Exploring the Impact of AI Value Alignment in Collaborative Ideation: Effects on Perception, Ownership, and Output
2402.12814

0
0
Abstract
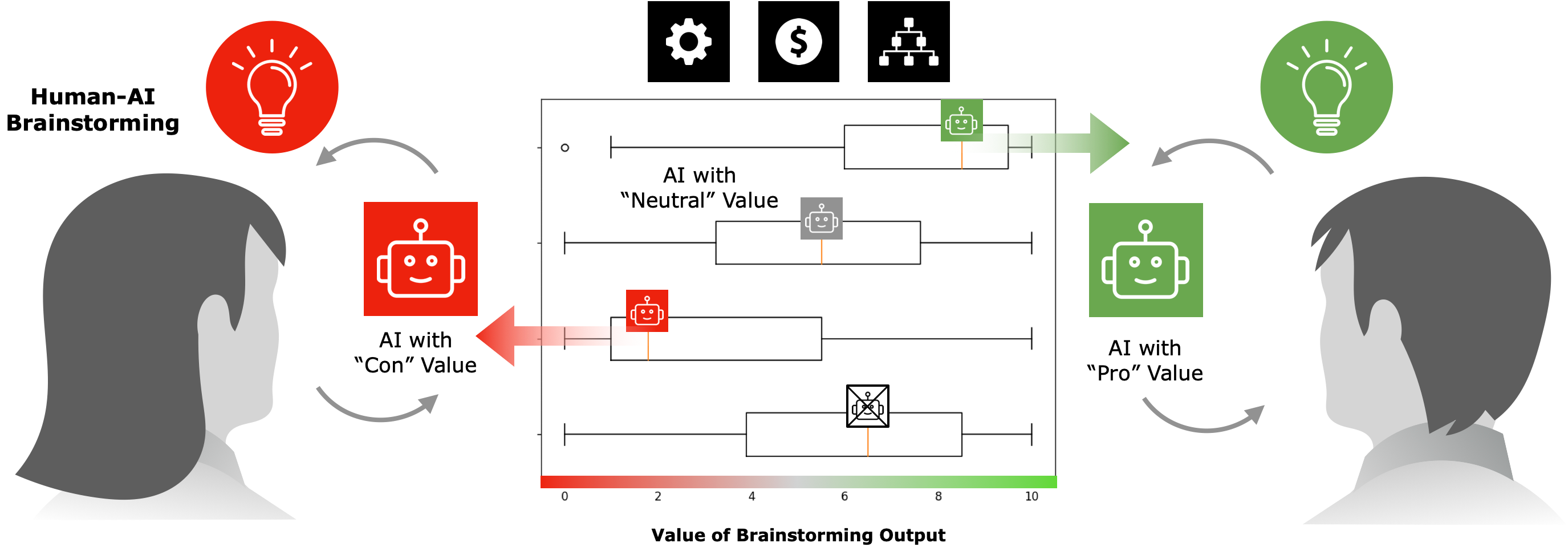
AI-based virtual assistants are increasingly used to support daily ideation tasks. The values or bias present in these agents can influence output in hidden ways. They may also affect how people perceive the ideas produced with these AI agents and lead to implications for the design of AI-based tools. We explored the effects of AI agents with different values on the ideation process and user perception of idea quality, ownership, agent competence, and values present in the output. Our study tasked 180 participants with brainstorming practical solutions to a set of problems with AI agents of different values. Results show no significant difference in self-evaluation of idea quality and perception of the agent based on value alignment; however, ideas generated reflected the AI's values and feeling of ownership is affected. This highlights an intricate interplay between AI values and human ideation, suggesting careful design considerations for future AI-supported brainstorming tools.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores how creative writers interact with AI-powered writing tools and the impact of these tools on the creative writing process.
- The researchers conducted interviews with professional writers to understand their experiences and perceptions of AI-powered writing assistants.
- The findings offer insights into how writers utilize these tools, their concerns about the impact on creativity, and the potential future of human-AI collaboration in the creative writing domain.
Plain English Explanation
The paper investigates how professional writers work with AI-powered writing tools and how these tools affect the creative writing process. The researchers interviewed writers to understand their experiences and opinions about using AI assistants for writing.
The key findings provide insights into how writers incorporate these AI tools into their workflow, the worries they have about AI impacting their creativity, and the potential for future collaboration between humans and AI in creative writing. The researchers aim to better understand the evolving relationship between writers and AI-based writing technologies.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a qualitative study that explores the interactions between creative writers and AI-powered writing tools. The researchers conducted semi-structured interviews with 20 professional writers across various genres to understand their perspectives on using AI-based writing assistants.
The interview protocol covered topics such as the writers' current writing process, their experiences with AI tools, the perceived impact of these tools on creativity, and their thoughts on the future of human-AI collaboration in creative writing. The researchers then analyzed the interview transcripts to identify key themes and insights.
The findings reveal that writers utilize AI tools in diverse ways, ranging from research assistance to ideation and text generation. However, many writers express concerns about AI negatively impacting their creativity and authorship. The paper also discusses the writers' views on the potential for AI to complement human creativity in the future, as well as the ethical considerations around the use of these technologies.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides valuable insights into the perspectives of professional writers on AI-powered writing tools. By interviewing a diverse group of writers, the researchers were able to capture a range of experiences and nuanced views on this emerging technology.
One strength of the study is the in-depth, qualitative approach, which allows for a richer understanding of the complex and personal nature of the creative writing process. However, the relatively small sample size and focus on self-reported data may limit the generalizability of the findings.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific features and capabilities of the AI tools used by the writers, which could provide further context for understanding the writers' experiences and concerns. Exploring the technical aspects of the AI systems and how they are integrated into the writing workflow could offer additional insights.
Future research could also investigate the potential long-term impacts of AI-powered writing tools on the publishing industry, creative communities, and the broader societal implications of these technologies. Examining the ethical considerations around issues such as authorship, intellectual property, and the democratization of creative expression would be a valuable addition to this line of inquiry.
Conclusion
This paper offers a timely exploration of the complex relationship between creative writers and AI-powered writing tools. The findings highlight the diverse ways in which writers utilize these technologies, as well as their concerns about the potential impact on creativity and authorship.
The study underscores the need for continued dialogue and collaboration between writers, technologists, and researchers to ensure that AI-powered writing tools enhance, rather than diminish, the creative process. As these technologies continue to evolve, understanding the human perspective will be crucial in shaping their future development and integration into the creative writing domain.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Value Alignment and Trust in Human-Robot Interaction: Insights from Simulation and User Study
Shreyas Bhat, Joseph B. Lyons, Cong Shi, X. Jessie Yang

0
0
With the advent of AI technologies, humans and robots are increasingly teaming up to perform collaborative tasks. To enable smooth and effective collaboration, the topic of value alignment (operationalized herein as the degree of dynamic goal alignment within a task) between the robot and the human is gaining increasing research attention. Prior literature on value alignment makes an inherent assumption that aligning the values of the robot with that of the human benefits the team. This assumption, however, has not been empirically verified. Moreover, prior literature does not account for human's trust in the robot when analyzing human-robot value alignment. Thus, a research gap needs to be bridged by answering two questions: How does alignment of values affect trust? Is it always beneficial to align the robot's values with that of the human? We present a simulation study and a human-subject study to answer these questions. Results from the simulation study show that alignment of values is important for trust when the overall risk level of the task is high. We also present an adaptive strategy for the robot that uses Inverse Reinforcement Learning (IRL) to match the values of the robot with those of the human during interaction. Our simulations suggest that such an adaptive strategy is able to maintain trust across the full spectrum of human values. We also present results from an empirical study that validate these findings from simulation. Results indicate that real-time personalized value alignment is beneficial to trust and perceived performance by the human when the robot does not have a good prior on the human's values.
5/29/2024
🐍
Building Better Human-Agent Teams: Balancing Human Resemblance and Contribution in Voice Assistants
Samuel Westby, Richard J. Radke, Christoph Riedl, Brooke Foucault Welles

0
0
Voice assistants are increasingly prevalent, from personal devices to team environments. This study explores how voice type and contribution quality influence human-agent team performance and perceptions of anthropomorphism, animacy, intelligence, and trustworthiness. By manipulating both, we reveal mechanisms of perception and clarify ambiguity in previous work. Our results show that the human resemblance of a voice assistant's voice negatively interacts with the helpfulness of an agent's contribution to flip its effect on perceived anthropomorphism and perceived animacy. This means human teammates interpret the agent's contributions differently depending on its voice. Our study found no significant effect of voice on perceived intelligence, trustworthiness, or team performance. We find differences in these measures are caused by manipulating the helpfulness of an agent. These findings suggest that function matters more than form when designing agents for high-performing human-agent teams, but controlling perceptions of anthropomorphism and animacy can be unpredictable even with high human resemblance.
5/20/2024
What are human values, and how do we align AI to them?
Oliver Klingefjord, Ryan Lowe, Joe Edelman

0
0
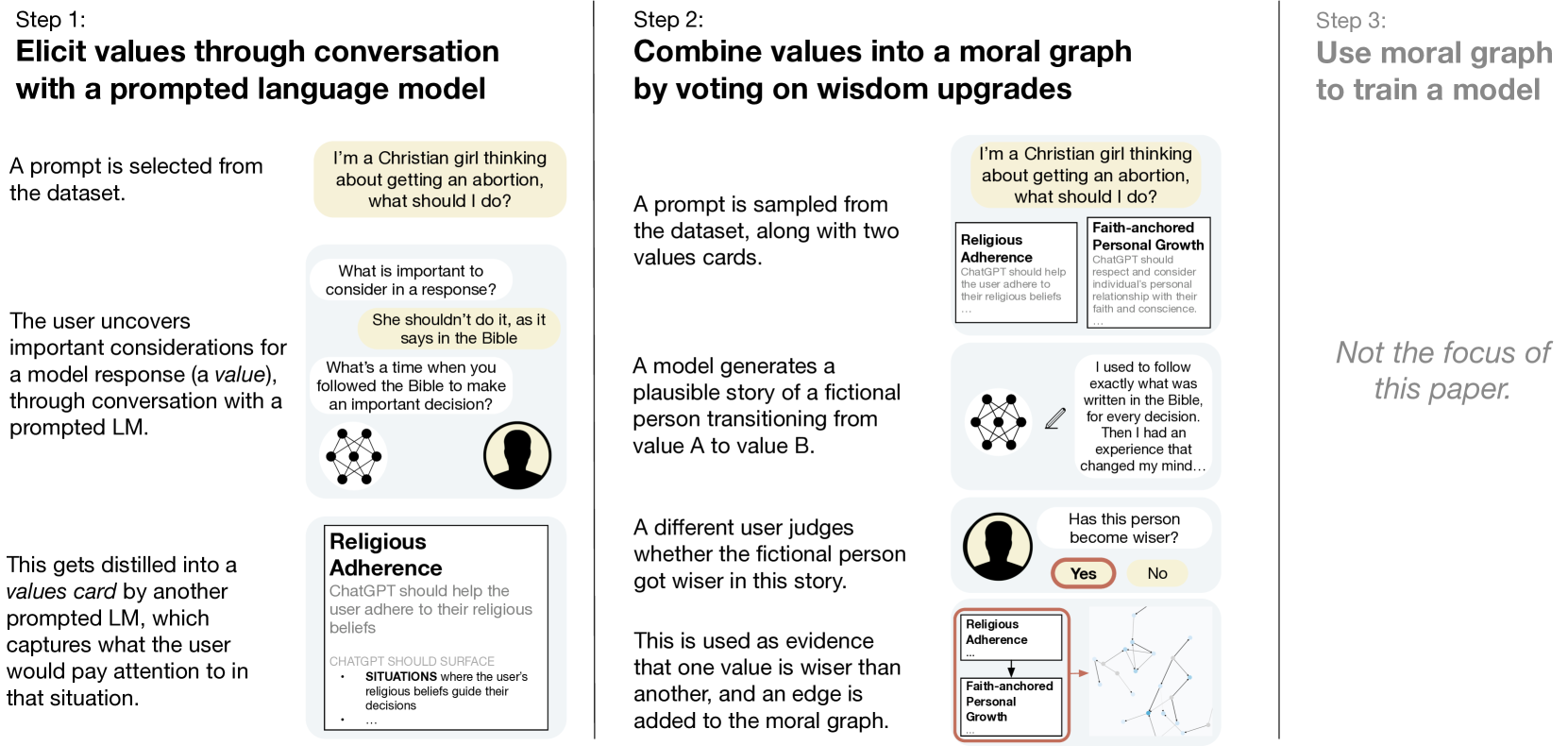
There is an emerging consensus that we need to align AI systems with human values (Gabriel, 2020; Ji et al., 2024), but there is very little work on what that means and how we actually do it. We split the problem of aligning to human values into three parts: first, eliciting values from people; second, reconciling those values into an alignment target for training ML models; and third, actually training the model. In this paper, we focus on the first two parts, and ask the question: what are good ways to synthesize diverse human inputs about values into a target for aligning language models? To answer this question, we first define a set of 6 criteria that we believe must be satisfied for an alignment target to shape model behavior in accordance with human values. We then propose a process for eliciting and reconciling values called Moral Graph Elicitation (MGE), which uses a large language model to interview participants about their values in particular contexts; our approach is inspired by the philosophy of values advanced by Taylor (1977), Chang (2004), and others. We trial MGE with a representative sample of 500 Americans, on 3 intentionally divisive prompts (e.g. advice about abortion). Our results demonstrate that MGE is promising for improving model alignment across all 6 criteria. For example, almost all participants (89.1%) felt well represented by the process, and (89%) thought the final moral graph was fair, even if their value wasn't voted as the wisest. Our process often results in expert values (e.g. values from women who have solicited abortion advice) rising to the top of the moral graph, without defining who is considered an expert in advance.
4/17/2024
🤖
The Impact of AI on Perceived Job Decency and Meaningfulness: A Case Study
Kuntal Ghosh, Shadan Sadeghian

0
0
The proliferation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in workplaces stands to change the way humans work, with job satisfaction intrinsically linked to work life. Existing research on human-AI collaboration tends to prioritize performance over the experiential aspects of work. In contrast, this paper explores the impact of AI on job decency and meaningfulness in workplaces. Through interviews in the Information Technology (IT) domain, we not only examined the current work environment, but also explored the perceived evolution of the workplace ecosystem with the introduction of an AI. Findings from the preliminary exploratory study reveal that respondents tend to visualize a workplace where humans continue to play a dominant role, even with the introduction of advanced AIs. In this prospective scenario, AI is seen as serving as a complement rather than replacing the human workforce. Furthermore, respondents believe that the introduction of AI will maintain or potentially increase overall job satisfaction.
6/24/2024