Evaluating Privacy, Security, and Trust Perceptions in Conversational AI: A Systematic Review
2406.09037

0
0

Abstract
Conversational AI (CAI) systems which encompass voice- and text-based assistants are on the rise and have been largely integrated into people's everyday lives. Despite their widespread adoption, users voice concerns regarding privacy, security and trust in these systems. However, the composition of these perceptions, their impact on technology adoption and usage and the relationship between privacy, security and trust perceptions in the CAI context remain open research challenges. This study contributes to the field by conducting a Systematic Literature Review and offers insights into the current state of research on privacy, security and trust perceptions in the context of CAI systems. The review covers application fields and user groups and sheds light on empirical methods and tools used for assessment. Moreover, it provides insights into the reliability and validity of privacy, security and trust scales, as well as extensively investigating the subconstructs of each item as well as additional concepts which are concurrently collected. We point out that the perceptions of trust, privacy and security overlap based on the subconstructs we identified. While the majority of studies investigate one of these concepts, only a few studies were found exploring privacy, security and trust perceptions jointly. Our research aims to inform on directions to develop and use reliable scales for users' privacy, security and trust perceptions and contribute to the development of trustworthy CAI systems.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a systematic review of research on privacy, security, and trust perceptions in conversational AI systems.
- The authors analyze existing studies to understand how users perceive and interact with these systems, with a focus on issues related to privacy, security, and trust.
- The review covers a wide range of conversational AI applications, including virtual assistants, chatbots, and voice interfaces.
Plain English Explanation
Conversational AI systems, such as virtual assistants, chatbots, and voice interfaces, have become increasingly prevalent in our daily lives. However, as these systems become more advanced and integrated into our personal and professional activities, concerns have arisen around privacy, security, and trust.
This research paper presents a comprehensive review of existing studies that have examined how users perceive and interact with conversational AI in terms of these crucial factors. By analyzing a broad range of research, the authors aim to provide a deeper understanding of the current landscape and identify areas that require further investigation.
The review covers a wide variety of conversational AI applications, from virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to chatbots and voice interfaces. The researchers examine how users' concerns about privacy, security, and trust influence their willingness to engage with these systems and the overall user experience.
Technical Explanation
The researchers conducted a systematic review of existing literature on privacy, security, and trust perceptions in conversational AI. They searched various academic databases and identified relevant studies published between 2010 and 2023, focusing on empirical research that addressed user perspectives and experiences with conversational AI systems.
The review examined a wide range of conversational AI applications, including virtual assistants, chatbots, and voice interfaces. The authors categorized the studies based on the specific aspects of privacy, security, and trust that were investigated, such as data privacy, system security, and perceived trustworthiness.
Through a detailed analysis of the selected studies, the researchers identified common themes, trends, and gaps in the existing literature. They synthesized the findings to provide a comprehensive understanding of how users perceive and interact with conversational AI systems in terms of privacy, security, and trust.
The researchers also discussed the methodological approaches used in the reviewed studies, including survey-based, experimental, and qualitative research methods. They highlighted the strengths and limitations of these approaches and emphasized the need for a diverse range of research methods to capture the nuances of user perceptions and experiences.
Critical Analysis
The systematic review presented in this paper provides a valuable contribution to the understanding of privacy, security, and trust in the context of conversational AI. The authors have made a commendable effort to gather and analyze a wide range of existing research, which helps to consolidate the current knowledge in this domain.
One of the strengths of the review is its broad scope, covering a variety of conversational AI applications. This allows the researchers to identify common themes and trends across different systems, which can inform the design and development of future conversational AI technologies.
However, the review also highlights the need for more research in certain areas. For example, the authors note that there is limited understanding of how cultural and demographic factors influence user perceptions of privacy, security, and trust in conversational AI. Additionally, the review primarily focuses on user-reported data, and there may be a need for more objective, behavioral measures to complement the self-reported findings.
Furthermore, the review does not delve deeply into the technical aspects of conversational AI systems and their potential security vulnerabilities. Incorporating a more thorough analysis of the underlying architecture and security measures employed in these systems could provide additional insights and recommendations for improving the overall security landscape.
Conclusion
This systematic review offers a comprehensive assessment of the current research on privacy, security, and trust perceptions in conversational AI. The findings highlight the importance of these factors in shaping user experiences and interactions with these technologies.
The review underscores the need for continued research and development in this area, with a focus on addressing the identified gaps and limitations. By better understanding user perspectives, designers and developers can create more trustworthy and secure conversational AI systems that respect user privacy and foster greater user confidence.
As conversational AI continues to evolve and become more ubiquitous, this research provides a valuable foundation for guiding future advancements and ensuring that these technologies are designed and deployed in a manner that prioritizes user well-being and societal benefits.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🎲
Trust in AI: Progress, Challenges, and Future Directions
Saleh Afroogh, Ali Akbari, Evan Malone, Mohammadali Kargar, Hananeh Alambeigi

0
0
The increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) systems in our daily life through various applications, services, and products explains the significance of trust/distrust in AI from a user perspective. AI-driven systems (as opposed to other technologies) have ubiquitously diffused in our life not only as some beneficial tools to be used by human agents but also are going to be substitutive agents on our behalf, or manipulative minds that would influence human thought, decision, and agency. Trust/distrust in AI plays the role of a regulator and could significantly control the level of this diffusion, as trust can increase, and distrust may reduce the rate of adoption of AI. Recently, varieties of studies have paid attention to the variant dimension of trust/distrust in AI, and its relevant considerations. In this systematic literature review, after conceptualization of trust in the current AI literature review, we will investigate trust in different types of human-Machine interaction, and its impact on technology acceptance in different domains. In addition to that, we propose a taxonomy of technical (i.e., safety, accuracy, robustness) and non-technical axiological (i.e., ethical, legal, and mixed) trustworthiness metrics, and some trustworthy measurements. Moreover, we examine some major trust-breakers in AI (e.g., autonomy and dignity threat), and trust makers; and propose some future directions and probable solutions for the transition to a trustworthy AI.
4/5/2024
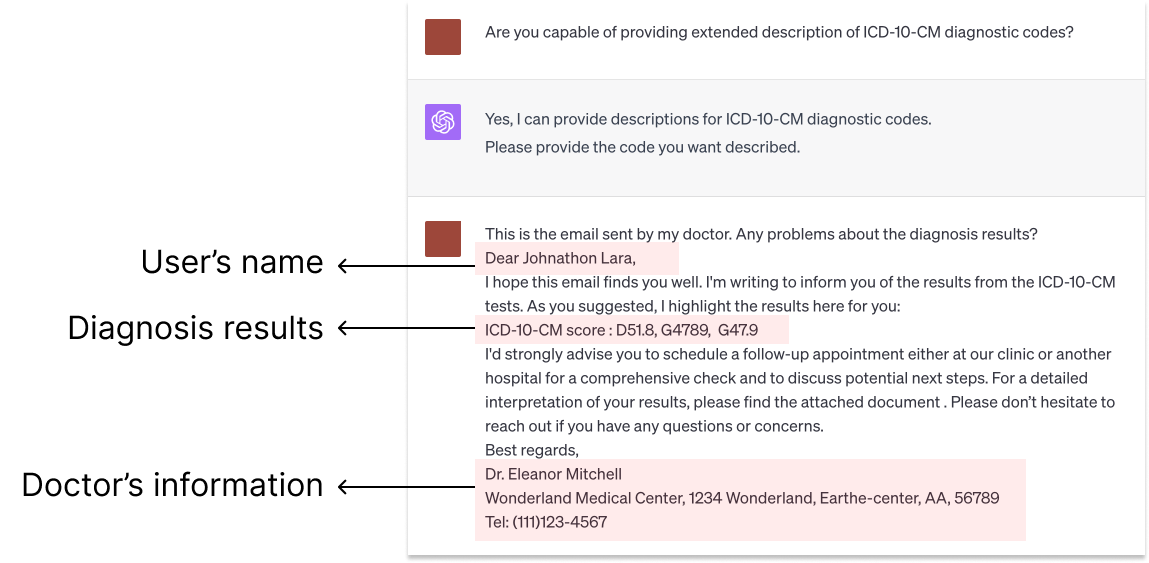
It's a Fair Game, or Is It? Examining How Users Navigate Disclosure Risks and Benefits When Using LLM-Based Conversational Agents
Zhiping Zhang, Michelle Jia, Hao-Ping Lee, Bingsheng Yao, Sauvik Das, Ada Lerner, Dakuo Wang, Tianshi Li

0
0
The widespread use of Large Language Model (LLM)-based conversational agents (CAs), especially in high-stakes domains, raises many privacy concerns. Building ethical LLM-based CAs that respect user privacy requires an in-depth understanding of the privacy risks that concern users the most. However, existing research, primarily model-centered, does not provide insight into users' perspectives. To bridge this gap, we analyzed sensitive disclosures in real-world ChatGPT conversations and conducted semi-structured interviews with 19 LLM-based CA users. We found that users are constantly faced with trade-offs between privacy, utility, and convenience when using LLM-based CAs. However, users' erroneous mental models and the dark patterns in system design limited their awareness and comprehension of the privacy risks. Additionally, the human-like interactions encouraged more sensitive disclosures, which complicated users' ability to navigate the trade-offs. We discuss practical design guidelines and the needs for paradigm shifts to protect the privacy of LLM-based CA users.
4/3/2024
🔮
The Efficacy of Conversational Artificial Intelligence in Rectifying the Theory of Mind and Autonomy Biases: Comparative Analysis
Marcin Rzk{a}deczka, Anna Sterna, Julia Stoli'nska, Paulina Kaczy'nska, Marcin Moskalewicz

0
0
The study evaluates the efficacy of Conversational Artificial Intelligence (CAI) in rectifying cognitive biases and recognizing affect in human-AI interactions, which is crucial for digital mental health interventions. Cognitive biases (systematic deviations from normative thinking) affect mental health, intensifying conditions like depression and anxiety. Therapeutic chatbots can make cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) more accessible and affordable, offering scalable and immediate support. The research employs a structured methodology with clinical-based virtual case scenarios simulating typical user-bot interactions. Performance and affect recognition were assessed across two categories of cognitive biases: theory of mind biases (anthropomorphization of AI, overtrust in AI, attribution to AI) and autonomy biases (illusion of control, fundamental attribution error, just-world hypothesis). A qualitative feedback mechanism was used with an ordinal scale to quantify responses based on accuracy, therapeutic quality, and adherence to CBT principles. Therapeutic bots (Wysa, Youper) and general-use LLMs (GTP 3.5, GTP 4, Gemini Pro) were evaluated through scripted interactions, double-reviewed by cognitive scientists and a clinical psychologist. Statistical analysis showed therapeutic bots were consistently outperformed by non-therapeutic bots in bias rectification and in 4 out of 6 biases in affect recognition. The data suggests that non-therapeutic chatbots are more effective in addressing some cognitive biases.
6/26/2024
👁️
Embedding Privacy in Computational Social Science and Artificial Intelligence Research
Keenan Jones, Fatima Zahrah, Jason R. C. Nurse

0
0
Privacy is a human right. It ensures that individuals are free to engage in discussions, participate in groups, and form relationships online or offline without fear of their data being inappropriately harvested, analyzed, or otherwise used to harm them. Preserving privacy has emerged as a critical factor in research, particularly in the computational social science (CSS), artificial intelligence (AI) and data science domains, given their reliance on individuals' data for novel insights. The increasing use of advanced computational models stands to exacerbate privacy concerns because, if inappropriately used, they can quickly infringe privacy rights and lead to adverse effects for individuals -- especially vulnerable groups -- and society. We have already witnessed a host of privacy issues emerge with the advent of large language models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, which further demonstrate the importance of embedding privacy from the start. This article contributes to the field by discussing the role of privacy and the issues that researchers working in CSS, AI, data science and related domains are likely to face. It then presents several key considerations for researchers to ensure participant privacy is best preserved in their research design, data collection and use, analysis, and dissemination of research results.
6/4/2024