An empirical study to understand how students use ChatGPT for writing essays and how it affects their ownership
2405.13890

0
0
🎯
Abstract
As large language models (LLMs) become more powerful and ubiquitous, systems like ChatGPT are increasingly used by students to help them with writing tasks. To better understand how these tools are used, we investigate how students might use an LLM for essay writing, for example, to study the queries asked to ChatGPT and the responses that ChatGPT gives. To that end, we plan to conduct a user study that will record the user writing process and present them with the opportunity to use ChatGPT as an AI assistant. This study's findings will help us understand how these tools are used and how practitioners -- such as educators and essay readers -- should consider writing education and evaluation based on essay writing.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- Researchers plan to conduct a user study to investigate how students use large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT for essay writing.
- The study will record the user writing process and give them the opportunity to use ChatGPT as an AI assistant.
- The findings will help understand how these tools are used and how practitioners like educators and essay readers should consider writing education and evaluation.
Plain English Explanation
As large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT become more powerful and widely available, students are increasingly using them to help with writing tasks. To better understand how these tools are being used, researchers want to study the specific questions students ask ChatGPT and the responses it provides.
The researchers plan to do a user study where they will record students as they write essays and give them the chance to use ChatGPT as an AI assistant. This will help them see how students actually use these language models in their writing process. The results of this study will provide insights for educators and essay readers on how to adapt writing education and evaluation to accommodate the use of these AI tools.
Technical Explanation
The researchers plan to conduct a user study to investigate how students leverage large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT for essay writing tasks. The study will involve recording the full user writing process, including giving participants the opportunity to interact with ChatGPT as an AI writing assistant.
The goal is to analyze the specific queries students ask ChatGPT and the responses it provides. This data will help the researchers understand how these powerful language models are being used in practice. The findings from the study can then inform how educators, essay readers, and other practitioners should adapt writing education and assessment to account for the growing use of AI tools like ChatGPT.
Critical Analysis
The proposed user study offers a promising approach to better understand the real-world usage of LLMs like ChatGPT in student writing. Recording the full writing process and interactions with the AI system will provide rich data to analyze. However, the study may be limited by its focus on a single language model (ChatGPT) and the specific context of essay writing. Expanding the scope to consider a wider range of LLM tools and writing tasks could yield additional insights.
Additionally, the study does not appear to address potential issues around academic integrity or the ethical implications of using AI assistants for writing assignments. These are important considerations that could be explored further in the research.
Overall, the planned study seems well-designed to shed light on a timely and important topic. The findings could have significant implications for how writing education and assessment evolve in the face of rapidly advancing AI technologies.
Conclusion
This user study aims to investigate how students leverage powerful large language models like ChatGPT to assist with essay writing. By recording the full writing process and analyzing the interactions with the AI system, the researchers hope to gain a better understanding of how these tools are being used in practice.
The results of this study could have important implications for writing education and evaluation, helping practitioners adapt to the growing prevalence of AI-powered writing assistance. As language models continue to advance, it will be crucial to understand both the benefits and potential challenges they present for student learning and academic integrity.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
✨
Beyond Code Generation: An Observational Study of ChatGPT Usage in Software Engineering Practice
Ranim Khojah, Mazen Mohamad, Philipp Leitner, Francisco Gomes de Oliveira Neto

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) are frequently discussed in academia and the general public as support tools for virtually any use case that relies on the production of text, including software engineering. Currently there is much debate, but little empirical evidence, regarding the practical usefulness of LLM-based tools such as ChatGPT for engineers in industry. We conduct an observational study of 24 professional software engineers who have been using ChatGPT over a period of one week in their jobs, and qualitatively analyse their dialogues with the chatbot as well as their overall experience (as captured by an exit survey). We find that, rather than expecting ChatGPT to generate ready-to-use software artifacts (e.g., code), practitioners more often use ChatGPT to receive guidance on how to solve their tasks or learn about a topic in more abstract terms. We also propose a theoretical framework for how (i) purpose of the interaction, (ii) internal factors (e.g., the user's personality), and (iii) external factors (e.g., company policy) together shape the experience (in terms of perceived usefulness and trust). We envision that our framework can be used by future research to further the academic discussion on LLM usage by software engineering practitioners, and to serve as a reference point for the design of future empirical LLM research in this domain.
5/22/2024
📊
Analyzing Chat Protocols of Novice Programmers Solving Introductory Programming Tasks with ChatGPT
Andreas Scholl, Daniel Schiffner, Natalie Kiesler

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have taken the world by storm, and students are assumed to use related tools at a great scale. In this research paper we aim to gain an understanding of how introductory programming students chat with LLMs and related tools, e.g., ChatGPT-3.5. To address this goal, computing students at a large German university were motivated to solve programming exercises with the assistance of ChatGPT as part of their weekly introductory course exercises. Then students (n=213) submitted their chat protocols (with 2335 prompts in sum) as data basis for this analysis. The data was analyzed w.r.t. the prompts, frequencies, the chats' progress, contents, and other use pattern, which revealed a great variety of interactions, both potentially supportive and concerning. Learning about students' interactions with ChatGPT will help inform and align teaching practices and instructions for future introductory programming courses in higher education.
5/30/2024
🌐
ChatGPT Is Here to Help, Not to Replace Anybody -- An Evaluation of Students' Opinions On Integrating ChatGPT In CS Courses
Bruno Pereira Cipriano, Pedro Alves

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT and Bard are capable of producing code based on textual descriptions, with remarkable efficacy. Such technology will have profound implications for computing education, raising concerns about cheating, excessive dependence, and a decline in computational thinking skills, among others. There has been extensive research on how teachers should handle this challenge but it is also important to understand how students feel about this paradigm shift. In this research, 52 first-year CS students were surveyed in order to assess their views on technologies with code-generation capabilities, both from academic and professional perspectives. Our findings indicate that while students generally favor the academic use of GPT, they don't over rely on it, only mildly asking for its help. Although most students benefit from GPT, some struggle to use it effectively, urging the need for specific GPT training. Opinions on GPT's impact on their professional lives vary, but there is a consensus on its importance in academic practice.
4/29/2024
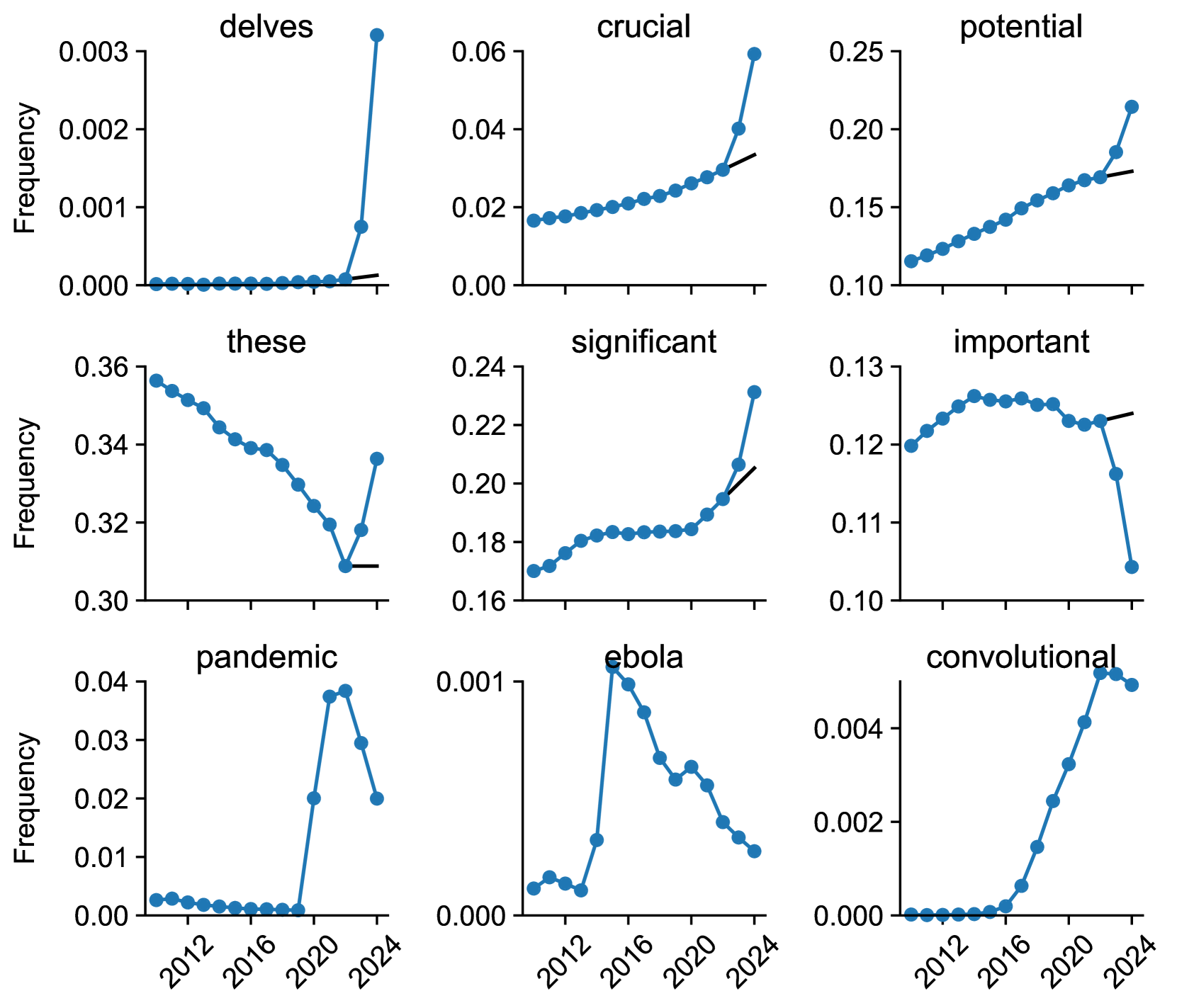
Delving into ChatGPT usage in academic writing through excess vocabulary
Dmitry Kobak, Rita Gonz'alez M'arquez, EmH{o}ke-'Agnes Horv'at, Jan Lause

0
0
Recent large language models (LLMs) can generate and revise text with human-level performance, and have been widely commercialized in systems like ChatGPT. These models come with clear limitations: they can produce inaccurate information, reinforce existing biases, and be easily misused. Yet, many scientists have been using them to assist their scholarly writing. How wide-spread is LLM usage in the academic literature currently? To answer this question, we use an unbiased, large-scale approach, free from any assumptions on academic LLM usage. We study vocabulary changes in 14 million PubMed abstracts from 2010-2024, and show how the appearance of LLMs led to an abrupt increase in the frequency of certain style words. Our analysis based on excess words usage suggests that at least 10% of 2024 abstracts were processed with LLMs. This lower bound differed across disciplines, countries, and journals, and was as high as 30% for some PubMed sub-corpora. We show that the appearance of LLM-based writing assistants has had an unprecedented impact in the scientific literature, surpassing the effect of major world events such as the Covid pandemic.
6/12/2024