Empathy Detection from Text, Audiovisual, Audio or Physiological Signals: Task Formulations and Machine Learning Methods
2311.00721

0
0
🔎
Abstract
Empathy indicates an individual's ability to understand others. Over the past few years, empathy has drawn attention from various disciplines, including but not limited to Affective Computing, Cognitive Science and Psychology. Detecting empathy has potential applications in society, healthcare and education. Despite being a broad and overlapping topic, the avenue of empathy detection leveraging Machine Learning remains underexplored from a systematic literature review perspective. We collected 828 papers from 10 well-known databases, systematically screened them and analysed the final 61 papers. Our analyses reveal several prominent task formulations $-$ including empathy on localised utterances or overall expressions, unidirectional or parallel empathy, and emotional contagion $-$ in monadic, dyadic and group interactions. Empathy detection methods are summarised based on four input modalities $-$ text, audiovisual, audio and physiological signals $-$ thereby presenting modality-specific network architecture design protocols. We discuss challenges, research gaps and potential applications in the Affective Computing-based empathy domain, which can facilitate new avenues of exploration. We further enlist the public availability of datasets and codes. We believe that our work is a stepping stone to developing a robust empathy detection system that can be deployed in practice to enhance the overall well-being of human life.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the topic of empathy detection using machine learning techniques.
- Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others, and it has applications in fields like affective computing, cognitive science, and psychology.
- The authors conducted a systematic literature review to analyze the current state of empathy detection using machine learning.
- They examined 828 papers from 10 databases and identified 61 relevant studies for in-depth analysis.
Plain English Explanation
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. It's an important skill for things like communication, relationships, and helping people. Over the past few years, researchers have been looking at how we can use machines, like computers and robots, to detect empathy.
The authors of this paper wanted to get a better understanding of the different ways researchers have been trying to detect empathy using machine learning. They looked at a lot of research papers on this topic and carefully selected 61 of them to analyze in-depth.
The key things they found were:
- There are different ways to think about empathy detection, like looking at specific conversations or overall interactions, or seeing if people are feeling the same emotions.
- Researchers have used different types of information to try to detect empathy, such as text, audio, video, and even physiological signals like heart rate.
- There are still some challenges and gaps in the research that need to be addressed to develop a really robust empathy detection system.
Overall, this paper provides a useful overview of the current state of empathy detection using machine learning. It could help guide future research and development in this important area.
Technical Explanation
The paper systematically reviews the current state of empathy detection using machine learning techniques. The authors collected 828 relevant papers from 10 well-known databases and carefully selected 61 for in-depth analysis.
Their analysis revealed several key task formulations for empathy detection:
- Detecting empathy in localized utterances or overall expressions
- Detecting unidirectional empathy (where one person empathizes with another) or parallel empathy (where both people empathize with each other)
- Detecting emotional contagion, where people's emotions synchronize
These empathy detection tasks were studied in the context of monadic (single person), dyadic (two-person), and group interactions.
The authors also summarized the different input modalities used for empathy detection, including text, audiovisual, audio, and physiological signals. They discussed the network architecture design protocols associated with each modality.
Additionally, the paper discusses the challenges, research gaps, and potential applications of empathy detection in the affective computing domain. The authors also list the public availability of relevant datasets and code.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of empathy detection using machine learning. However, there are a few limitations and areas for further research:
- The systematic review only included 61 papers out of an initial 828, so there may be other relevant work not captured in the analysis.
- The paper focuses on the technical aspects of empathy detection, but does not delve deeply into the ethical considerations or potential biases in the underlying datasets and models.
- While the paper discusses potential applications, it does not provide a critical assessment of the real-world feasibility and impact of deploying empathy detection systems, especially in sensitive domains like healthcare and education.
Future research could explore these areas in more depth, as well as investigate the generalizability of empathy detection models across different cultures and contexts. Additionally, more work is needed to understand the relationship between machine-detected empathy and human-perceived empathy.
Conclusion
This paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of empathy detection using machine learning techniques. It identifies key task formulations, input modalities, and architectural design protocols for empathy detection. The authors also discuss the challenges, research gaps, and potential applications of this technology.
While the paper highlights the progress made in this field, it also underscores the need for further research to address the ethical considerations, real-world feasibility, and cross-cultural generalizability of empathy detection systems. Ultimately, the development of robust and responsible empathy detection capabilities could have significant implications for enhancing human well-being in various domains.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Can Machines Resonate with Humans? Evaluating the Emotional and Empathic Comprehension of LMs
Muhammad Arslan Manzoor, Yuxia Wang, Minghan Wang, Preslav Nakov

0
0
Empathy plays a pivotal role in fostering prosocial behavior, often triggered by the sharing of personal experiences through narratives. However, modeling empathy using NLP approaches remains challenging due to its deep interconnection with human interaction dynamics. Previous approaches, which involve fine-tuning language models (LMs) on human-annotated empathic datasets, have had limited success. In our pursuit of improving empathy understanding in LMs, we propose several strategies, including contrastive learning with masked LMs and supervised fine-tuning with Large Language Models (LLMs). While these methods show improvements over previous methods, the overall results remain unsatisfactory. To better understand this trend, we performed an analysis which reveals a low agreement among annotators. This lack of consensus hinders training and highlights the subjective nature of the task. We also explore the cultural impact on annotations. To study this, we meticulously collected story pairs in Urdu language and find that subjectivity in interpreting empathy among annotators appears to be independent of cultural background. The insights from our systematic exploration of LMs' understanding of empathy suggest that there is considerable room for exploration in both task formulation and modeling.
6/18/2024

Can we say a cat is a cat? Understanding the challenges in annotating physiological signal-based emotion data
Pragya Singh, Mohan Kumar, Pushpendra Singh

0
0
Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms, trained on emotion data extracted from physiological signals, provide a promising approach to monitoring emotions, affect, and mental well-being. However, the field encounters challenges because there is a lack of effective methods for collecting high-quality data in everyday settings that genuinely reflect changes in emotion or affect. This paper presents a position discussion on the current technique of annotating physiological signal-based emotion data. Our discourse underscores the importance of adopting a nuanced understanding of annotation processes, paving the way for a more insightful exploration of the intricate relationship between physiological signals and human emotions.
6/24/2024
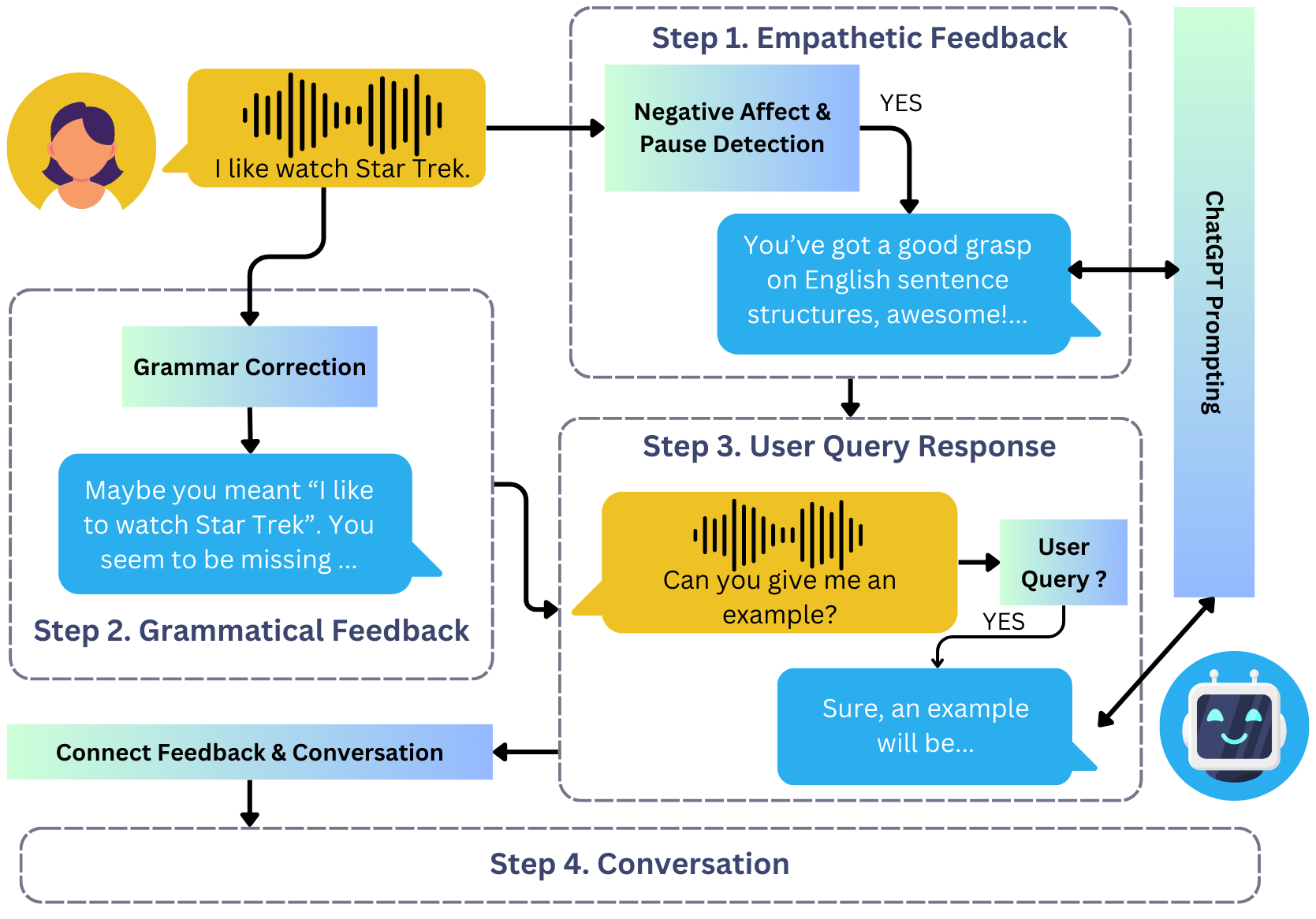
Using Adaptive Empathetic Responses for Teaching English
Li Siyan, Teresa Shao, Zhou Yu, Julia Hirschberg

0
0
Existing English-teaching chatbots rarely incorporate empathy explicitly in their feedback, but empathetic feedback could help keep students engaged and reduce learner anxiety. Toward this end, we propose the task of negative emotion detection via audio, for recognizing empathetic feedback opportunities in language learning. We then build the first spoken English-teaching chatbot with adaptive, empathetic feedback. This feedback is synthesized through automatic prompt optimization of ChatGPT and is evaluated with English learners. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our system through a preliminary user study.
4/23/2024
🖼️
EmpathyEar: An Open-source Avatar Multimodal Empathetic Chatbot
Hao Fei, Han Zhang, Bin Wang, Lizi Liao, Qian Liu, Erik Cambria

0
0
This paper introduces EmpathyEar, a pioneering open-source, avatar-based multimodal empathetic chatbot, to fill the gap in traditional text-only empathetic response generation (ERG) systems. Leveraging the advancements of a large language model, combined with multimodal encoders and generators, EmpathyEar supports user inputs in any combination of text, sound, and vision, and produces multimodal empathetic responses, offering users, not just textual responses but also digital avatars with talking faces and synchronized speeches. A series of emotion-aware instruction-tuning is performed for comprehensive emotional understanding and generation capabilities. In this way, EmpathyEar provides users with responses that achieve a deeper emotional resonance, closely emulating human-like empathy. The system paves the way for the next emotional intelligence, for which we open-source the code for public access.
6/24/2024