Generating Games via LLMs: An Investigation with Video Game Description Language
2404.08706

0
0
Abstract
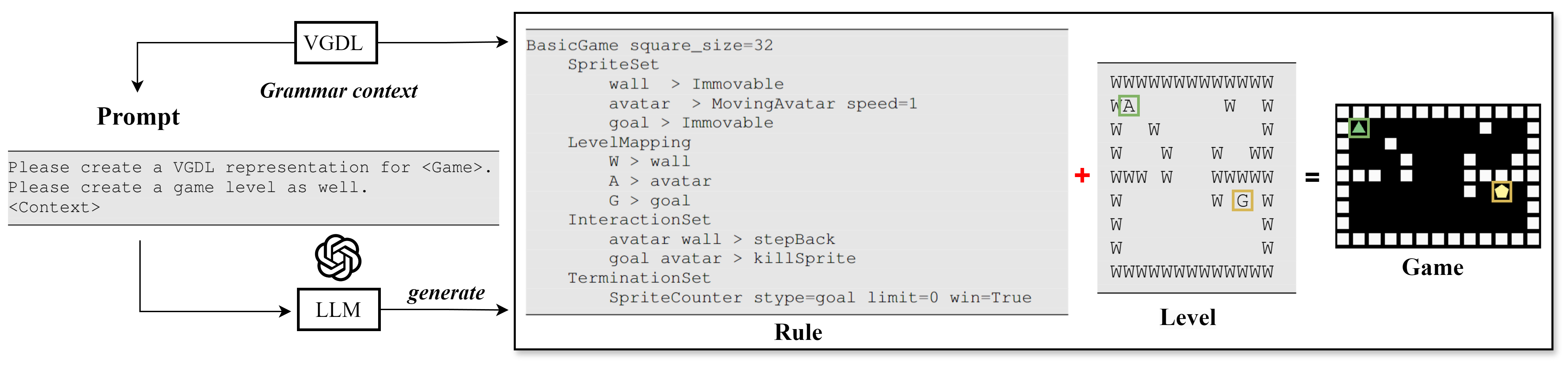
Recently, the emergence of large language models (LLMs) has unlocked new opportunities for procedural content generation. However, recent attempts mainly focus on level generation for specific games with defined game rules such as Super Mario Bros. and Zelda. This paper investigates the game generation via LLMs. Based on video game description language, this paper proposes an LLM-based framework to generate game rules and levels simultaneously. Experiments demonstrate how the framework works with prompts considering different combinations of context. Our findings extend the current applications of LLMs and offer new insights for generating new games in the area of procedural content generation.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper investigates the use of large language models (LLMs) to generate video games described in the Video Game Description Language (VGDL).
- The researchers explore the potential of LLMs to act as game designers, generating new game mechanics, levels, and overall game experiences.
- The study examines the capabilities and limitations of LLMs in this domain, aiming to understand the feasibility and challenges of using these models for procedural game content generation.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at using powerful AI language models, known as large language models (LLMs), to create new video games. The researchers focus on a special language called the Video Game Description Language (VGDL), which allows games to be described in a concise, structured way.
The goal is to see if LLMs can take these VGDL game descriptions and use them to generate entirely new game mechanics, levels, and overall gameplay experiences. This could be useful for automating parts of the game design process and coming up with creative new game ideas.
The researchers investigate how well LLMs perform at this task, what they are capable of, and what challenges they still face. This helps understand the potential and limitations of using LLMs for procedural game content generation.
Technical Explanation
The paper explores the use of large language models (LLMs) to generate new video games described in the Video Game Description Language (VGDL). VGDL provides a concise, structured way to specify game mechanics, levels, and other game elements.
The researchers investigate whether LLMs can use these VGDL game descriptions as a starting point to generate new, creative game content. This includes designing novel game mechanics, levels, and overall game experiences. The study examines the capabilities and limitations of LLMs in this domain, aiming to understand the feasibility and challenges of using these models for procedural game content generation.
The paper presents experiments where LLMs are trained on a dataset of VGDL game descriptions and then prompted to generate new games. The researchers analyze the outputs, looking at factors such as game coherence, novelty, and playability. They also discuss the potential for LLMs to act as game designers, automating parts of the game creation process and coming up with creative new ideas.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a valuable exploration of the capabilities and limitations of LLMs in the context of procedural game content generation. The researchers acknowledge that while LLMs show promise in this domain, there are still significant challenges to overcome.
One key limitation mentioned is the ability of LLMs to maintain coherence and logical consistency when generating complex game mechanics and levels. The paper notes that the models sometimes produce incoherent or unplayable game content, suggesting a need for further research and techniques to improve the reliability and quality of LLM-generated games.
Additionally, the paper highlights the need for better evaluation metrics and methodologies to assess the creativity and novelty of the generated games. Evaluating the outputs of LLMs can be a complex task, and the researchers acknowledge the difficulty in defining and measuring these qualities objectively.
Overall, the paper presents a thoughtful and nuanced investigation into the use of LLMs for procedural game content generation. While the results are promising, the researchers rightly identify areas for further research and development to fully realize the potential of this approach.
Conclusion
This paper explores the use of large language models (LLMs) to generate new video games described in the Video Game Description Language (VGDL). The researchers investigate the capabilities and limitations of LLMs in this domain, examining their ability to design novel game mechanics, levels, and overall gameplay experiences.
The findings suggest that LLMs show promise in acting as game designers, automating parts of the game creation process and coming up with creative new ideas. However, the paper also highlights the need for further research and development to address challenges around maintaining coherence, logical consistency, and evaluating the quality and novelty of the generated game content.
Overall, this study provides valuable insights into the potential and limitations of using LLMs for procedural game content generation, laying the groundwork for future advancements in this area of AI-assisted game design.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🤖
A Survey on Generative AI and LLM for Video Generation, Understanding, and Streaming
Pengyuan Zhou, Lin Wang, Zhi Liu, Yanbin Hao, Pan Hui, Sasu Tarkoma, Jussi Kangasharju

0
0
This paper offers an insightful examination of how currently top-trending AI technologies, i.e., generative artificial intelligence (Generative AI) and large language models (LLMs), are reshaping the field of video technology, including video generation, understanding, and streaming. It highlights the innovative use of these technologies in producing highly realistic videos, a significant leap in bridging the gap between real-world dynamics and digital creation. The study also delves into the advanced capabilities of LLMs in video understanding, demonstrating their effectiveness in extracting meaningful information from visual content, thereby enhancing our interaction with videos. In the realm of video streaming, the paper discusses how LLMs contribute to more efficient and user-centric streaming experiences, adapting content delivery to individual viewer preferences. This comprehensive review navigates through the current achievements, ongoing challenges, and future possibilities of applying Generative AI and LLMs to video-related tasks, underscoring the immense potential these technologies hold for advancing the field of video technology related to multimedia, networking, and AI communities.
4/26/2024
3D Building Generation in Minecraft via Large Language Models
Shiying Hu, Zengrong Huang, Chengpeng Hu, Jialin Liu

0
0
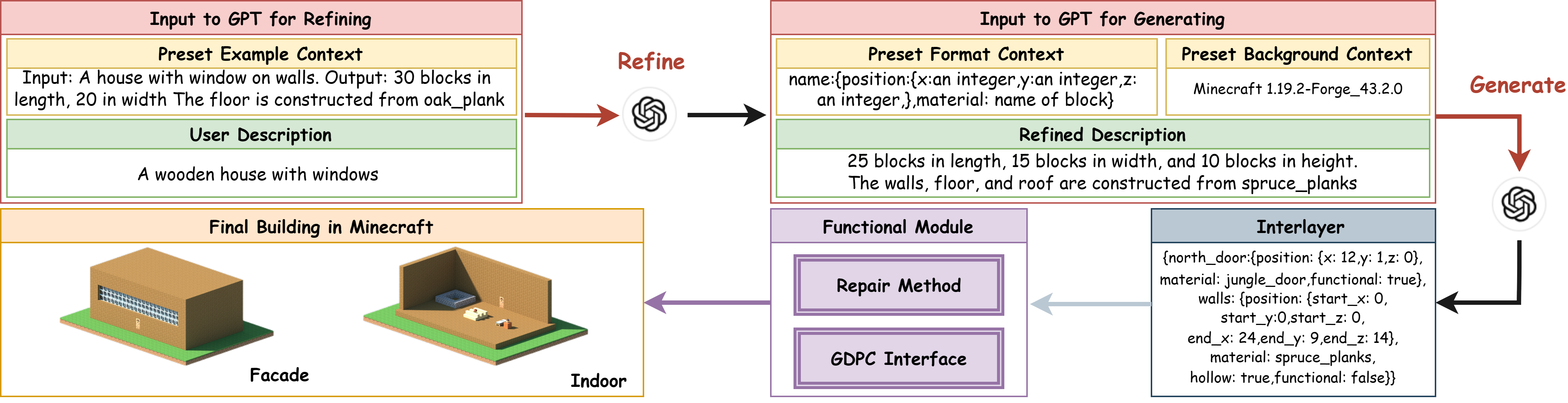
Recently, procedural content generation has exhibited considerable advancements in the domain of 2D game level generation such as Super Mario Bros. and Sokoban through large language models (LLMs). To further validate the capabilities of LLMs, this paper explores how LLMs contribute to the generation of 3D buildings in a sandbox game, Minecraft. We propose a Text to Building in Minecraft (T2BM) model, which involves refining prompts, decoding interlayer representation and repairing. Facade, indoor scene and functional blocks like doors are supported in the generation. Experiments are conducted to evaluate the completeness and satisfaction of buildings generated via LLMs. It shows that LLMs hold significant potential for 3D building generation. Given appropriate prompts, LLMs can generate correct buildings in Minecraft with complete structures and incorporate specific building blocks such as windows and beds, meeting the specified requirements of human users.
6/14/2024

Word2World: Generating Stories and Worlds through Large Language Models
Muhammad U. Nasir, Steven James, Julian Togelius

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have proven their worth across a diverse spectrum of disciplines. LLMs have shown great potential in Procedural Content Generation (PCG) as well, but directly generating a level through a pre-trained LLM is still challenging. This work introduces Word2World, a system that enables LLMs to procedurally design playable games through stories, without any task-specific fine-tuning. Word2World leverages the abilities of LLMs to create diverse content and extract information. Combining these abilities, LLMs can create a story for the game, design narrative, and place tiles in appropriate places to create coherent worlds and playable games. We test Word2World with different LLMs and perform a thorough ablation study to validate each step. We open-source the code at https://github.com/umair-nasir14/Word2World.
5/14/2024
A Survey on Large Language Model-Based Game Agents
Sihao Hu, Tiansheng Huang, Fatih Ilhan, Selim Tekin, Gaowen Liu, Ramana Kompella, Ling Liu

0
0
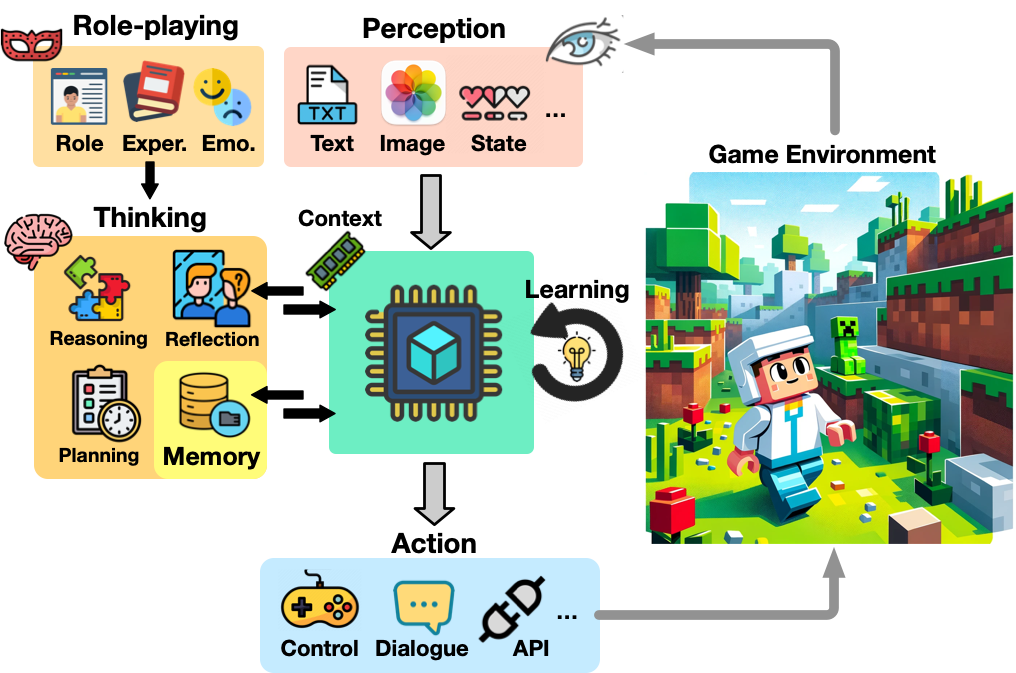
The development of game agents holds a critical role in advancing towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). The progress of LLMs and their multimodal counterparts (MLLMs) offers an unprecedented opportunity to evolve and empower game agents with human-like decision-making capabilities in complex computer game environments. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of LLM-based game agents from a holistic viewpoint. First, we introduce the conceptual architecture of LLM-based game agents, centered around six essential functional components: perception, memory, thinking, role-playing, action, and learning. Second, we survey existing representative LLM-based game agents documented in the literature with respect to methodologies and adaptation agility across six genres of games, including adventure, communication, competition, cooperation, simulation, and crafting & exploration games. Finally, we present an outlook of future research and development directions in this burgeoning field. A curated list of relevant papers is maintained and made accessible at: https://github.com/git-disl/awesome-LLM-game-agent-papers.
4/3/2024