Feature 3DGS: Supercharging 3D Gaussian Splatting to Enable Distilled Feature Fields
2312.03203

0
0
✨
Abstract
3D scene representations have gained immense popularity in recent years. Methods that use Neural Radiance fields are versatile for traditional tasks such as novel view synthesis. In recent times, some work has emerged that aims to extend the functionality of NeRF beyond view synthesis, for semantically aware tasks such as editing and segmentation using 3D feature field distillation from 2D foundation models. However, these methods have two major limitations: (a) they are limited by the rendering speed of NeRF pipelines, and (b) implicitly represented feature fields suffer from continuity artifacts reducing feature quality. Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting has shown state-of-the-art performance on real-time radiance field rendering. In this work, we go one step further: in addition to radiance field rendering, we enable 3D Gaussian splatting on arbitrary-dimension semantic features via 2D foundation model distillation. This translation is not straightforward: naively incorporating feature fields in the 3DGS framework encounters significant challenges, notably the disparities in spatial resolution and channel consistency between RGB images and feature maps. We propose architectural and training changes to efficiently avert this problem. Our proposed method is general, and our experiments showcase novel view semantic segmentation, language-guided editing and segment anything through learning feature fields from state-of-the-art 2D foundation models such as SAM and CLIP-LSeg. Across experiments, our distillation method is able to provide comparable or better results, while being significantly faster to both train and render. Additionally, to the best of our knowledge, we are the first method to enable point and bounding-box prompting for radiance field manipulation, by leveraging the SAM model. Project website at: https://feature-3dgs.github.io/
Create account to get full access
The paper introduces a novel approach that combines 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) with feature field distillation from 2D foundation models. This enables real-time rendering of radiance fields along with semantically aware tasks such as editing and segmentation. The method addresses limitations of existing NeRF-based approaches, which suffer from slow rendering speeds and continuity artifacts in implicitly represented feature fields.
The authors propose architectural and training modifications to efficiently incorporate feature fields into the 3DGS framework, overcoming challenges related to spatial resolution and channel consistency disparities between RGB images and feature maps. The proposed method demonstrates its versatility through experiments on novel view semantic segmentation, language-guided editing, and segment anything using state-of-the-art 2D foundation models like SAM and CLIP-LSeg.
Compared to existing methods, this distillation approach provides comparable or better results while significantly reducing training and rendering times. Additionally, the paper introduces the first method to enable point and bounding-box prompting for radiance field manipulation by leveraging the SAM model.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Recent Advances in 3D Gaussian Splatting
Tong Wu, Yu-Jie Yuan, Ling-Xiao Zhang, Jie Yang, Yan-Pei Cao, Ling-Qi Yan, Lin Gao

0
0
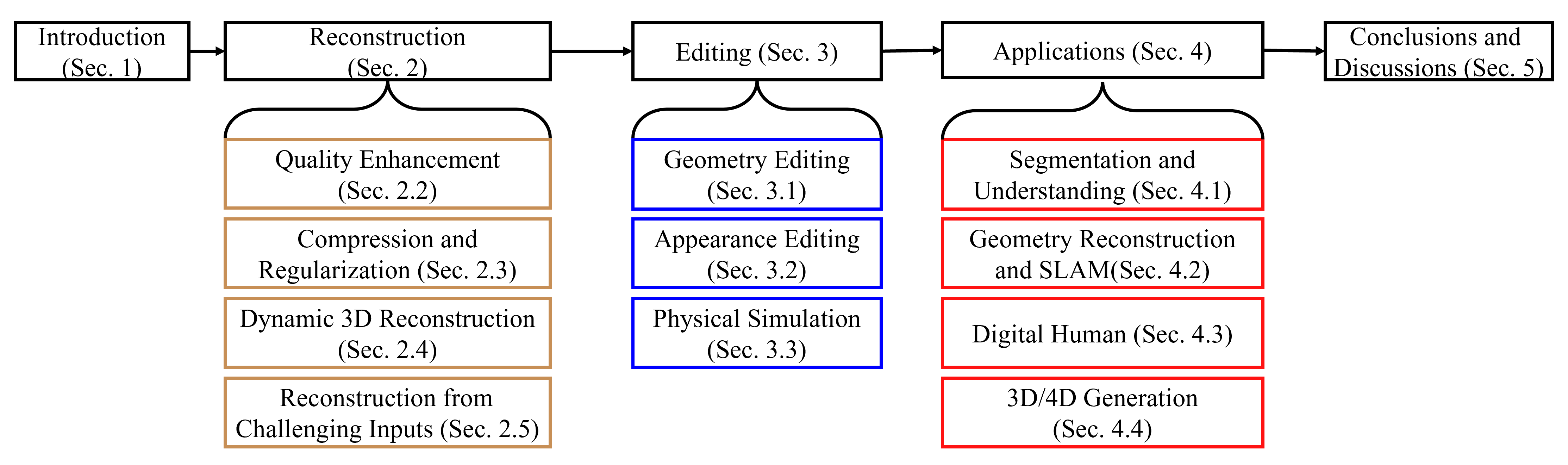
The emergence of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has greatly accelerated the rendering speed of novel view synthesis. Unlike neural implicit representations like Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) that represent a 3D scene with position and viewpoint-conditioned neural networks, 3D Gaussian Splatting utilizes a set of Gaussian ellipsoids to model the scene so that efficient rendering can be accomplished by rasterizing Gaussian ellipsoids into images. Apart from the fast rendering speed, the explicit representation of 3D Gaussian Splatting facilitates editing tasks like dynamic reconstruction, geometry editing, and physical simulation. Considering the rapid change and growing number of works in this field, we present a literature review of recent 3D Gaussian Splatting methods, which can be roughly classified into 3D reconstruction, 3D editing, and other downstream applications by functionality. Traditional point-based rendering methods and the rendering formulation of 3D Gaussian Splatting are also illustrated for a better understanding of this technique. This survey aims to help beginners get into this field quickly and provide experienced researchers with a comprehensive overview, which can stimulate the future development of the 3D Gaussian Splatting representation.
4/16/2024
Gaussian Splatting Decoder for 3D-aware Generative Adversarial Networks
Florian Barthel, Arian Beckmann, Wieland Morgenstern, Anna Hilsmann, Peter Eisert

0
0
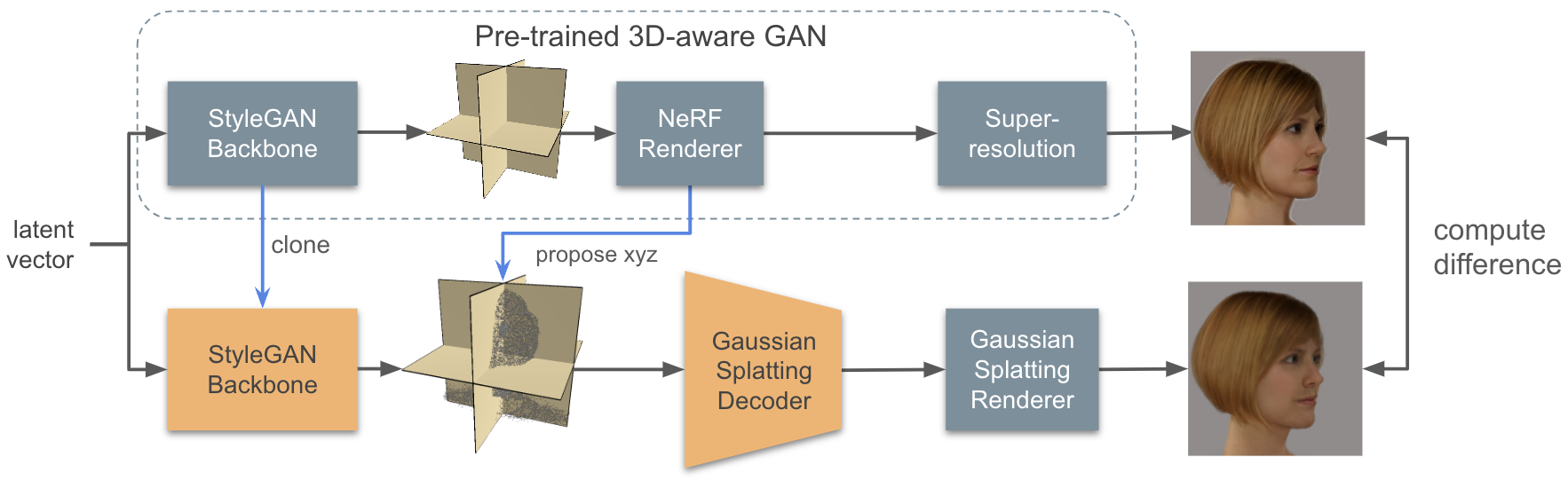
NeRF-based 3D-aware Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) like EG3D or GIRAFFE have shown very high rendering quality under large representational variety. However, rendering with Neural Radiance Fields poses challenges for 3D applications: First, the significant computational demands of NeRF rendering preclude its use on low-power devices, such as mobiles and VR/AR headsets. Second, implicit representations based on neural networks are difficult to incorporate into explicit 3D scenes, such as VR environments or video games. 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) overcomes these limitations by providing an explicit 3D representation that can be rendered efficiently at high frame rates. In this work, we present a novel approach that combines the high rendering quality of NeRF-based 3D-aware GANs with the flexibility and computational advantages of 3DGS. By training a decoder that maps implicit NeRF representations to explicit 3D Gaussian Splatting attributes, we can integrate the representational diversity and quality of 3D GANs into the ecosystem of 3D Gaussian Splatting for the first time. Additionally, our approach allows for a high resolution GAN inversion and real-time GAN editing with 3D Gaussian Splatting scenes. Project page: florian-barthel.github.io/gaussian_decoder
6/19/2024
2D Gaussian Splatting for Geometrically Accurate Radiance Fields
Binbin Huang, Zehao Yu, Anpei Chen, Andreas Geiger, Shenghua Gao

0
0
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently revolutionized radiance field reconstruction, achieving high quality novel view synthesis and fast rendering speed without baking. However, 3DGS fails to accurately represent surfaces due to the multi-view inconsistent nature of 3D Gaussians. We present 2D Gaussian Splatting (2DGS), a novel approach to model and reconstruct geometrically accurate radiance fields from multi-view images. Our key idea is to collapse the 3D volume into a set of 2D oriented planar Gaussian disks. Unlike 3D Gaussians, 2D Gaussians provide view-consistent geometry while modeling surfaces intrinsically. To accurately recover thin surfaces and achieve stable optimization, we introduce a perspective-correct 2D splatting process utilizing ray-splat intersection and rasterization. Additionally, we incorporate depth distortion and normal consistency terms to further enhance the quality of the reconstructions. We demonstrate that our differentiable renderer allows for noise-free and detailed geometry reconstruction while maintaining competitive appearance quality, fast training speed, and real-time rendering.
6/11/2024
RT-GS2: Real-Time Generalizable Semantic Segmentation for 3D Gaussian Representations of Radiance Fields
Mihnea-Bogdan Jurca, Remco Royen, Ion Giosan, Adrian Munteanu

0
0
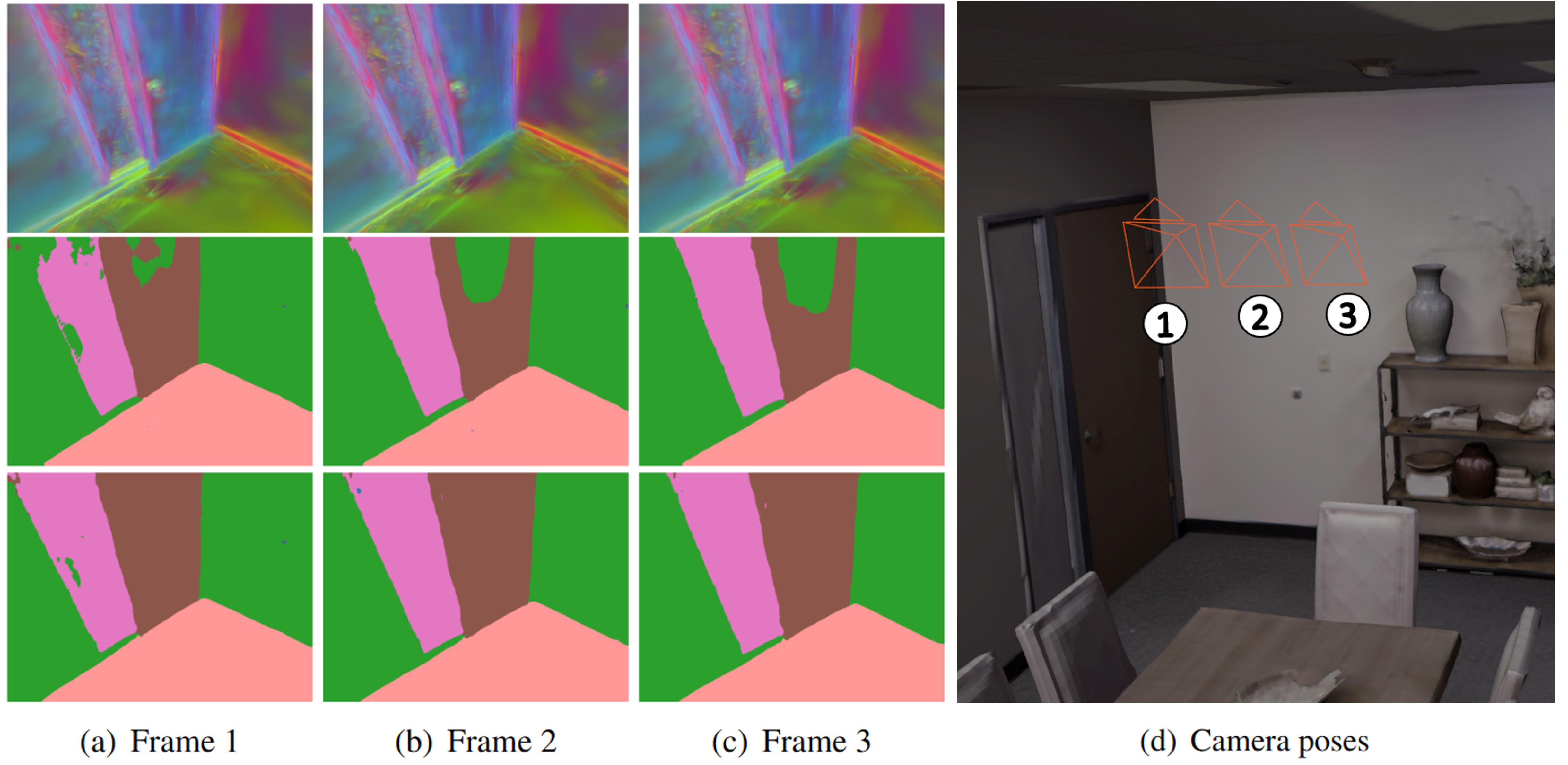
Gaussian Splatting has revolutionized the world of novel view synthesis by achieving high rendering performance in real-time. Recently, studies have focused on enriching these 3D representations with semantic information for downstream tasks. In this paper, we introduce RT-GS2, the first generalizable semantic segmentation method employing Gaussian Splatting. While existing Gaussian Splatting-based approaches rely on scene-specific training, RT-GS2 demonstrates the ability to generalize to unseen scenes. Our method adopts a new approach by first extracting view-independent 3D Gaussian features in a self-supervised manner, followed by a novel View-Dependent / View-Independent (VDVI) feature fusion to enhance semantic consistency over different views. Extensive experimentation on three different datasets showcases RT-GS2's superiority over the state-of-the-art methods in semantic segmentation quality, exemplified by a 8.01% increase in mIoU on the Replica dataset. Moreover, our method achieves real-time performance of 27.03 FPS, marking an astonishing 901 times speedup compared to existing approaches. This work represents a significant advancement in the field by introducing, to the best of our knowledge, the first real-time generalizable semantic segmentation method for 3D Gaussian representations of radiance fields.
5/29/2024