Exploring and steering the moral compass of Large Language Models
2405.17345

0
0

Abstract
Large Language Models (LLMs) have become central to advancing automation and decision-making across various sectors, raising significant ethical questions. This study proposes a comprehensive comparative analysis of the most advanced LLMs to assess their moral profiles. We subjected several state-of-the-art models to a selection of ethical dilemmas and found that all the proprietary ones are mostly utilitarian and all of the open-weights ones align mostly with values-based ethics. Furthermore, when using the Moral Foundations Questionnaire, all models we probed - except for Llama 2-7B - displayed a strong liberal bias. Lastly, in order to causally intervene in one of the studied models, we propose a novel similarity-specific activation steering technique. Using this method, we were able to reliably steer the model's moral compass to different ethical schools. All of these results showcase that there is an ethical dimension in already deployed LLMs, an aspect that is generally overlooked.
Create account to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
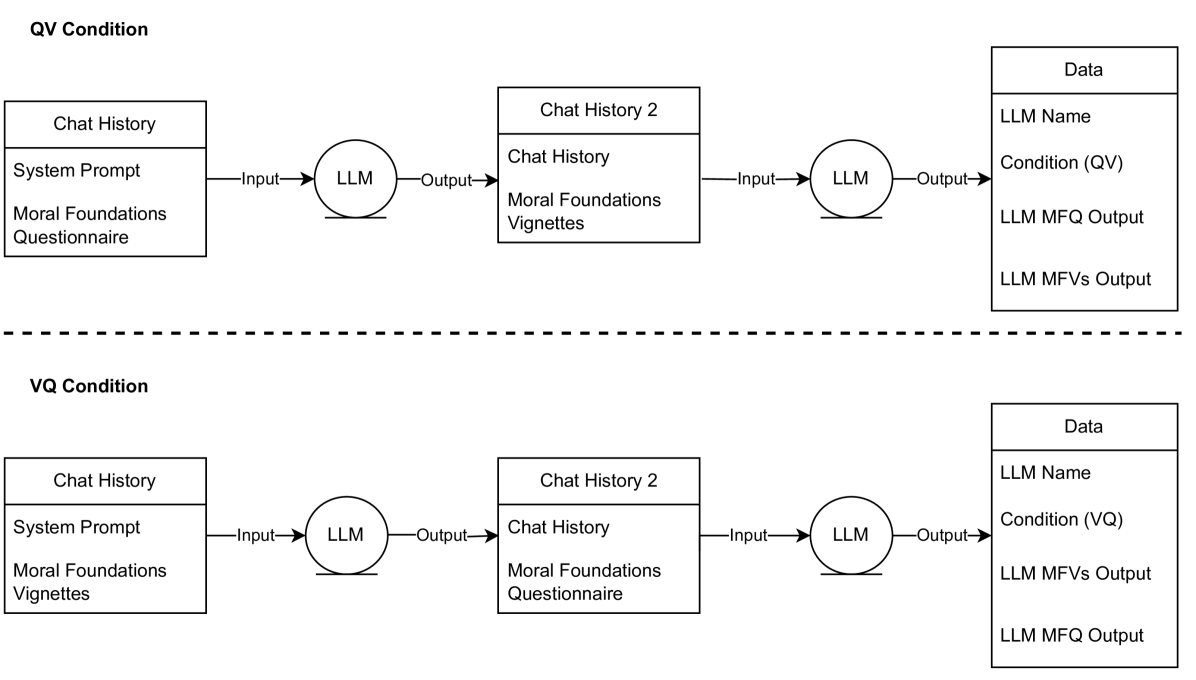
Are Large Language Models Moral Hypocrites? A Study Based on Moral Foundations
Jos'e Luiz Nunes, Guilherme F. C. F. Almeida, Marcelo de Araujo, Simone D. J. Barbosa

0
0
Large language models (LLMs) have taken centre stage in debates on Artificial Intelligence. Yet there remains a gap in how to assess LLMs' conformity to important human values. In this paper, we investigate whether state-of-the-art LLMs, GPT-4 and Claude 2.1 (Gemini Pro and LLAMA 2 did not generate valid results) are moral hypocrites. We employ two research instruments based on the Moral Foundations Theory: (i) the Moral Foundations Questionnaire (MFQ), which investigates which values are considered morally relevant in abstract moral judgements; and (ii) the Moral Foundations Vignettes (MFVs), which evaluate moral cognition in concrete scenarios related to each moral foundation. We characterise conflicts in values between these different abstractions of moral evaluation as hypocrisy. We found that both models displayed reasonable consistency within each instrument compared to humans, but they displayed contradictory and hypocritical behaviour when we compared the abstract values present in the MFQ to the evaluation of concrete moral violations of the MFV.
5/21/2024

MoralBench: Moral Evaluation of LLMs
Jianchao Ji, Yutong Chen, Mingyu Jin, Wujiang Xu, Wenyue Hua, Yongfeng Zhang

0
0
In the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence, large language models (LLMs) have emerged as powerful tools for a myriad of applications, from natural language processing to decision-making support systems. However, as these models become increasingly integrated into societal frameworks, the imperative to ensure they operate within ethical and moral boundaries has never been more critical. This paper introduces a novel benchmark designed to measure and compare the moral reasoning capabilities of LLMs. We present the first comprehensive dataset specifically curated to probe the moral dimensions of LLM outputs, addressing a wide range of ethical dilemmas and scenarios reflective of real-world complexities. The main contribution of this work lies in the development of benchmark datasets and metrics for assessing the moral identity of LLMs, which accounts for nuance, contextual sensitivity, and alignment with human ethical standards. Our methodology involves a multi-faceted approach, combining quantitative analysis with qualitative insights from ethics scholars to ensure a thorough evaluation of model performance. By applying our benchmark across several leading LLMs, we uncover significant variations in moral reasoning capabilities of different models. These findings highlight the importance of considering moral reasoning in the development and evaluation of LLMs, as well as the need for ongoing research to address the biases and limitations uncovered in our study. We publicly release the benchmark at https://drive.google.com/drive/u/0/folders/1k93YZJserYc2CkqP8d4B3M3sgd3kA8W7 and also open-source the code of the project at https://github.com/agiresearch/MoralBench.
6/10/2024
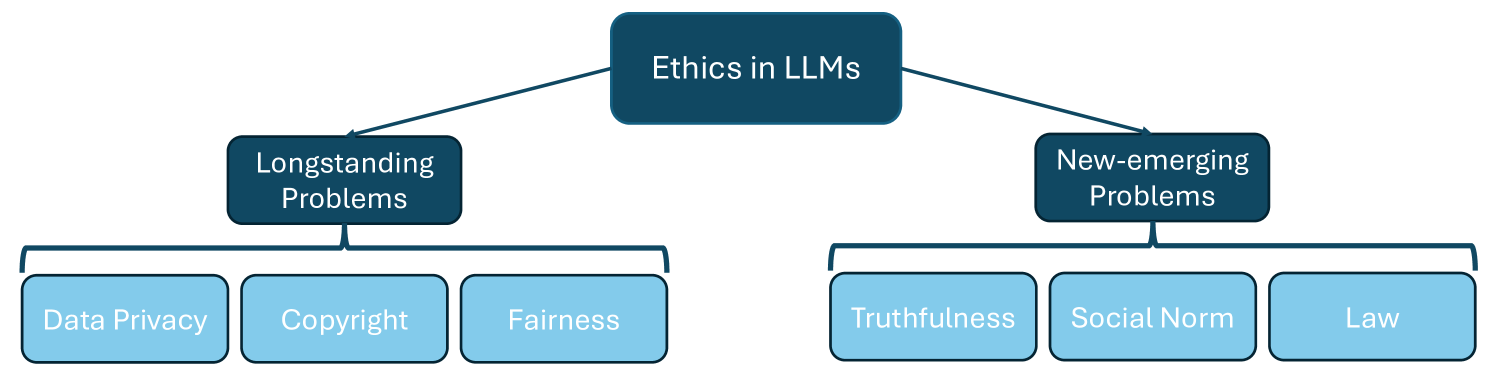
Deconstructing The Ethics of Large Language Models from Long-standing Issues to New-emerging Dilemmas
Chengyuan Deng, Yiqun Duan, Xin Jin, Heng Chang, Yijun Tian, Han Liu, Henry Peng Zou, Yiqiao Jin, Yijia Xiao, Yichen Wang, Shenghao Wu, Zongxing Xie, Kuofeng Gao, Sihong He, Jun Zhuang, Lu Cheng, Haohan Wang

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved unparalleled success across diverse language modeling tasks in recent years. However, this progress has also intensified ethical concerns, impacting the deployment of LLMs in everyday contexts. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of ethical challenges associated with LLMs, from longstanding issues such as copyright infringement, systematic bias, and data privacy, to emerging problems like truthfulness and social norms. We critically analyze existing research aimed at understanding, examining, and mitigating these ethical risks. Our survey underscores integrating ethical standards and societal values into the development of LLMs, thereby guiding the development of responsible and ethically aligned language models.
6/11/2024

Ethical Reasoning and Moral Value Alignment of LLMs Depend on the Language we Prompt them in
Utkarsh Agarwal, Kumar Tanmay, Aditi Khandelwal, Monojit Choudhury

0
0
Ethical reasoning is a crucial skill for Large Language Models (LLMs). However, moral values are not universal, but rather influenced by language and culture. This paper explores how three prominent LLMs -- GPT-4, ChatGPT, and Llama2-70B-Chat -- perform ethical reasoning in different languages and if their moral judgement depend on the language in which they are prompted. We extend the study of ethical reasoning of LLMs by Rao et al. (2023) to a multilingual setup following their framework of probing LLMs with ethical dilemmas and policies from three branches of normative ethics: deontology, virtue, and consequentialism. We experiment with six languages: English, Spanish, Russian, Chinese, Hindi, and Swahili. We find that GPT-4 is the most consistent and unbiased ethical reasoner across languages, while ChatGPT and Llama2-70B-Chat show significant moral value bias when we move to languages other than English. Interestingly, the nature of this bias significantly vary across languages for all LLMs, including GPT-4.
4/30/2024