Ephemeral Rollups are All you Need

1
🤖
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Envisions open and composable gaming platforms where users actively expand, create, engage, and immerse themselves
- Focuses on fully on-chain (FOC) games, where game state and logic reside on the blockchain for maximum composability
- Addresses inherent limitations and tradeoffs, particularly in terms of costs and scalability
Plain English Explanation
The paper presents a vision for gaming platforms that allow users to deeply engage, create, and customize their experiences. One promising approach is fully on-chain (FOC) games, where the entire game is hosted on the blockchain. This maximizes the ability to "compose" different game elements together.
However, FOC games face challenges around cost and scalability. The paper introduces a framework called BOLT that leverages the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) to address these limitations. BOLT uses a modular, Entity-Component-System (ECS) design to make it easier to build and combine game logic.
To improve scalability, BOLT introduces "Ephemeral Rollups" (ERs) - specialized runtimes that can be optimized for speed, customized ticking mechanisms, and gasless transactions. This allows FOC games to scale without compromising the benefits of being fully on-chain.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes the BOLT framework to enable scalable, composable FOC games on the Solana blockchain. BOLT uses the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) to host game logic and state on-chain.
A key innovation is BOLT's modular, Entity-Component-System (ECS) architecture. This allows game developers to discover, utilize, and publish reusable "components" of game logic. These components can then be easily combined to create new gameplay experiences.
To address scalability challenges, BOLT introduces "Ephemeral Rollups" (ERs) - specialized runtimes that can be customized for high performance, configurable ticking, and gasless transactions. ERs overcome the tradeoffs often seen in Layer 2 scaling solutions, allowing FOC games to scale without sacrificing composability.
The paper also discusses techniques for ensuring the security and integrity of these ephemeral runtimes, including sequencer-level security and leveraging innovations like EIP-4844 for more efficient data management.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a compelling vision for scalable, composable on-chain gaming. The BOLT framework addresses key limitations of existing FOC games, such as high costs and poor scalability. The use of modular ECS architecture and Ephemeral Rollups are innovative approaches to these challenges.
However, the paper does not fully address potential drawbacks or areas for further research. For example, the security and trust assumptions of the ephemeral runtimes require deeper exploration, especially in light of recent issues with rollup-based systems.
Additionally, the paper does not delve into the potential impact of efficient data management techniques on the overall system design and performance. These aspects could be important considerations for the long-term viability of the BOLT framework.
Overall, the paper presents a promising direction for on-chain gaming, but further research and real-world testing would be needed to fully evaluate the feasibility and trade-offs of the proposed approach.
Conclusion
The BOLT framework offers a compelling solution for building scalable, composable on-chain games on the Solana blockchain. By leveraging the Solana Virtual Machine and introducing modular ECS architecture and Ephemeral Rollups, the paper addresses key limitations of existing fully on-chain gaming platforms.
While the paper presents an innovative vision, further exploration of security, trust assumptions, and data management considerations would be beneficial to fully understand the potential and limitations of the BOLT approach. Nonetheless, the ideas presented in this paper could pave the way for a new era of engaging, user-driven gaming experiences built directly on the blockchain.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤖

1
Ephemeral Rollups are All you Need
Gabriele Picco, Andrea Fortugno
In the realm of open and composable gaming, we envision platforms where users actively expand, create, engage, and immerse themselves in a rich world of entertainment. One promising avenue for achieving this vision is through fully on-chain (FOC) games, where both game state and logic reside on the blockchain, maximizing composability. However, we must grapple with inherent limitations and trade-offs, particularly in terms of costs and scalability. This paper proposes a framework that leverages the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) to scale FOC games without state fragmentation or compromised trust assumptions. The framework introduces a systematic approach for discovering, utilizing, and publishing modular pieces of logic as components deeply rooted in the Entity-Component-System (ECS) pattern. To enhance scalability and resource optimization, we introduce the concept of Ephemeral Rollups (ERs) that overcome the tradeoffs of L2s horizontal scaling. These dedicated runtimes can be customized to provide higher operational speed, configurable ticking mechanisms, provable sessions and gasless transactions without composability-scalability tradeoffs.
Read more5/24/2024

0
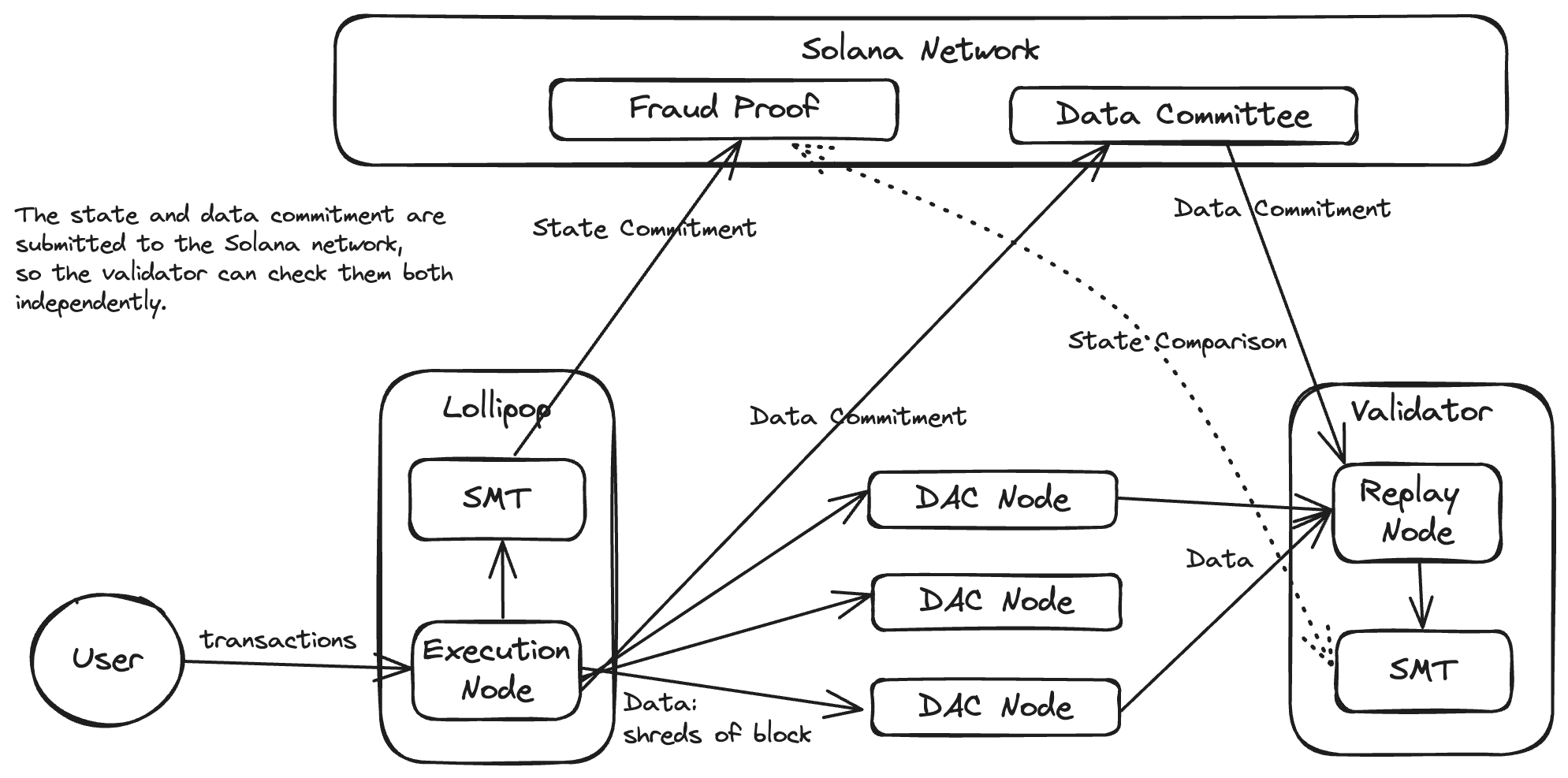
Lollipop: SVM Rollups on Solana
Irvin Steve Cardenas, Yugart Song
We present a formal specification for the implementation of Solana virtual machine (SVM) rollups deployed on top of the Solana Layer 1 (L1) blockchain. We further discuss our motivation, implementation, design decisions, limitations, and preliminary results. Overall, this paper is intended to serve as an initial introduction to building such system(s) on top of the Solana L1 blockchain, but does not represent an absolute. Lastly, we comment discuss on extensions of this specification to support SVM rollups on other well-established L1 blockchains systems such as Ethereum.
Read more5/16/2024
👨🏫

0
A Rollup Comparison Framework
Jan Gorzny, Martin Derka
Rollups are a popular blockchain paradigm where one blockchain network is anchored to a different blockchain network, typically though smart contracts and data commitments. The rollup executes transactions on its own network and periodically publishes them along with the state root of the rollup network. The state root is determined to be final by a protocol, often enforced by smart contracts on the anchoring blockchain, which may let the state roots be challenged or verify an accompanying validity proof. While this core functionality is universal to existing rollups, these systems have introduced unique features as they vie for users and market dominance. In this paper, we aim to classify ways in which these rollups differ in order to establish a common ground of understanding. We explore various dimensions in which these system can differ: familiarity, finality time, modularity, and maturity. The result is a framework that can be used to understand and compare the properties of rollups.
Read more4/26/2024


0
Fast and Secure Decentralized Optimistic Rollups Using Setchain
Margarita Capretto, Mart'in Ceresa, Antonio Fern'andez Anta, Pedro Moreno-S'anchez, C'esar S'anchez
Modern blockchains face a scalability challenge due to the intrinsic throughput limitations of consensus protocols. Layer 2 optimistic rollups (L2) are a faster alternative that offer the same interface in terms of smart contract development and user interaction. Optimistic rollups perform most computations offchain and make light use of an underlying blockchain (L1) to guarantee correct behavior, implementing a cheaper blockchain on a blockchain solution. With optimistic rollups, a sequencer calculates offchain batches of L2 transactions and commits batches (compressed or hashed) to the L1 blockchain. The use of hashes requires a data service to translate hashes into their corresponding batches. Current L2 implementations consist of a centralized sequencer (central authority) and an optional data availability committee (DAC). In this paper, we propose a decentralized L2 optimistic rollup based on Setchain, a decentralized Byzantine-tolerant implementation of sets. The main contribution is a fully decentralized arranger where arrangers are a formal definition combining sequencers and DACs. We prove our implementation correct and show empirical evidence that our solution scales. A final contribution is a system of incentives (payments) for servers that implement the sequencer and data availability committee protocols correctly, and a fraud-proof mechanism to detect violations of the protocol.
Read more6/5/2024