GENEVA: GENErating and Visualizing branching narratives using LLMs
2311.09213

0
0
🤿
Abstract
Dialogue-based Role Playing Games (RPGs) require powerful storytelling. The narratives of these may take years to write and typically involve a large creative team. In this work, we demonstrate the potential of large generative text models to assist this process. textbf{GENEVA}, a prototype tool, generates a rich narrative graph with branching and reconverging storylines that match a high-level narrative description and constraints provided by the designer. A large language model (LLM), GPT-4, is used to generate the branching narrative and to render it in a graph format in a two-step process. We illustrate the use of GENEVA in generating new branching narratives for four well-known stories under different contextual constraints. This tool has the potential to assist in game development, simulations, and other applications with game-like properties.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the use of large language models (LLMs) to assist in the creation of branching narratives for dialogue-based role-playing games (RPGs).
- The authors present a prototype tool called GENEVA that generates a rich narrative graph with branching and reconverging storylines based on high-level narrative descriptions and constraints provided by the game designer.
- The system utilizes GPT-4, a powerful LLM, to generate the branching narrative and represent it in a graph format.
- The paper showcases the use of GENEVA in generating new branching narratives for four well-known stories under different contextual constraints.
- The authors suggest this tool has the potential to assist in game development, simulations, and other applications with game-like properties.
Plain English Explanation
Dialogue-based role-playing games (RPGs) often have complex narratives that can take years to write and require a large team of creative professionals. This paper demonstrates how large language models (LLMs) can be used to assist in the storytelling process.
The authors created a prototype tool called GENEVA that can generate a rich, branching narrative based on high-level descriptions and constraints provided by the game designer. GENEVA uses a powerful LLM called GPT-4 to generate the branching storylines and represent them in a visual graph format.
The researchers showcased GENEVA's capabilities by using it to create new branching narratives for four well-known stories, each with different contextual constraints. This suggests the tool could be valuable for game developers, simulation creators, and others working on projects that require dynamic, interactive storytelling.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a prototype tool called GENEVA that leverages large language models (LLMs) to generate branching narratives for dialogue-based role-playing games (RPGs). The key elements of the system are as follows:
- Narrative Graph Generation: GENEVA takes a high-level narrative description and a set of constraints provided by the game designer as input. It then uses GPT-4, a powerful LLM, to generate a rich narrative graph with branching and reconverging storylines.
- Two-Step Process: The system operates in two steps: 1) The LLM generates the branching narrative, and 2) GENEVA renders the narrative in a graph format.
- Evaluation: The authors illustrate the use of GENEVA by generating new branching narratives for four well-known stories under different contextual constraints.
The paper builds on previous work exploring the use of LLMs for game narrative generation and prompting techniques for role-playing generation and evaluation. The authors suggest that GENEVA has the potential to assist in game development, simulations, and other applications with game-like properties.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to leveraging large language models for the creation of branching narratives in dialogue-based RPGs. However, it is important to consider several caveats and areas for further research:
- Narrative Coherence: While the tool can generate a rich narrative graph, the authors do not extensively explore the coherence and logical flow of the resulting storylines. Maintaining narrative coherence is a significant challenge when working with generative models.
- Scalability and Complexity: The paper focuses on a relatively small set of well-known stories. It remains to be seen how well the system would scale to more complex, longer-form narratives with a larger number of branching points and constraints.
- Authorial Control: The paper emphasizes the potential for LLMs to assist the game designer, but it does not address the degree of control the designer would have over the narrative generation process. Striking the right balance between automation and authorial control is an important consideration.
- Evaluation Metrics: The evaluation in the paper is largely qualitative. Developing robust, quantitative metrics to assess the quality and interactivity of the generated narratives would be a valuable area for further research.
Overall, the paper demonstrates the promising potential of using large language models to aid in the creation of branching narratives for dialogue-based RPGs. However, further research is needed to address the challenges of narrative coherence, scalability, authorial control, and comprehensive evaluation.
Conclusion
This paper explores the use of large language models (LLMs) to assist in the creation of branching narratives for dialogue-based role-playing games (RPGs). The authors present a prototype tool called GENEVA that generates a rich narrative graph with branching and reconverging storylines based on high-level narrative descriptions and constraints provided by the game designer.
By leveraging the power of GPT-4, a powerful LLM, GENEVA demonstrates the potential for LLMs to streamline the narrative development process for complex, interactive storytelling. The paper showcases the use of GENEVA in generating new branching narratives for four well-known stories under different contextual constraints, suggesting the tool's applicability for game development, simulations, and other applications with game-like properties.
While the paper presents a promising approach, further research is needed to address challenges related to narrative coherence, scalability, authorial control, and comprehensive evaluation. Nonetheless, this work highlights the growing role of large language models in assisting creative professionals in the realm of interactive storytelling.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
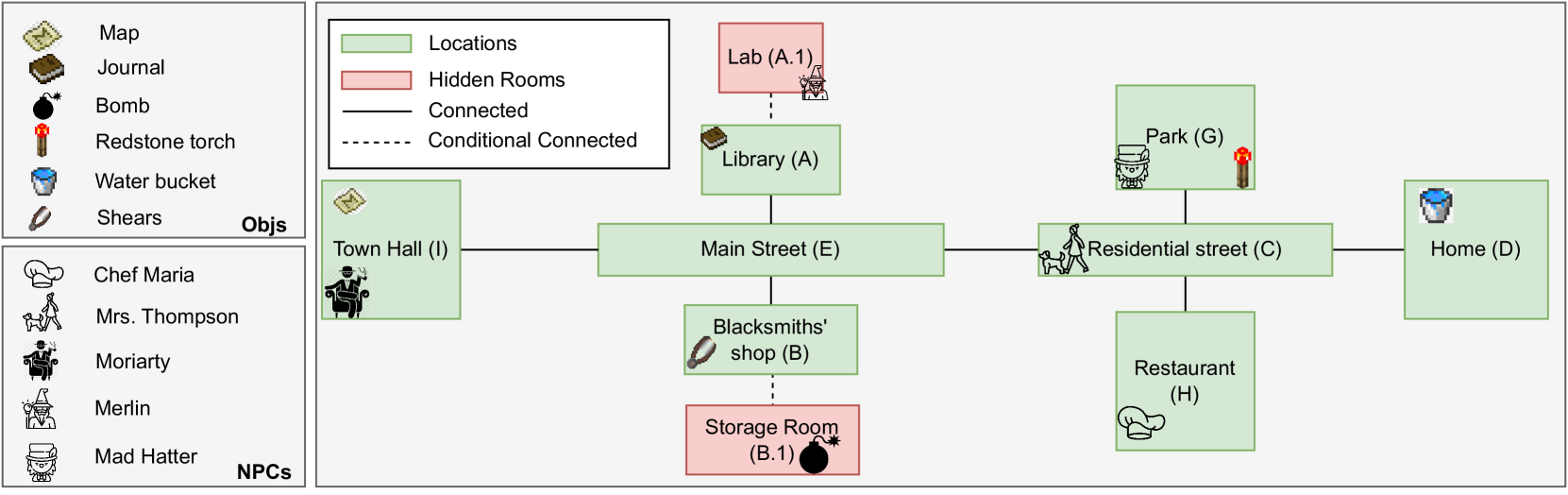
Player-Driven Emergence in LLM-Driven Game Narrative
Xiangyu Peng, Jessica Quaye, Sudha Rao, Weijia Xu, Portia Botchway, Chris Brockett, Nebojsa Jojic, Gabriel DesGarennes, Ken Lobb, Michael Xu, Jorge Leandro, Claire Jin, Bill Dolan

0
0
We explore how interaction with large language models (LLMs) can give rise to emergent behaviors, empowering players to participate in the evolution of game narratives. Our testbed is a text-adventure game in which players attempt to solve a mystery under a fixed narrative premise, but can freely interact with non-player characters generated by GPT-4, a large language model. We recruit 28 gamers to play the game and use GPT-4 to automatically convert the game logs into a node-graph representing the narrative in the player's gameplay. We find that through their interactions with the non-deterministic behavior of the LLM, players are able to discover interesting new emergent nodes that were not a part of the original narrative but have potential for being fun and engaging. Players that created the most emergent nodes tended to be those that often enjoy games that facilitate discovery, exploration and experimentation.
6/5/2024
👁️
StoryVerse: Towards Co-authoring Dynamic Plot with LLM-based Character Simulation via Narrative Planning
Yi Wang, Qian Zhou, David Ledo

0
0
Automated plot generation for games enhances the player's experience by providing rich and immersive narrative experience that adapts to the player's actions. Traditional approaches adopt a symbolic narrative planning method which limits the scale and complexity of the generated plot by requiring extensive knowledge engineering work. Recent advancements use Large Language Models (LLMs) to drive the behavior of virtual characters, allowing plots to emerge from interactions between characters and their environments. However, the emergent nature of such decentralized plot generation makes it difficult for authors to direct plot progression. We propose a novel plot creation workflow that mediates between a writer's authorial intent and the emergent behaviors from LLM-driven character simulation, through a novel authorial structure called abstract acts. The writers define high-level plot outlines that are later transformed into concrete character action sequences via an LLM-based narrative planning process, based on the game world state. The process creates living stories that dynamically adapt to various game world states, resulting in narratives co-created by the author, character simulation, and player. We present StoryVerse as a proof-of-concept system to demonstrate this plot creation workflow. We showcase the versatility of our approach with examples in different stories and game environments.
5/24/2024

Prompt Framework for Role-playing: Generation and Evaluation
Xun Liu, Zhengwei Ni

0
0
Large language models (LLM) have demonstrated remarkable abilities in generating natural language, understanding user instruction, and mimicking human language use. These capabilities have garnered considerable interest in applications such as role-playing. However, the process of collecting individual role scripts (or profiles) data and manually evaluating the performance can be costly. We introduce a framework that uses prompts to leverage the state-of-the-art (SOTA) LLMs to construct role-playing dialogue datasets and evaluate the role-playing performance. Additionally, we employ recall-oriented evaluation Rouge-L metric to support the result of the LLM evaluator.
6/4/2024
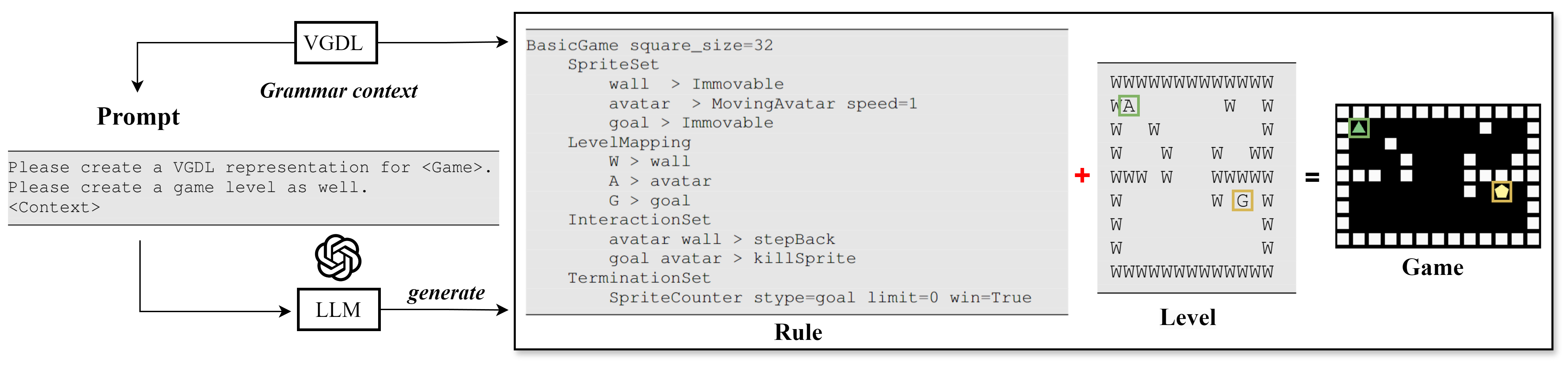
Generating Games via LLMs: An Investigation with Video Game Description Language
Chengpeng Hu, Yunlong Zhao, Jialin Liu

0
0
Recently, the emergence of large language models (LLMs) has unlocked new opportunities for procedural content generation. However, recent attempts mainly focus on level generation for specific games with defined game rules such as Super Mario Bros. and Zelda. This paper investigates the game generation via LLMs. Based on video game description language, this paper proposes an LLM-based framework to generate game rules and levels simultaneously. Experiments demonstrate how the framework works with prompts considering different combinations of context. Our findings extend the current applications of LLMs and offer new insights for generating new games in the area of procedural content generation.
5/31/2024