Enhancing Financial Inclusion and Regulatory Challenges: A Critical Analysis of Digital Banks and Alternative Lenders Through Digital Platforms, Machine Learning, and Large Language Models Integration

0
💬
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the role of digital banks and alternative lenders in promoting financial inclusion, and the regulatory challenges their business models present.
- It analyzes how the integration of digital platforms, machine learning (ML), and Large Language Models (LLMs) can enhance accessibility to financial services for underserved populations.
- The paper also addresses significant regulatory concerns, such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, financial stability, and consumer protection.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at how new digital banks and alternative lending platforms are changing the financial industry and affecting access to banking and credit. These digital companies are using advanced technologies like machine learning and large language models to reach people who have traditionally had a hard time getting basic financial services.
On one hand, this is helping more people, especially those with low incomes or poor credit, access things like bank accounts, loans, and other financial products. This can improve their financial situation and overall well-being. However, these new business models also raise some tricky regulatory issues around things like protecting customer data, making sure the technology used is fair and unbiased, and ensuring the financial system remains stable and secure.
The researchers take a close look at how these digital finance companies operate and the pros and cons of their approaches. They aim to provide guidance to regulators, financial institutions, and tech providers on how to foster a more inclusive and stable financial system by thoughtfully integrating digital technologies.
Technical Explanation
The paper employs a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative analysis of financial data with qualitative insights from industry experts. This allows the researchers to develop a comprehensive understanding of how digital banks and alternative lenders are impacting financial inclusion and the associated regulatory challenges.
The analysis focuses on the operational frameworks and technological infrastructures underpinning these new financial service providers. The researchers identify key mechanisms that facilitate broader access to banking and credit, such as the use of digital platforms, machine learning, and large language models. These technologies enable the collection and analysis of alternative data sources, allowing the companies to assess creditworthiness and reach previously underserved populations.
However, the paper also delves into the significant regulatory concerns posed by these new business models. Issues such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, financial stability, and consumer protection are examined in detail. The researchers underscore the need for evolving regulatory frameworks that can balance innovation with comprehensive risk management.
Critical Analysis
The paper acknowledges that while digital finance technologies hold promise for improving financial inclusion, there are also significant risks and challenges that must be addressed. For example, the use of alternative data and algorithms in credit decisions raises concerns about potential bias and discrimination, which could undermine the goal of increased access.
Additionally, the researchers note that the rapid growth of digital finance platforms and their interconnectedness with the traditional financial system may introduce new systemic risks. Regulators will need to carefully monitor these developments and ensure appropriate safeguards are in place to protect the stability of the overall financial system.
While the paper provides a thorough analysis of the topic, it could have delved deeper into some areas, such as the specific technological approaches used by large language models in financial services, or the potential societal impacts of improved financial inclusion. Additionally, the researchers could have explored alternative perspectives or critiques of the digital finance industry's approach to serving underbanked populations.
Conclusion
This research paper offers a comprehensive examination of the dual impact of digital banks and alternative lenders on financial inclusion, as well as the significant regulatory challenges their business models present. By integrating digital platforms, machine learning, and large language models, these new financial service providers are expanding access to banking and credit for previously underserved populations.
However, the paper also highlights the need for evolving regulatory frameworks that can balance innovation with robust risk management. Policymakers, financial institutions, and technology providers must work together to cultivate a more inclusive and stable financial ecosystem, one that leverages the power of digital technologies while prioritizing consumer protection and financial system integrity.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬

0
Enhancing Financial Inclusion and Regulatory Challenges: A Critical Analysis of Digital Banks and Alternative Lenders Through Digital Platforms, Machine Learning, and Large Language Models Integration
Luke Lee
This paper explores the dual impact of digital banks and alternative lenders on financial inclusion and the regulatory challenges posed by their business models. It discusses the integration of digital platforms, machine learning (ML), and Large Language Models (LLMs) in enhancing financial services accessibility for underserved populations. Through a detailed analysis of operational frameworks and technological infrastructures, this research identifies key mechanisms that facilitate broader financial access and mitigate traditional barriers. Additionally, the paper addresses significant regulatory concerns involving data privacy, algorithmic bias, financial stability, and consumer protection. Employing a mixed-methods approach, which combines quantitative financial data analysis with qualitative insights from industry experts, this paper elucidates the complexities of leveraging digital technology to foster financial inclusivity. The findings underscore the necessity of evolving regulatory frameworks that harmonize innovation with comprehensive risk management. This paper concludes with policy recommendations for regulators, financial institutions, and technology providers, aiming to cultivate a more inclusive and stable financial ecosystem through prudent digital technology integration.
Read more4/19/2024

1
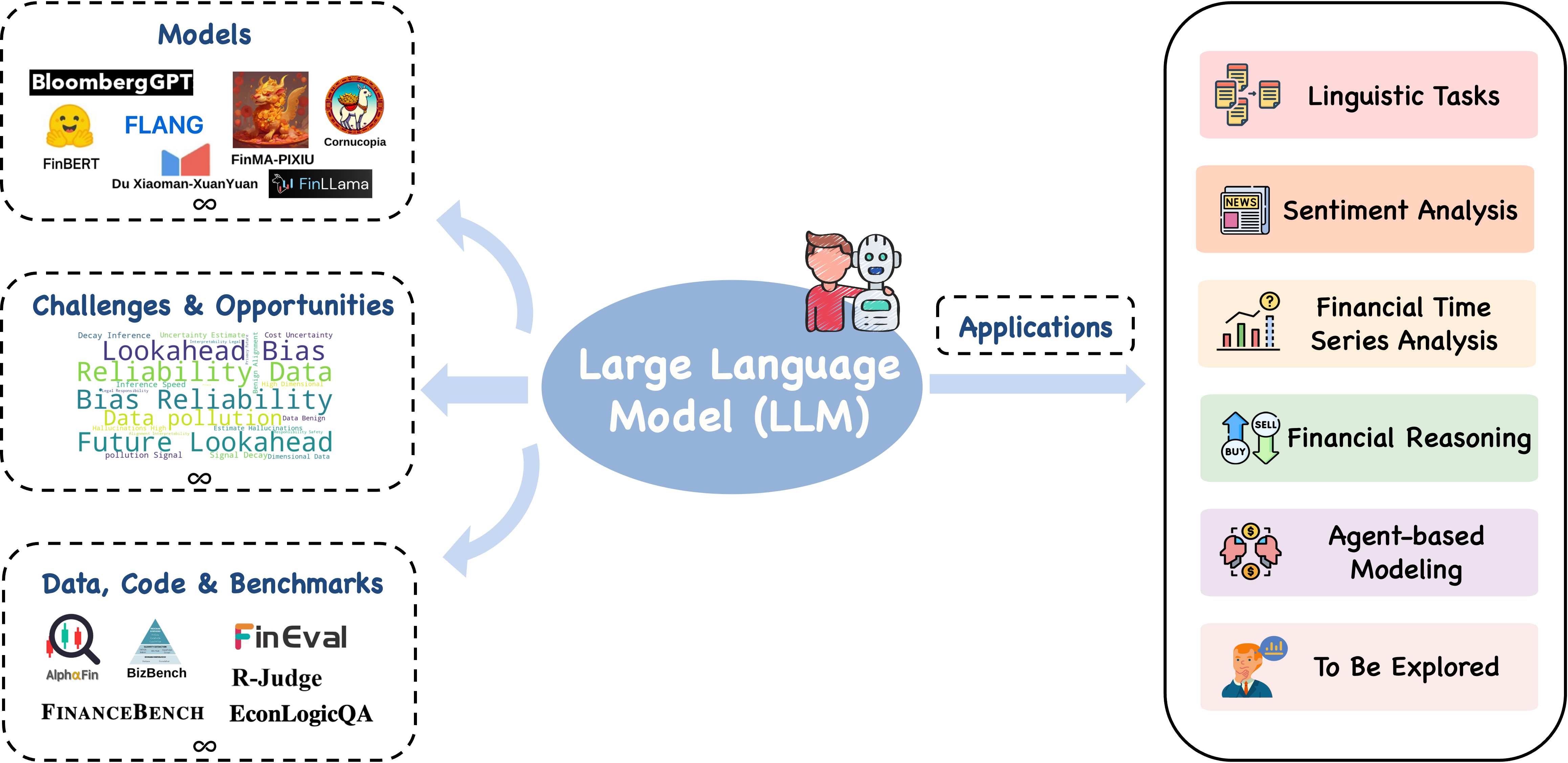
A Survey of Large Language Models for Financial Applications: Progress, Prospects and Challenges
Yuqi Nie, Yaxuan Kong, Xiaowen Dong, John M. Mulvey, H. Vincent Poor, Qingsong Wen, Stefan Zohren
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have unlocked novel opportunities for machine learning applications in the financial domain. These models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in understanding context, processing vast amounts of data, and generating human-preferred contents. In this survey, we explore the application of LLMs on various financial tasks, focusing on their potential to transform traditional practices and drive innovation. We provide a discussion of the progress and advantages of LLMs in financial contexts, analyzing their advanced technologies as well as prospective capabilities in contextual understanding, transfer learning flexibility, complex emotion detection, etc. We then highlight this survey for categorizing the existing literature into key application areas, including linguistic tasks, sentiment analysis, financial time series, financial reasoning, agent-based modeling, and other applications. For each application area, we delve into specific methodologies, such as textual analysis, knowledge-based analysis, forecasting, data augmentation, planning, decision support, and simulations. Furthermore, a comprehensive collection of datasets, model assets, and useful codes associated with mainstream applications are presented as resources for the researchers and practitioners. Finally, we outline the challenges and opportunities for future research, particularly emphasizing a number of distinctive aspects in this field. We hope our work can help facilitate the adoption and further development of LLMs in the financial sector.
Read more6/19/2024

0
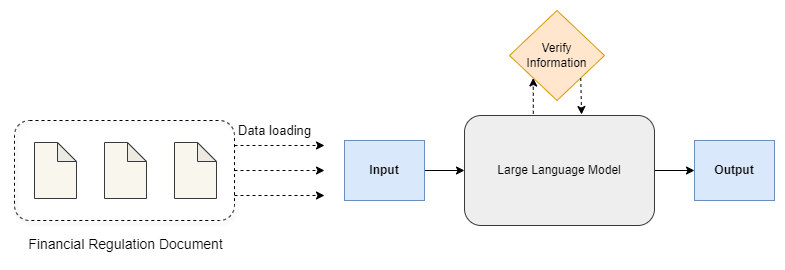
Large Language Model in Financial Regulatory Interpretation
Zhiyu Cao, Zachary Feinstein
This study explores the innovative use of Large Language Models (LLMs) as analytical tools for interpreting complex financial regulations. The primary objective is to design effective prompts that guide LLMs in distilling verbose and intricate regulatory texts, such as the Basel III capital requirement regulations, into a concise mathematical framework that can be subsequently translated into actionable code. This novel approach aims to streamline the implementation of regulatory mandates within the financial reporting and risk management systems of global banking institutions. A case study was conducted to assess the performance of various LLMs, demonstrating that GPT-4 outperforms other models in processing and collecting necessary information, as well as executing mathematical calculations. The case study utilized numerical simulations with asset holdings -- including fixed income, equities, currency pairs, and commodities -- to demonstrate how LLMs can effectively implement the Basel III capital adequacy requirements. Keywords: Large Language Models, Prompt Engineering, LLMs in Finance, Basel III, Minimum Capital Requirements, LLM Ethics
Read more7/11/2024
💬

0
Large Language Models in Finance: A Survey
Yinheng Li, Shaofei Wang, Han Ding, Hang Chen
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have opened new possibilities for artificial intelligence applications in finance. In this paper, we provide a practical survey focused on two key aspects of utilizing LLMs for financial tasks: existing solutions and guidance for adoption. First, we review current approaches employing LLMs in finance, including leveraging pretrained models via zero-shot or few-shot learning, fine-tuning on domain-specific data, and training custom LLMs from scratch. We summarize key models and evaluate their performance improvements on financial natural language processing tasks. Second, we propose a decision framework to guide financial professionals in selecting the appropriate LLM solution based on their use case constraints around data, compute, and performance needs. The framework provides a pathway from lightweight experimentation to heavy investment in customized LLMs. Lastly, we discuss limitations and challenges around leveraging LLMs in financial applications. Overall, this survey aims to synthesize the state-of-the-art and provide a roadmap for responsibly applying LLMs to advance financial AI.
Read more7/10/2024