Statistical QoS Provisioning Architecture for 6G Satellite-Terrestrial Integrated Networks
2406.04685

0
0
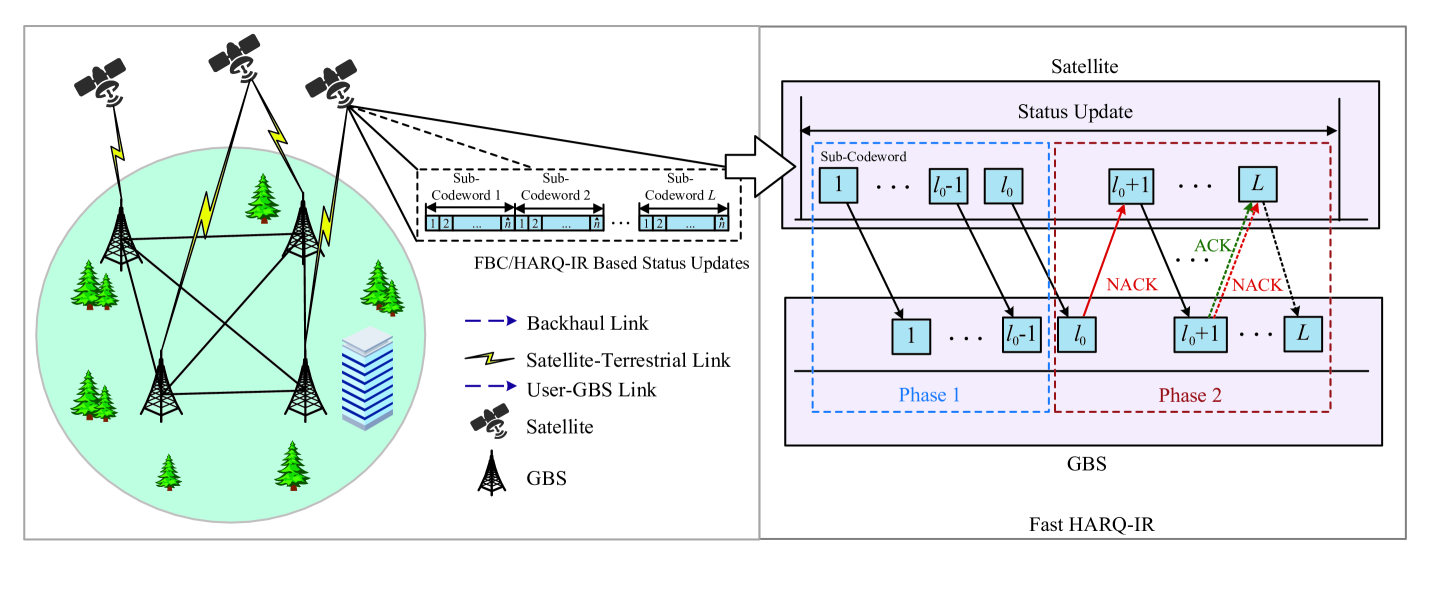
Abstract
The emergence of massive ultra-reliable and low latency communications (mURLLC) as a category of time/reliability-sensitive service over 6G networks has received considerable research attention, which has presented unprecedented challenges. As one of the key enablers for 6G, satellite-terrestrial integrated networks (STIN) have been developed to offer more expansive connectivity and comprehensive 3D coverage in space-aerial-terrestrial domains for supporting 6G mission-critical mURLLC applications while fulfilling diverse and rigorous quality of service (QoS) requirements. In the context of these mURLLC-driven satellite services, data freshness assumes paramount importance, as outdated data may engender unpredictable or catastrophic outcomes. To effectively measure data freshness in satellite-terrestrial integrated communications, age of information (AoI) has recently surfaced as a new dimension of QoS metric to support time-sensitive applications. It is crucial to design new analytical models that ensure stringent and diverse QoS metrics bounded by different key parameters, including AoI, delay, and reliability, over 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks. However, due to the complicated and dynamic nature of satellite-terrestrial integrated network environments, the research on efficiently defining new statistical QoS schemes while taking into account varying degrees of freedom has still been in their infancy. To remedy these deficiencies, in this paper we develop statistical QoS provisioning schemes over 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks in the finite blocklength regime. Particularly, we firstly introduce and review key technologies for supporting mURLLC. Secondly, we formulate a number of novel fundamental statistical-QoS metrics in the finite blocklength regime. Finally, we conduct a set of simulations to evaluate our developed statistical QoS schemes.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper proposes a statistical QoS provisioning architecture for 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks.
- Key elements include: statistical QoS provisioning, mobile ultra-reliable and low-latency communication (mURLLC), peak Age of Information (AoI), finite blocklength coding, and Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest (HARQ).
- The architecture aims to optimize QoS performance for 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks.
Plain English Explanation
The paper presents a new system architecture to help manage the quality of service (QoS) in future 6G wireless networks that combine satellite and ground-based cellular networks. These integrated networks will need to support a wide range of applications with different QoS requirements, from delay-sensitive communications to reliable data transfer.
The proposed approach uses statistical techniques to provision QoS, meaning it provides a probabilistic guarantee of meeting QoS targets rather than an absolute guarantee. This is important because it allows the network to efficiently utilize resources while still meeting the needs of different applications.
Some key elements of the architecture include:
- Mobile ultra-reliable and low-latency communication (mURLLC): Enabling ultra-reliable and low-latency communications for mobile devices.
- Peak Age of Information (AoI): Minimizing the freshness of information received by applications.
- Finite blocklength coding: Improving efficiency by optimizing the coding of data packets.
- Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest (HARQ): Enhancing reliability through retransmission of lost or corrupted data packets.
By incorporating these techniques, the proposed architecture aims to provide effective QoS management and optimization for the diverse requirements of 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a statistical QoS provisioning architecture for 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks. The key elements of the architecture include:
-
Statistical QoS Provisioning: Rather than providing absolute QoS guarantees, the architecture uses statistical techniques to offer probabilistic QoS assurances. This allows for more efficient resource utilization while still meeting application requirements.
-
Mobile Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communication (mURLLC): The architecture supports mURLLC, which enables ultra-reliable and low-latency communications for mobile devices. This is crucial for time-sensitive applications in 6G integrated networks.
-
Peak Age of Information (AoI): The system minimizes the peak AoI, which measures the freshness of information received by applications. Keeping the peak AoI low is important for applications that require timely data.
-
Finite Blocklength Coding: The architecture employs finite blocklength coding to improve the efficiency of data transmission. This is particularly relevant for short data packets that are common in 6G networks.
-
Hybrid Automatic Repeat reQuest (HARQ): The system incorporates HARQ to enhance the reliability of data transmission by retransmitting lost or corrupted packets. This helps meet the stringent reliability requirements of 6G applications.
The paper presents an analytical model to characterize the QoS performance of the proposed architecture. It also provides a numerical evaluation to demonstrate the effectiveness of the statistical QoS provisioning approach in achieving the desired QoS targets for 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a well-designed statistical QoS provisioning architecture that addresses the diverse requirements of 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks. The incorporation of techniques like mURLLC, peak AoI, finite blocklength coding, and HARQ is a comprehensive approach to QoS management.
One potential limitation of the research is the focus on analytical modeling and numerical evaluation. While these provide valuable insights, real-world implementation and testing would be necessary to fully validate the performance and feasibility of the proposed architecture. Evaluating the architecture in realistic 6G network simulations or trials would provide additional practical insights.
Additionally, the paper does not extensively discuss the challenges and tradeoffs involved in coordinating QoS provisioning between the satellite and terrestrial components of the integrated network. Further research could explore the operational complexities and potential bottlenecks in integrating these two network domains.
Overall, the proposed statistical QoS provisioning architecture represents a significant step forward in addressing the QoS requirements of 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks. However, additional validation and research on practical implementation considerations would strengthen the insights provided by this work.
Conclusion
This paper presents a statistical QoS provisioning architecture for 6G satellite-terrestrial integrated networks. The key elements of the architecture include statistical QoS provisioning, mURLLC, peak AoI, finite blocklength coding, and HARQ. By incorporating these techniques, the proposed system aims to effectively manage and optimize the QoS performance for the diverse range of applications and requirements in future 6G networks.
The analytical modeling and numerical evaluation provided in the paper demonstrate the potential of the statistical QoS provisioning approach to meet the QoS targets for 6G integrated networks. However, further research on real-world implementation and operational challenges would be valuable to fully validate the feasibility and practicality of the proposed architecture.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
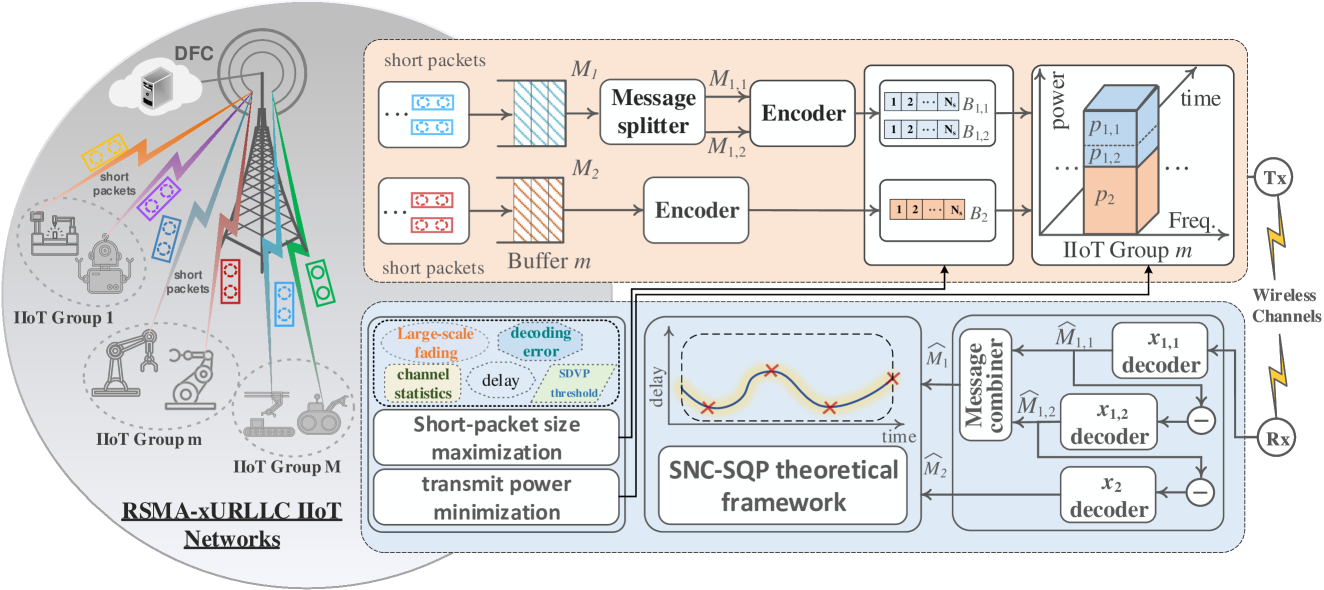
Performance Optimization in RSMA-assisted Uplink xURLLC IIoT Networks with Statistical QoS Provisioning
Yuang Chen, Hancheng Lu, Chang Wu, Langtian Qin, Xiaobo Guo

0
0
Industry 5.0 and beyond networks have driven the emergence of numerous mission-critical applications, prompting contemplation of the neXt-generation ultra-reliable low-latency communication (xURLLC). To guarantee low-latency requirements, xURLLC heavily relies on short-blocklength packets with sporadic arrival traffic. As a disruptive multi-access technique, rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) has emerged as a promising avenue to enhance quality of service (QoS) and flexibly manage interference for next-generation communication networks. In this paper, we investigate an innovative RSMA-assisted uplink xURLLC industrial internet-of-things (IIoT) (RSMA-xURLLC-IIoT) network. To unveil reliable insights into the statistical QoS provisioning (SQP) for our proposed network with sporadic arrival traffic, we leverage stochastic network calculus (SNC) to develop a dependable theoretical framework. Building upon this theoretical framework, we formulate the SQP-driven short-packet size maximization problem and the SQP-driven transmit power minimization problem, aiming to guarantee the SQP performance to latency, decoding, and reliability while maximizing the short-packet size and minimizing the transmit power, respectively. By exploiting Monte-Carlo methods, we have thoroughly validated the dependability of the developed theoretical framework. Moreover, through extensive comparison analysis with state-of-the-art multi-access techniques, including non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and orthogonal multiple access (OMA), we have demonstrated the superior performance gains achieved by the proposed RSMA-xURLLC-IIoT networks.
5/28/2024

Fairness-aware Age-of-Information Minimization in WPT-Assisted Short-Packet THz Communications for mURLLC
Yao Zhu, Xiaopeng Yuan, Yulin Hu, Bo Ai, Ruikang Wang, Bin Han, Anke Schmeink

0
0
The technological landscape is swiftly advancing towards large-scale systems, creating significant opportunities, particularly in the domain of Terahertz (THz) communications. Networks designed for massive connectivity, comprising numerous Internet of Things (IoT) devices, are at the forefront of this advancement. In this paper, we consider Wireless Power Transfer (WPT)-enabled networks that support these IoT devices with massive Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communication (mURLLC) services.The focus of such networks is information freshness, with the Age-of-Information (AoI) serving as the pivotal performance metric. In particular, we aim to minimize the maximum AoI among IoT devices by optimizing the scheduling policy. Our analytical findings establish the convexity property of the problem, which can be solved efficiently. Furthermore, we introduce the concept of AoI-oriented cluster capacity, examining the relationship between the number of supported devices and the AoI performance in the network. Numerical simulations validate the advantage of our proposed approach in enhancing AoI performance, indicating its potential to guide the design of future THz communication systems for IoT applications requiring mURLLC services.
4/4/2024

Quality of Service-Constrained Online Routing in High Throughput Satellites
Olivier B'elanger, Olfa Ben Yahia, St'ephane Martel, Antoine Lesage-Landry, Gunes Karabulut Kurt

0
0
High throughput satellites (HTSs) outpace traditional satellites due to their multi-beam transmission. The rise of low Earth orbit mega constellations amplifies HTS data rate demands to terabits/second with acceptable latency. This surge in data rate necessitates multiple modems, often exceeding single device capabilities. Consequently, satellites employ several processors, forming a complex packet-switch network. This can lead to potential internal congestion and challenges in adhering to strict quality of service (QoS) constraints. While significant research exists on constellation-level routing, a literature gap remains on the internal routing within a single HTS. The intricacy of this internal network architecture presents a significant challenge to achieve high data rates. This paper introduces an online optimal flow allocation and scheduling method for HTSs. The problem is presented as a multi-commodity flow instance with different priority data streams. An initial full time horizon model is proposed as a benchmark. We apply a model predictive control (MPC) approach to enable adaptive routing based on current information and the forecast within the prediction time horizon while allowing for deviation of the latter. Importantly, MPC is inherently suited to handle uncertainty in incoming flows. Our approach minimizes the packet loss by optimally and adaptively managing the priority queue schedulers and flow exchanges between satellite processing modules. Central to our method is a routing model focusing on optimal priority scheduling to enhance data rates and maintain QoS. The model's stages are critically evaluated, and results are compared to traditional methods via numerical simulations. Through simulations, our method demonstrates performance nearly on par with the hindsight optimum, showcasing its efficiency and adaptability in addressing satellite communication challenges.
6/3/2024

Data Service Maximization in Integrated Terrestrial-Non-Terrestrial 6G Networks: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach
Nway Nway Ei, Kitae Kim, Yan Kyaw Tun, Choong Seon Hong

0
0
Integrating terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks has emerged as a promising paradigm to fulfill the constantly growing demand for connectivity, low transmission delay, and quality of services (QoS). This integration brings together the strengths of terrestrial and non-terrestrial networks, such as the reliability of terrestrial networks, broad coverage, and service continuity of non-terrestrial networks like low earth orbit (LEO) satellites. In this work, we study a data service maximization problem in an integrated terrestrial-non-terrestrial network (I-TNT) where the ground base stations (GBSs) and LEO satellites cooperatively serve the coexisting aerial users (AUs) and ground users (GUs). Then, by considering the spectrum scarcity, interference, and QoS requirements of the users, we jointly optimize the user association, AUE's trajectory, and power allocation. To tackle the formulated mixed-integer non-convex problem, we disintegrate it into two subproblems: 1) user association problem and 2) trajectory and power allocation problem. Since the user association problem is a binary integer programming problem, we use the standard convex optimization method to solve it. Meanwhile, the trajectory and power allocation problem is solved by the deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG) method to cope with the problem's non-convexity and dynamic network environments. Then, the two subproblems are alternately solved by the proposed iterative algorithm. By comparing with the baselines in the existing literature, extensive simulations are conducted to evaluate the performance of the proposed framework.
5/31/2024