Exploiting the Margin: How Capitalism Fuels AI at the Expense of Minoritized Groups
2403.06332

0
0
🤖
Abstract
This paper explores the intricate relationship between capitalism, racial injustice, and artificial intelligence (AI), arguing that AI acts as a contemporary vehicle for age-old forms of exploitation. By linking historical patterns of racial and economic oppression with current AI practices, this study illustrates how modern technology perpetuates and deepens societal inequalities. It specifically examines how AI is implicated in the exploitation of marginalized communities through underpaid labor in the gig economy, the perpetuation of biases in algorithmic decision-making, and the reinforcement of systemic barriers that prevent these groups from benefiting equitably from technological advances. Furthermore, the paper discusses the role of AI in extending and intensifying the social, economic, and psychological burdens faced by these communities, highlighting the problematic use of AI in surveillance, law enforcement, and mental health contexts. The analysis concludes with a call for transformative changes in how AI is developed and deployed. Advocating for a reevaluation of the values driving AI innovation, the paper promotes an approach that integrates social justice and equity into the core of technological design and policy. This shift is crucial for ensuring that AI serves as a tool for societal improvement, fostering empowerment and healing rather than deepening existing divides.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores how capitalism and the pursuit of profit have shaped the development of AI systems, often at the expense of marginalized communities.
- It examines how the drive for economic gain has led to the creation of AI systems that reinforce existing social inequalities and biases.
- The paper argues that the current AI ecosystem is structured in a way that prioritizes the interests of dominant groups over the well-being of minoritized populations.
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses how the development of AI systems is often driven by the pursuit of profit and economic gain, rather than by a genuine concern for the well-being of all people. It suggests that the current AI landscape is designed in a way that benefits the dominant groups in society, while neglecting the needs and interests of marginalized communities.
The authors argue that the capitalist system, which prioritizes the accumulation of wealth and power, has shaped the way AI is developed and deployed. This has led to the creation of AI systems that reinforce existing social inequalities and biases. These systems may perpetuate discrimination, underrepresentation, and exclusion, particularly for minoritized groups.
The paper suggests that the current power dynamics in the AI industry, where a small number of large tech companies and powerful individuals hold significant influence, have contributed to this problem. It calls for a more ethical and inclusive approach to the development and deployment of AI, one that prioritizes the well-being of all people, not just those who stand to profit the most.
Technical Explanation
The paper's central argument is that the capitalist system, with its emphasis on profit maximization, has shaped the development of AI in ways that disproportionately benefit dominant social groups and marginalize minoritized populations. The authors analyze how the current AI ecosystem is structured to prioritize the interests of those with economic and political power, often at the expense of the well-being of marginalized communities.
The paper examines several case studies that illustrate how AI systems can perpetuate and exacerbate existing social inequalities. For example, it discusses how facial recognition technology has been shown to be less accurate for women and people of color, leading to biased outcomes in law enforcement and other domains. It also explores how algorithmic decision-making systems used in areas like hiring and lending have been found to discriminate against certain groups.
The authors argue that the power dynamics within the AI industry, where a small number of large tech companies and influential individuals hold significant sway, have contributed to these problems. They suggest that the prioritization of profit over societal well-being has led to the creation of AI systems that are designed to maximize economic gain rather than to serve the needs of all people equally.
Critical Analysis
The paper raises important concerns about the social and ethical implications of AI development in a capitalist system. The authors make a compelling case that the current AI ecosystem is structured in a way that perpetuates and exacerbates existing social inequalities, often at the expense of marginalized communities.
One potential limitation of the paper is that it focuses primarily on the negative impacts of capitalism on AI development, without delving deeply into potential solutions or alternative approaches. While the authors do call for a more ethical and inclusive approach to AI, they could have provided more detailed recommendations or frameworks for how to achieve this.
Additionally, the paper could have explored the role of other factors, such as historical biases, institutional racism, and the lack of diversity within the AI industry, in shaping the development of AI systems. While it touches on these issues, a more comprehensive analysis could have strengthened the paper's arguments.
Overall, the paper makes a valuable contribution to the ongoing debate around the societal impacts of AI and the need to address the systemic issues that have influenced its development. It encourages readers to think critically about the complex relationship between capitalism, technology, and social justice.
Conclusion
This paper offers a critical examination of how the capitalist system and the pursuit of profit have shaped the development of AI in ways that often marginalize and harm minoritized groups. The authors argue that the current AI ecosystem is structured to prioritize the interests of dominant social groups over the well-being of all people, and they call for a more ethical and inclusive approach to AI development and deployment.
The paper's key takeaway is that the social and ethical implications of AI cannot be divorced from the broader economic and political systems in which it is embedded. As the field of AI continues to evolve, it is crucial that we challenge the assumptions and power structures that have influenced its trajectory, and work towards the creation of AI systems that truly serve the needs of all people, not just those at the top of the economic hierarchy.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
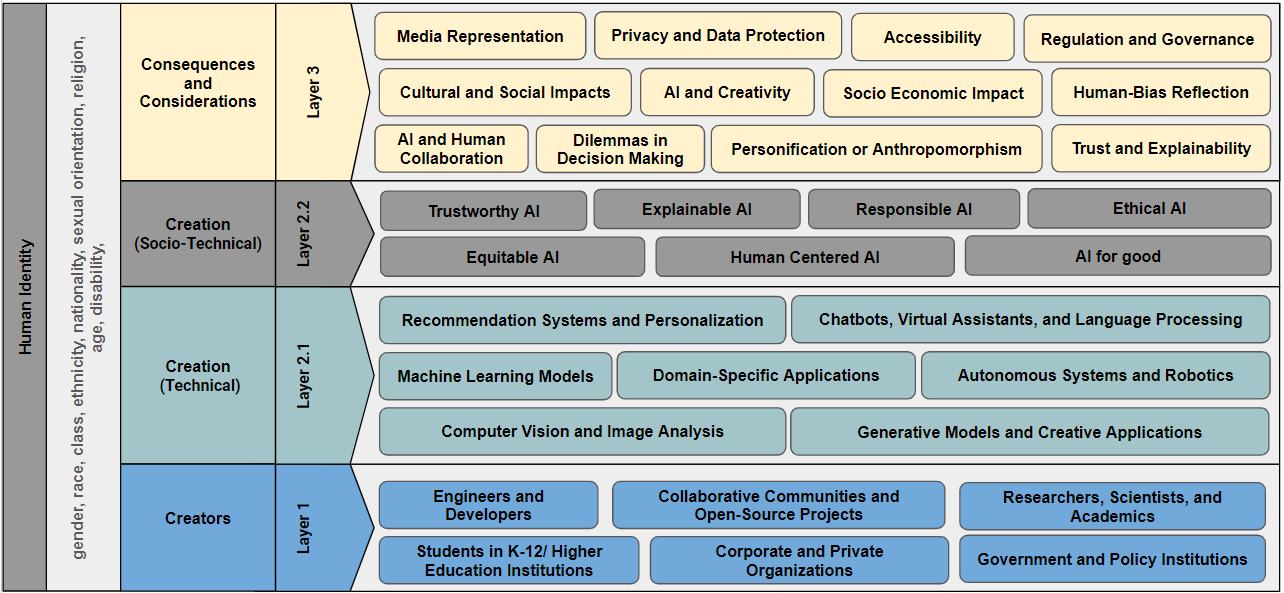
AI and Identity
Sri Yash Tadimalla, Mary Lou Maher

0
0
AI-empowered technologies' impact on the world is undeniable, reshaping industries, revolutionizing how humans interact with technology, transforming educational paradigms, and redefining social codes. However, this rapid growth is accompanied by two notable challenges: a lack of diversity within the AI field and a widening AI divide. In this context, This paper examines the intersection of AI and identity as a pathway to understand biases, inequalities, and ethical considerations in AI development and deployment. We present a multifaceted definition of AI identity, which encompasses its creators, applications, and their broader impacts. Understanding AI's identity involves understanding the associations between the individuals involved in AI's development, the technologies produced, and the social, ethical, and psychological implications. After exploring the AI identity ecosystem and its societal dynamics, We propose a framework that highlights the need for diversity in AI across three dimensions: Creators, Creations, and Consequences through the lens of identity. This paper proposes the need for a comprehensive approach to fostering a more inclusive and responsible AI ecosystem through the lens of identity.
4/12/2024

Thinking beyond Bias: Analyzing Multifaceted Impacts and Implications of AI on Gendered Labour
Satyam Mohla, Bishnupriya Bagh, Anupam Guha

0
0
Artificial Intelligence with its multifaceted technologies and integral role in global production significantly impacts gender dynamics particularly in gendered labor. This paper emphasizes the need to explore AIs broader impacts on gendered labor beyond its current emphasis on the generation and perpetuation of epistemic biases. We draw attention to how the AI industry as an integral component of the larger economic structure is transforming the nature of work. It is expanding the prevalence of platform based work models and exacerbating job insecurity particularly for women. Of critical concern is the increasing exclusion of women from meaningful engagement in the digital labor force. This issue often overlooked demands urgent attention from the AI research community. Understanding AIs multifaceted role in gendered labor requires a nuanced examination of economic transformation and its implications for gender equity. By shedding light on these intersections this paper aims to stimulate in depth discussions and catalyze targeted actions aimed at mitigating the gender disparities accentuated by AI driven transformations.
6/26/2024
👀
Position: Cracking the Code of Cascading Disparity Towards Marginalized Communities
Golnoosh Farnadi, Mohammad Havaei, Negar Rostamzadeh

0
0
The rise of foundation models holds immense promise for advancing AI, but this progress may amplify existing risks and inequalities, leaving marginalized communities behind. In this position paper, we discuss that disparities towards marginalized communities - performance, representation, privacy, robustness, interpretability and safety - are not isolated concerns but rather interconnected elements of a cascading disparity phenomenon. We contrast foundation models with traditional models and highlight the potential for exacerbated disparity against marginalized communities. Moreover, we emphasize the unique threat of cascading impacts in foundation models, where interconnected disparities can trigger long-lasting negative consequences, specifically to the people on the margin. We define marginalized communities within the machine learning context and explore the multifaceted nature of disparities. We analyze the sources of these disparities, tracing them from data creation, training and deployment procedures to highlight the complex technical and socio-technical landscape. To mitigate the pressing crisis, we conclude with a set of calls to action to mitigate disparity at its source.
6/5/2024
🐍
The impact of generative artificial intelligence on socioeconomic inequalities and policy making
Valerio Capraro, Austin Lentsch, Daron Acemoglu, Selin Akgun, Aisel Akhmedova, Ennio Bilancini, Jean-Franc{c}ois Bonnefon, Pablo Bra~nas-Garza, Luigi Butera, Karen M. Douglas, Jim A. C. Everett, Gerd Gigerenzer, Christine Greenhow, Daniel A. Hashimoto, Julianne Holt-Lunstad, Jolanda Jetten, Simon Johnson, Chiara Longoni, Pete Lunn, Simone Natale, Iyad Rahwan, Neil Selwyn, Vivek Singh, Siddharth Suri, Jennifer Sutcliffe, Joe Tomlinson, Sander van der Linden, Paul A. M. Van Lange, Friederike Wall, Jay J. Van Bavel, Riccardo Viale

0
0
Generative artificial intelligence has the potential to both exacerbate and ameliorate existing socioeconomic inequalities. In this article, we provide a state-of-the-art interdisciplinary overview of the potential impacts of generative AI on (mis)information and three information-intensive domains: work, education, and healthcare. Our goal is to highlight how generative AI could worsen existing inequalities while illuminating how AI may help mitigate pervasive social problems. In the information domain, generative AI can democratize content creation and access, but may dramatically expand the production and proliferation of misinformation. In the workplace, it can boost productivity and create new jobs, but the benefits will likely be distributed unevenly. In education, it offers personalized learning, but may widen the digital divide. In healthcare, it might improve diagnostics and accessibility, but could deepen pre-existing inequalities. In each section we cover a specific topic, evaluate existing research, identify critical gaps, and recommend research directions, including explicit trade-offs that complicate the derivation of a priori hypotheses. We conclude with a section highlighting the role of policymaking to maximize generative AI's potential to reduce inequalities while mitigating its harmful effects. We discuss strengths and weaknesses of existing policy frameworks in the European Union, the United States, and the United Kingdom, observing that each fails to fully confront the socioeconomic challenges we have identified. We propose several concrete policies that could promote shared prosperity through the advancement of generative AI. This article emphasizes the need for interdisciplinary collaborations to understand and address the complex challenges of generative AI.
5/7/2024