersonal communication plays a key role in managing people's emotions, especially on digital platforms. Studies have shown that people use social media and consume online content to regulate their emotions and find support for rest and recovery. However, these platforms are not designed for emotion regulation, which limits their effectiveness in this regard. To address this issue, we propose an approach to enhance Interpersonal Emotion Regulation (IER) on online platforms through content recommendation. The objective is to empower users to regulate their emotions while actively or passively engaging in online platforms by crafting media content that aligns with IER strategies, particularly empathic responding. The proposed recommendation system is expected to blend system-initiated and user-initiated emotion regulation, paving the way for real-time IER practices on digital media platforms. To assess the efficacy of this approach, a mixed-method research design is used, including the analysis of text-based social media data and a user survey. Digital applications has served as facilitators in this process, given the widespread recognition of digital media applications for Digital Emotion Regulation (DER). The study collects 37.5K instances of user posts and interactions on Reddit over a year to design a Contextual Multi-Armed Bandits (CMAB) based recommendation system using features from user activity and preferences. The experimentation shows that the empathic recommendations generated by the proposed recommendation system are preferred by users over widely accepted ER strategies such as distraction and avoidance.
Read more8/16/2024


0
Quantification of the Self-Excited Emotion Dynamics in Online Interactions
Yishan (Ivy), Luo, Didier Sornette, Sandro Claudio Lera
Emotions are essential for guiding human behavior, particularly in social interactions. In modern societies, a growing share of human interactions are taking place online which has been shown to amplify and distort the expression and perception of emotions. However, the entanglement across different emotions is not fully understood. We use a multivariate Hawkes self-excited point process to model and calibrate the temporal expressions of six basic emotions in YouTube live chats. This allows us to understand interdependencies among emotions, but also to disentangle the influence from the video content and social interactions with peers. Positive emotions are found to be more contagious, while negative emotions tend to leave a longer-lasting impression on users' memories. Furthermore, we quantify the endogeneity of online emotion dynamics and find that peer interactions drive user emotional expressions 3-5 times more than passive content consumption. This underscores the powerful incentives of social interactions and the potential risk of emotional manipulation through the use of modern chatbots.
Read more8/13/2024
🤿

0
The Role of Emotions in Informational Support Question-Response Pairs in Online Health Communities: A Multimodal Deep Learning Approach
Mohsen Jozani, Jason A. Williams, Ahmed Aleroud, Sarbottam Bhagat
This study explores the relationship between informational support seeking questions, responses, and helpfulness ratings in online health communities. We created a labeled data set of question-response pairs and developed multimodal machine learning and deep learning models to reliably predict informational support questions and responses. We employed explainable AI to reveal the emotions embedded in informational support exchanges, demonstrating the importance of emotion in providing informational support. This complex interplay between emotional and informational support has not been previously researched. The study refines social support theory and lays the groundwork for the development of user decision aids. Further implications are discussed.
Read more5/24/2024
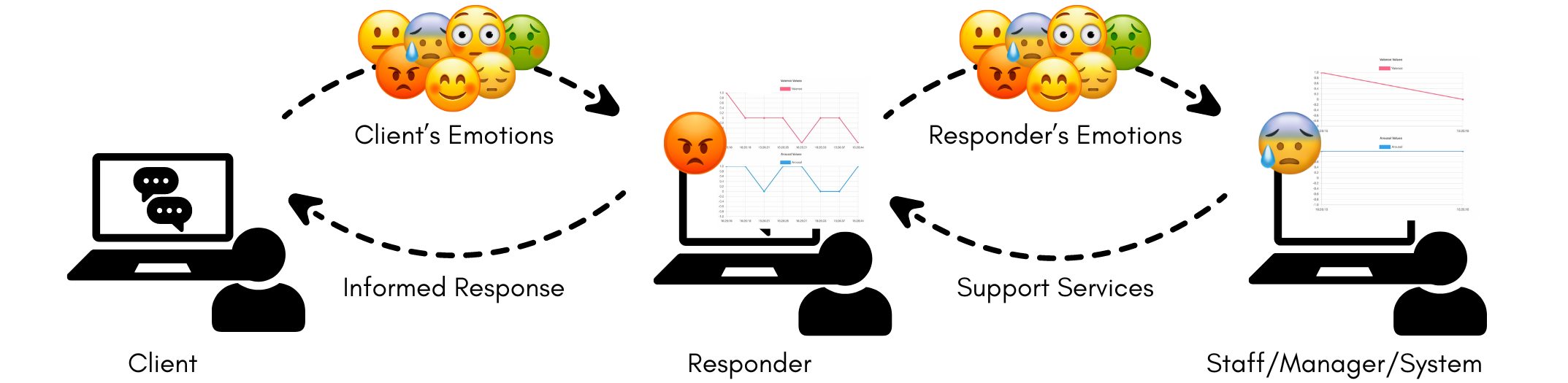

0
Towards Understanding Emotions for Engaged Mental Health Conversations
Kellie Yu Hui Sim, Kohleen Tijing Fortuno, Kenny Tsu Wei Choo
Providing timely support and intervention is crucial in mental health settings. As the need to engage youth comfortable with texting increases, mental health providers are exploring and adopting text-based media such as chatbots, community-based forums, online therapies with licensed professionals, and helplines operated by trained responders. To support these text-based media for mental health--particularly for crisis care--we are developing a system to perform passive emotion-sensing using a combination of keystroke dynamics and sentiment analysis. Our early studies of this system posit that the analysis of short text messages and keyboard typing patterns can provide emotion information that may be used to support both clients and responders. We use our preliminary findings to discuss the way forward for applying AI to support mental health providers in providing better care.
Read more6/18/2024