Impact of EIP-4844 on Ethereum: Consensus Security, Ethereum Usage, Rollup Transaction Dynamics, and Blob Gas Fee Markets

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- EIP-4844, a proposed Ethereum upgrade, aims to improve data availability and reduce transaction fees for rollup-based scaling.
- The paper examines the potential impact of EIP-4844 on Ethereum's consensus security, usage, rollup transaction dynamics, and blob gas fee markets.
- The research combines theoretical analysis, simulations, and empirical studies to assess the implications of the proposed upgrade.
Plain English Explanation
Consensus Security
EIP-4844 aims to improve Ethereum's data availability, making it harder for attackers to disrupt the network. By increasing the amount of data that can be stored on the blockchain, it becomes more difficult for bad actors to censor or hide important information, helping to maintain the integrity of the consensus protocol.
Ethereum Usage
The upgrade is expected to reduce transaction fees for Layer 2 rollups, which are Ethereum-based scaling solutions. This could lead to increased adoption and usage of the Ethereum network, as more users and applications take advantage of the lower costs and improved efficiency.
Rollup Transaction Dynamics
Rollup-based scaling is a key focus of the research. EIP-4844 is designed to optimize the handling of "blobs" of data associated with rollup transactions, potentially improving the overall performance and throughput of the Ethereum ecosystem.
Blob Gas Fee Markets
The paper also explores the potential emergence of a new "blob gas fee market," where users would pay a separate fee to include data blobs in their transactions. This could introduce additional complexity to Ethereum's fee structure, but may also enable more efficient pricing of different types of transaction data.
Technical Explanation
The paper combines theoretical analysis, simulations, and empirical studies to assess the potential impact of EIP-4844 on Ethereum's consensus security, usage, rollup transaction dynamics, and blob gas fee markets.
Consensus Security
The researchers analyze how the proposed upgrade could affect Ethereum's consensus security and confirmation rule. They find that by increasing data availability, EIP-4844 could make it more difficult for attackers to disrupt the network and undermine the integrity of the consensus protocol.
Ethereum Usage
The paper examines the potential impact of reduced transaction fees on Ethereum's adoption and usage. Simulations suggest that the upgrade could lead to a significant increase in the number of users and transactions on the network, as more applications and users take advantage of the improved cost-efficiency.
Rollup Transaction Dynamics
The researchers focus on the impact of EIP-4844 on rollup-based scaling solutions. They analyze how the optimization of "blobs" of data associated with rollup transactions could enhance the overall performance and throughput of the Ethereum ecosystem.
Blob Gas Fee Markets
The paper explores the potential emergence of a new "blob gas fee market," where users would pay a separate fee to include data blobs in their transactions. The researchers investigate the implications of this new fee structure, including its impact on transaction pricing and market dynamics.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the potential impact of EIP-4844, but it also acknowledges several caveats and areas for further research. For example, the researchers note that the simulations and empirical studies rely on certain assumptions and simplifications, which may not fully capture the complexities of the real-world Ethereum ecosystem.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the societal implications of the proposed upgrade, such as its potential impact on the broader blockchain ecosystem or the distribution of wealth and power within the Ethereum network.
While the research offers valuable insights, it is essential for readers to critically evaluate the findings and form their own opinions, taking into account the limitations of the study and considering the broader context and potential implications of the proposed changes to the Ethereum network.
Conclusion
The paper presents a comprehensive analysis of the potential impact of EIP-4844, a proposed Ethereum upgrade aimed at improving data availability and reducing transaction fees for rollup-based scaling. The researchers combine theoretical analysis, simulations, and empirical studies to assess the upgrade's implications for Ethereum's consensus security, usage, rollup transaction dynamics, and blob gas fee markets.
The findings suggest that EIP-4844 could enhance the integrity of Ethereum's consensus protocol, lead to increased adoption and usage of the network, and optimize the performance of rollup-based scaling solutions. However, the paper also acknowledges various caveats and areas for further research, encouraging readers to think critically about the proposed changes and their broader implications.
Overall, the research provides valuable insights into the potential impact of EIP-4844, which could have significant implications for the future development and adoption of the Ethereum ecosystem.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Impact of EIP-4844 on Ethereum: Consensus Security, Ethereum Usage, Rollup Transaction Dynamics, and Blob Gas Fee Markets
Seongwan Park, Bosul Mun, Seungyun Lee, Woojin Jeong, Jaewook Lee, Hyeonsang Eom, Huisu Jang
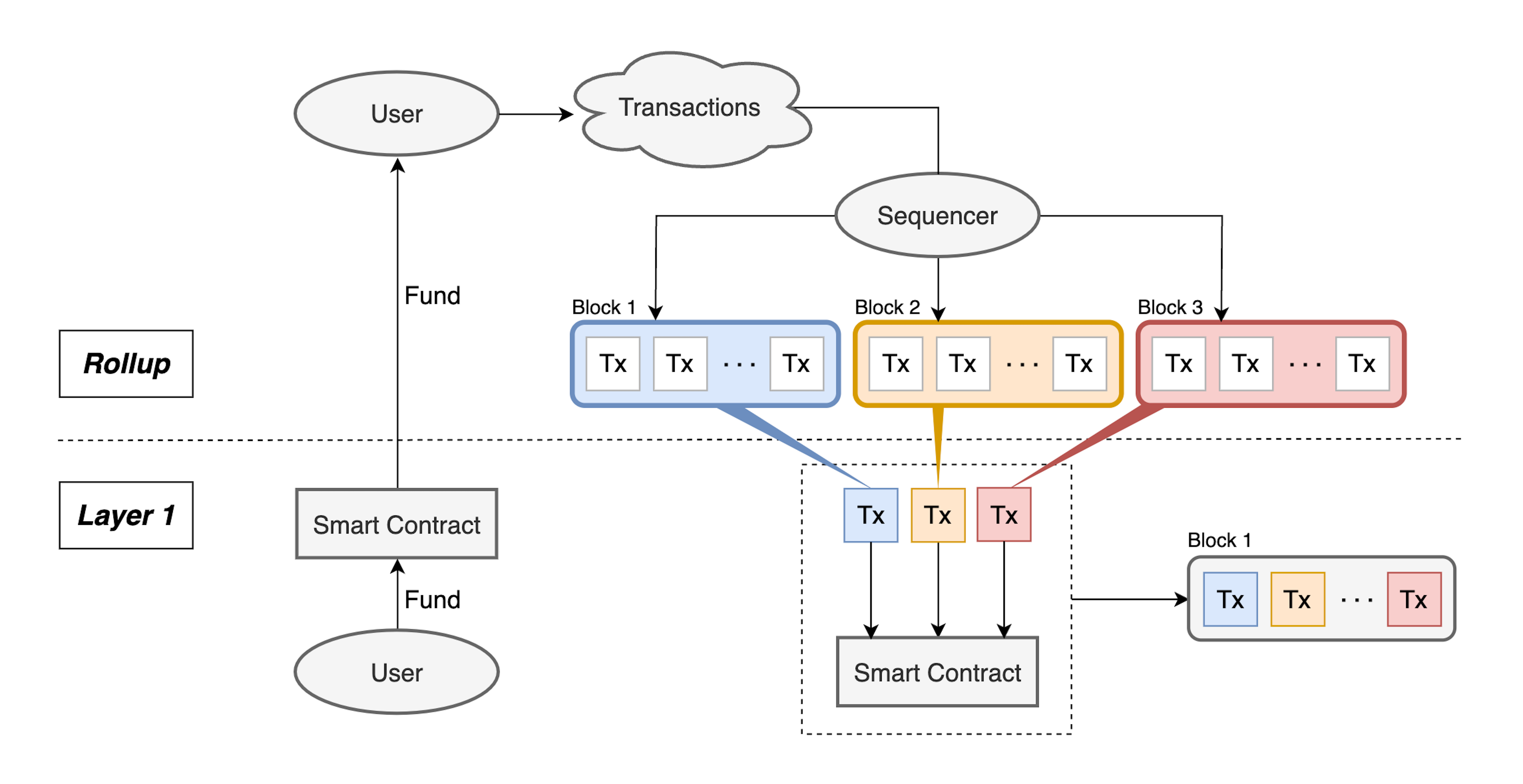
On March 13, 2024, Ethereum implemented EIP-4844, designed to enhance its role as a data availability layer. While this upgrade reduces data posting costs for rollups, it also raises concerns about its impact on the consensus layer due to increased propagation sizes. Moreover, the broader effects on the overall Ethereum ecosystem remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we conduct an empirical analysis of the impact of EIP-4844 on consensus security, Ethereum usage, rollup transaction dynamics, and the blob gas fee mechanism. We explore changes in synchronization times, provide quantitative assessments of rollup and user behaviors, and deepen the understanding of the blob gas fee mechanism, highlighting both enhancements and areas of concern post-upgrade.
Read more5/7/2024

0
Delay Analysis of EIP-4844
Pourya Soltani, Farid Ashtiani
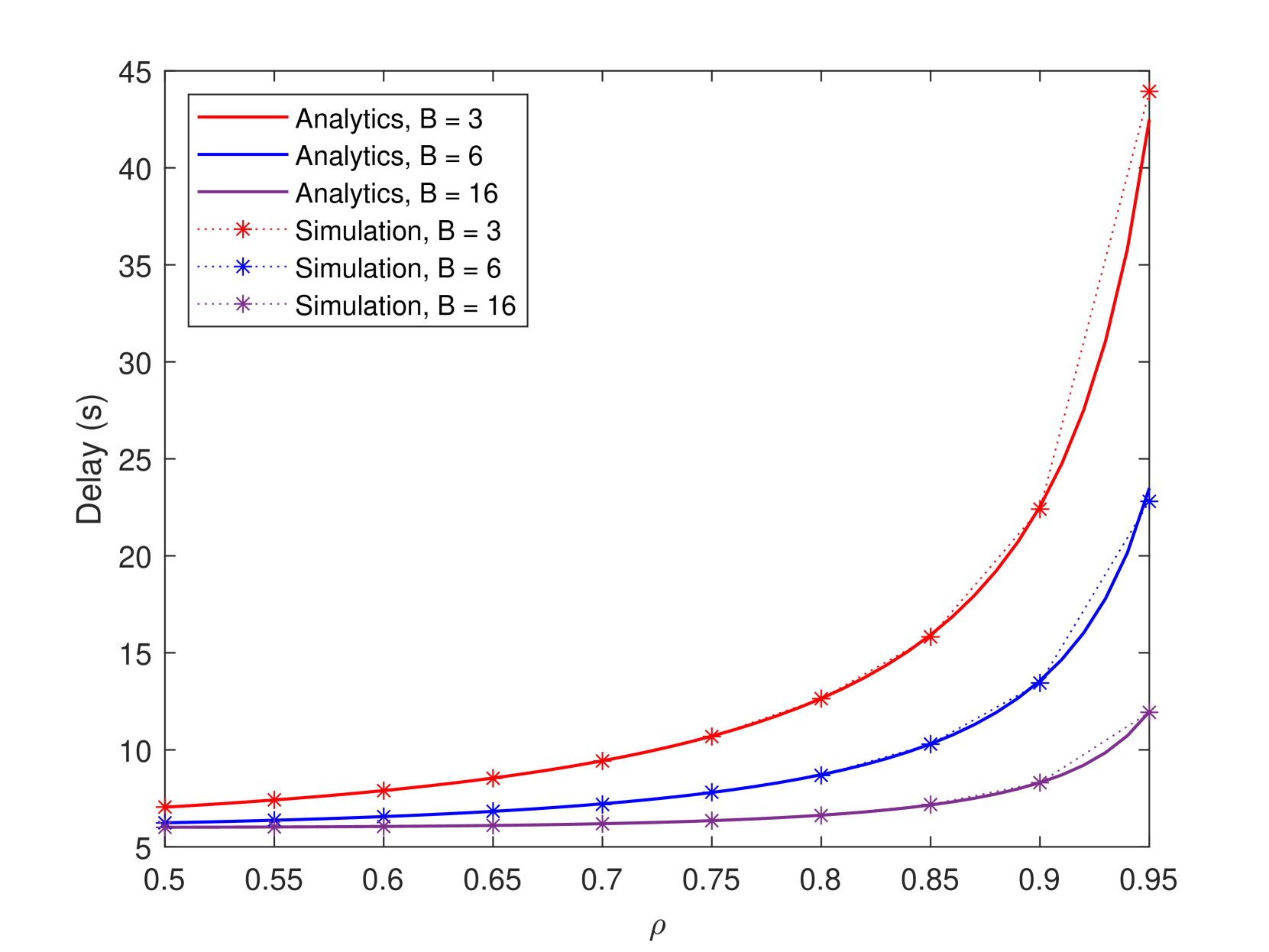
Proto-Danksharding, proposed in Ethereum Improvement Proposal 4844 (EIP-4844), aims to incrementally improve the scalability of the Ethereum blockchain by introducing a new type of transaction known as blob-carrying transactions. These transactions incorporate binary large objects (blobs) of data that are stored off-chain but referenced and verified on-chain to ensure data availability. By decoupling data availability from transaction execution, Proto-Danksharding alleviates network congestion and reduces gas fees, laying the groundwork for future, more advanced sharding solutions. This letter provides an analytical model to derive the delay for these new transactions. We model the system as an $mathrm{M/D}^B/1$ queue which we then find its steady state distribution through embedding a Markov chain and use of supplementary variable method. We show that transactions with more blobs but less frequent impose higher delays on the system compared to lower blobs but more frequent.
Read more9/18/2024
🤖

1
Ephemeral Rollups are All you Need
Gabriele Picco, Andrea Fortugno
In the realm of open and composable gaming, we envision platforms where users actively expand, create, engage, and immerse themselves in a rich world of entertainment. One promising avenue for achieving this vision is through fully on-chain (FOC) games, where both game state and logic reside on the blockchain, maximizing composability. However, we must grapple with inherent limitations and trade-offs, particularly in terms of costs and scalability. This paper proposes a framework that leverages the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) to scale FOC games without state fragmentation or compromised trust assumptions. The framework introduces a systematic approach for discovering, utilizing, and publishing modular pieces of logic as components deeply rooted in the Entity-Component-System (ECS) pattern. To enhance scalability and resource optimization, we introduce the concept of Ephemeral Rollups (ERs) that overcome the tradeoffs of L2s horizontal scaling. These dedicated runtimes can be customized to provide higher operational speed, configurable ticking mechanisms, provable sessions and gasless transactions without composability-scalability tradeoffs.
Read more5/24/2024
🖼️

0
Towards Single Slot Finality: Evaluating Consensus Mechanisms and Methods for Faster Ethereum Finality
Lincoln Murr
Ethereum's current Gasper consensus mechanism, which combines the Latest Message Driven Greediest Heaviest Observed SubTree (LMD-GHOST) fork choice rule with the probabilistic Casper the Friendly Finality Gadget (FFG) finality overlay, finalizes transactions in 64 to 95 blocks, an approximate 15-minute delay. This finalization latency impacts user experience and exposes the network to short-term chain reorganization risks, potentially enabling transaction censorship or frontrunning by validators without severe penalties. As the ecosystem pursues a rollup-centric roadmap to scale Ethereum into a secure global settlement layer, faster finality allows cross-layer and inter-rollup communication with greater immediacy, reducing capital inefficiencies. Single slot finality (SSF), wherein transactions are finalized within the same slot they are proposed, promises to advance the Ethereum protocol and enable better user experiences by enabling near-instant economic finality. This thesis systematically studies distributed consensus protocols through propose-vote-merge, PBFT-inspired, and graded agreement families - scrutinizing their capacities to enhance or replace LMD-GHOST. The analysis delves into the intricate tradeoffs between safety, liveness, and finality, shedding light on the challenges and opportunities in designing an optimal consensus protocol for Ethereum. It also explores different design decisions and mechanisms by which single slot or fast finality can be enabled, including cumulative finality, subsampling, and application-layer fast finality. Furthermore, this work introduces SSF-enabled and streamlined fast finality constructions based on a single-vote total order broadcast protocol. The insights and recommendations in this thesis provide a solid foundation for the Ethereum community to make informed decisions regarding the future direction of the protocol's consensus.
Read more6/17/2024