Towards Understanding Emotions for Engaged Mental Health Conversations
2406.11135

0
0
Abstract
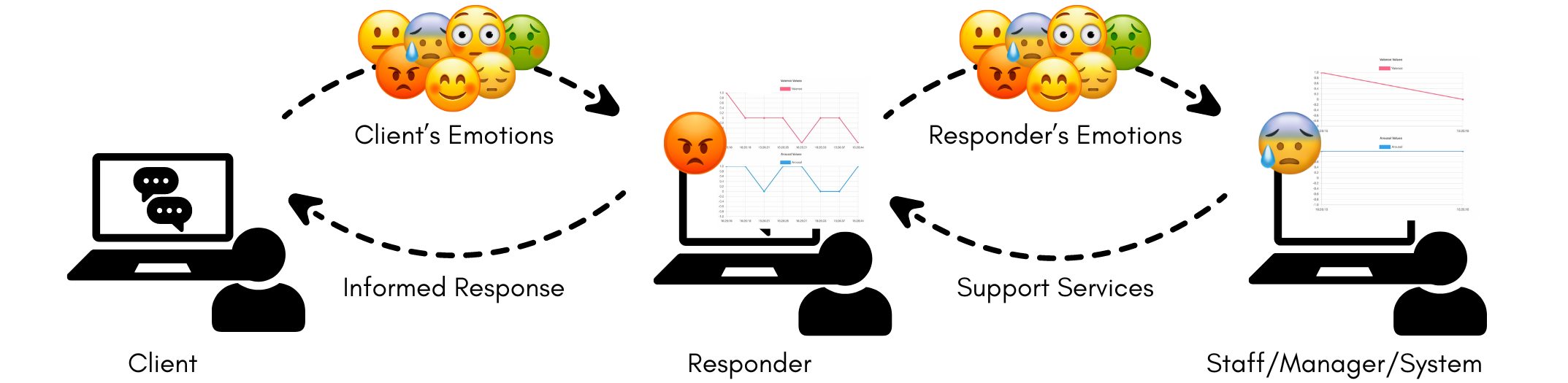
Providing timely support and intervention is crucial in mental health settings. As the need to engage youth comfortable with texting increases, mental health providers are exploring and adopting text-based media such as chatbots, community-based forums, online therapies with licensed professionals, and helplines operated by trained responders. To support these text-based media for mental health--particularly for crisis care--we are developing a system to perform passive emotion-sensing using a combination of keystroke dynamics and sentiment analysis. Our early studies of this system posit that the analysis of short text messages and keyboard typing patterns can provide emotion information that may be used to support both clients and responders. We use our preliminary findings to discuss the way forward for applying AI to support mental health providers in providing better care.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the use of emotion detection and analysis to improve mental health conversations.
- It investigates how various verbal cues, such as keystroke dynamics and sentiment analysis, can be leveraged to create more empathetic conversational interfaces for depression diagnosis and mental health support.
- The research aims to develop more effective digital mental health interventions that can foster engaged and meaningful conversations.
Plain English Explanation
This paper explores how technology can be used to better understand the emotional states of people during mental health conversations. The researchers looked at different ways to detect a person's emotions, such as by analyzing the speed and pattern of their typing (keystroke dynamics) or the sentiment expressed in their written responses (sentiment analysis).
The goal is to create conversational interfaces, like chatbots or virtual assistants, that can be more empathetic and engage people more effectively when discussing mental health issues like depression. By picking up on emotional cues, these systems could have more natural and supportive dialogues, potentially improving the delivery of digital mental health services.
The researchers want to develop technologies that can foster more engaged and meaningful conversations around mental health, which could lead to better outcomes for people seeking support or treatment.
Technical Explanation
The paper investigates how various verbal cues can be leveraged to create more empathetic and engaging conversational interfaces for mental health applications. Specifically, it explores the use of keystroke dynamics and sentiment analysis to passively detect user emotions during text-based interactions.
The researchers hypothesize that by incorporating these emotional signals, conversational interfaces can be designed to provide more personalized and responsive support for individuals dealing with mental health issues, such as depression.
Through a series of experiments and user studies, the paper examines how these verbal cues can be used to build digital mental health interventions that foster more engaged and meaningful conversations. The insights from this research aim to advance the development of empathetic and effective conversational agents for mental health applications.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to improving mental health conversations through the integration of emotion detection techniques. However, it acknowledges several limitations and areas for further research.
One key caveat is the reliance on text-based interactions, which may not fully capture the nuances of human emotional expression. Incorporating multimodal signals, such as facial expressions and vocal cues, could provide a more holistic understanding of user emotional states.
Additionally, the paper notes the need for longitudinal studies to assess the long-term impact of these conversational interfaces on user engagement and mental health outcomes. Careful consideration must be given to potential ethical and privacy concerns when deploying such technologies in sensitive mental health contexts.
Further research is also required to ensure the reliability and accuracy of the emotion detection algorithms, as misinterpreting user emotions could lead to unintended consequences.
Conclusion
This paper presents a compelling approach to enhancing mental health conversations through the integration of emotion detection technologies. By leveraging verbal cues like keystroke dynamics and sentiment analysis, the researchers aim to create more empathetic and engaging conversational interfaces for digital mental health interventions.
The insights from this work have the potential to advance the development of effective and personalized mental health support systems. However, careful consideration of the limitations and continued research in this area are necessary to ensure the safe and ethical deployment of such technologies in sensitive mental health contexts.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Revolutionizing Mental Health Support: An Innovative Affective Mobile Framework for Dynamic, Proactive, and Context-Adaptive Conversational Agents
Rahul Islam, Sang Won Bae

0
0
As we build towards developing interactive systems that can recognize human emotional states and respond to individual needs more intuitively and empathetically in more personalized and context-aware computing time. This is especially important regarding mental health support, with a rising need for immediate, non-intrusive help tailored to each individual. Individual mental health and the complex nature of human emotions call for novel approaches beyond conventional proactive and reactive-based chatbot approaches. In this position paper, we will explore how to create Chatbots that can sense, interpret, and intervene in emotional signals by combining real-time facial expression analysis, physiological signal interpretation, and language models. This is achieved by incorporating facial affect detection into existing practical and ubiquitous passive sensing contexts, thus empowering them with the capabilities to the ubiquity of sensing behavioral primitives to recognize, interpret, and respond to human emotions. In parallel, the system employs cognitive-behavioral therapy tools such as cognitive reframing and mood journals, leveraging the therapeutic intervention potential of Chatbots in mental health contexts. Finally, we propose a project to build a system that enhances the emotional understanding of Chatbots to engage users in chat-based intervention, thereby helping manage their mood.
6/26/2024
🏋️
Narrative Review of Support for Emotional Expressions in Virtual Reality: Psychophysiology of speech-to-text interfaces
Sunday David Ubur, Denis Gracanin

0
0
This narrative review on emotional expression in Speech-to-Text (STT) interfaces with Virtual Reality (VR) aims to identify advancements, limitations, and research gaps in incorporating emotional expression into transcribed text generated by STT systems. Using a rigorous search strategy, relevant articles published between 2020 and 2024 are extracted and categorized into themes such as communication enhancement technologies, innovations in captioning, emotion recognition in AR and VR, and empathic machines. The findings reveal the evolution of tools and techniques to meet the needs of individuals with hearing impairments, showcasing innovations in live transcription, closed captioning, AR, VR, and emotion recognition technologies. Despite improvements in accessibility, the absence of emotional nuance in transcribed text remains a significant communication challenge. The study underscores the urgency for innovations in STT technology to capture emotional expressions. The research discusses integrating emotional expression into text through strategies like animated text captions, emojilization tools, and models associating emotions with animation properties. Extending these efforts into AR and VR environments opens new possibilities for immersive and emotionally resonant experiences, especially in educational contexts. The study also explores empathic applications in healthcare, education, and human-robot interactions, highlighting the potential for personalized and effective interactions. The multidisciplinary nature of the literature underscores the potential for collaborative and interdisciplinary research.
5/24/2024

Incorporating Different Verbal Cues to Improve Text-Based Computer-Delivered Health Messaging
Samuel Rhys Cox

0
0
The ubiquity of smartphones has led to an increase in on demand healthcare being supplied. For example, people can share their illness-related experiences with others similar to themselves, and healthcare experts can offer advice for better treatment and care for remediable, terminal and mental illnesses. As well as this human-to-human communication, there has been an increased use of human-to-computer digital health messaging, such as chatbots. These can prove advantageous as they offer synchronous and anonymous feedback without the need for a human conversational partner. However, there are many subtleties involved in human conversation that a computer agent may not properly exhibit. For example, there are various conversational styles, etiquettes, politeness strategies or empathic responses that need to be chosen appropriately for the conversation. Encouragingly, computers are social actors (CASA) posits that people apply the same social norms to computers as they would do to people. On from this, previous studies have focused on applying conversational strategies to computer agents to make them embody more favourable human characteristics. However, if a computer agent fails in this regard it can lead to negative reactions from users. Therefore, in this dissertation we describe a series of studies we carried out to lead to more effective human-to-computer digital health messaging. In our first study, we use the crowd [...] Our second study investigates the effect of a health chatbot's conversational style [...] In our final study, we investigate the format used by a chatbot when [...] In summary, we have researched how to create more effective digital health interventions starting from generating health messages, to choosing an appropriate formality of messaging, and finally to formatting messages which reference a user's previous utterances.
4/23/2024
🚀
Empathy Through Multimodality in Conversational Interfaces
Mahyar Abbasian, Iman Azimi, Mohammad Feli, Amir M. Rahmani, Ramesh Jain

0
0
Agents represent one of the most emerging applications of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI, with their effectiveness hinging on multimodal capabilities to navigate complex user environments. Conversational Health Agents (CHAs), a prime example of this, are redefining healthcare by offering nuanced support that transcends textual analysis to incorporate emotional intelligence. This paper introduces an LLM-based CHA engineered for rich, multimodal dialogue-especially in the realm of mental health support. It adeptly interprets and responds to users' emotional states by analyzing multimodal cues, thus delivering contextually aware and empathetically resonant verbal responses. Our implementation leverages the versatile openCHA framework, and our comprehensive evaluation involves neutral prompts expressed in diverse emotional tones: sadness, anger, and joy. We evaluate the consistency and repeatability of the planning capability of the proposed CHA. Furthermore, human evaluators critique the CHA's empathic delivery, with findings revealing a striking concordance between the CHA's outputs and evaluators' assessments. These results affirm the indispensable role of vocal (soon multimodal) emotion recognition in strengthening the empathetic connection built by CHAs, cementing their place at the forefront of interactive, compassionate digital health solutions.
5/9/2024