Harnessing the Power of Artificial Intelligence to Vitalize Endangered Indigenous Languages: Technologies and Experiences

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Explores the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to revitalize endangered indigenous languages
- Discusses technologies and experiences in harnessing AI for language preservation and revitalization
- Highlights the importance of preserving linguistic diversity in the face of declining indigenous languages
Plain English Explanation
This paper examines how artificial intelligence (AI) technologies can be used to help protect and revive endangered indigenous languages around the world. Many of these languages are at risk of disappearing as fewer people speak them, often due to the dominance of larger, more widely used languages.
The researchers describe various AI-powered tools and techniques that can be leveraged to document, preserve, and even revitalize these endangered languages. This includes using AI models to analyze speech patterns, create language learning applications, and automate the translation of content into indigenous languages.
The paper also shares real-world experiences and lessons learned from AI-based indigenous language preservation projects around the world. These examples highlight both the potential of AI as well as the challenges in ensuring these technologies are developed and deployed in culturally sensitive and equitable ways.
Ultimately, the research emphasizes the critical need to protect linguistic diversity and support the continuity of indigenous languages and cultures, which are an invaluable part of our global heritage. AI offers promising tools, but must be harnessed thoughtfully and in partnership with indigenous communities to have a meaningful impact.
Technical Explanation
The paper explores the use of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to support the documentation, preservation, and revitalization of endangered indigenous languages around the world. It discusses a range of AI-powered tools and techniques that can be leveraged for this purpose, including automatic speech recognition, machine translation, language modeling, and the development of interactive language learning applications.
The researchers present several case studies and experiences from AI-based indigenous language preservation projects, highlighting both the potential benefits as well as the challenges encountered. For example, they describe how AI models were used to analyze speech patterns and create conversational interfaces to help teach endangered languages. They also discuss the importance of engaging local communities and addressing issues of cultural sensitivity, data privacy, and equitable access when deploying these technologies.
The paper emphasizes the critical need to preserve linguistic diversity and support the continuity of indigenous languages and cultures, which are an invaluable part of our global heritage. It argues that AI offers promising tools and technologies to aid in these efforts, but must be harnessed thoughtfully and in close collaboration with indigenous communities to have a meaningful and sustainable impact.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the potential for AI technologies to support the preservation and revitalization of endangered indigenous languages. The researchers present a range of compelling use cases and real-world experiences that demonstrate the value of these tools, while also acknowledging the important caveats and challenges that must be addressed.
One key limitation highlighted in the paper is the need to ensure that AI-based language preservation efforts are developed and deployed in close partnership with indigenous communities. There is a risk of these technologies being imposed in a top-down manner, or of failing to account for cultural nuances and community needs. The researchers rightfully emphasize the importance of centering local voices and priorities throughout the process.
Additionally, the paper raises concerns about data privacy and the potential for AI systems to inadvertently entrench existing inequities within indigenous communities. These are critical issues that must be carefully navigated to ensure the responsible and equitable development of AI-powered language preservation tools.
Overall, the research presented in this paper makes a strong case for the transformative potential of AI in supporting endangered indigenous languages. However, it also underscores the need for a thoughtful, community-centric approach that prioritizes cultural sensitivity, ethical data practices, and the self-determination of indigenous peoples.
Conclusion
This paper explores the promising role of artificial intelligence (AI) in helping to preserve and revitalize endangered indigenous languages around the world. It presents a range of AI-powered tools and techniques that can be leveraged to document, teach, and breathe new life into these threatened linguistic traditions.
The researchers provide compelling real-world examples of how AI-based language preservation projects have been implemented, highlighting both the benefits and the challenges encountered. Ultimately, the paper emphasizes the critical importance of preserving linguistic diversity and supporting the continuity of indigenous cultures, which are an invaluable part of our global heritage.
While AI offers transformative potential in this domain, the researchers caution that these technologies must be developed and deployed in close collaboration with indigenous communities. Ensuring cultural sensitivity, ethical data practices, and equitable access are essential to realizing the full promise of AI-powered language revitalization efforts.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Harnessing the Power of Artificial Intelligence to Vitalize Endangered Indigenous Languages: Technologies and Experiences
Claudio Pinhanez, Paulo Cavalin, Luciana Storto, Thomas Finbow, Alexander Cobbinah, Julio Nogima, Marisa Vasconcelos, Pedro Domingues, Priscila de Souza Mizukami, Nicole Grell, Majo'i Gongora, Isabel Gonc{c}alves
Since 2022 we have been exploring application areas and technologies in which Artificial Intelligence (AI) and modern Natural Language Processing (NLP), such as Large Language Models (LLMs), can be employed to foster the usage and facilitate the documentation of Indigenous languages which are in danger of disappearing. We start by discussing the decreasing diversity of languages in the world and how working with Indigenous languages poses unique ethical challenges for AI and NLP. To address those challenges, we propose an alternative development AI cycle based on community engagement and usage. Then, we report encouraging results in the development of high-quality machine learning translators for Indigenous languages by fine-tuning state-of-the-art (SOTA) translators with tiny amounts of data and discuss how to avoid some common pitfalls in the process. We also present prototypes we have built in projects done in 2023 and 2024 with Indigenous communities in Brazil, aimed at facilitating writing, and discuss the development of Indigenous Language Models (ILMs) as a replicable and scalable way to create spell-checkers, next-word predictors, and similar tools. Finally, we discuss how we envision a future for language documentation where dying languages are preserved as interactive language models.
Read more7/30/2024

0
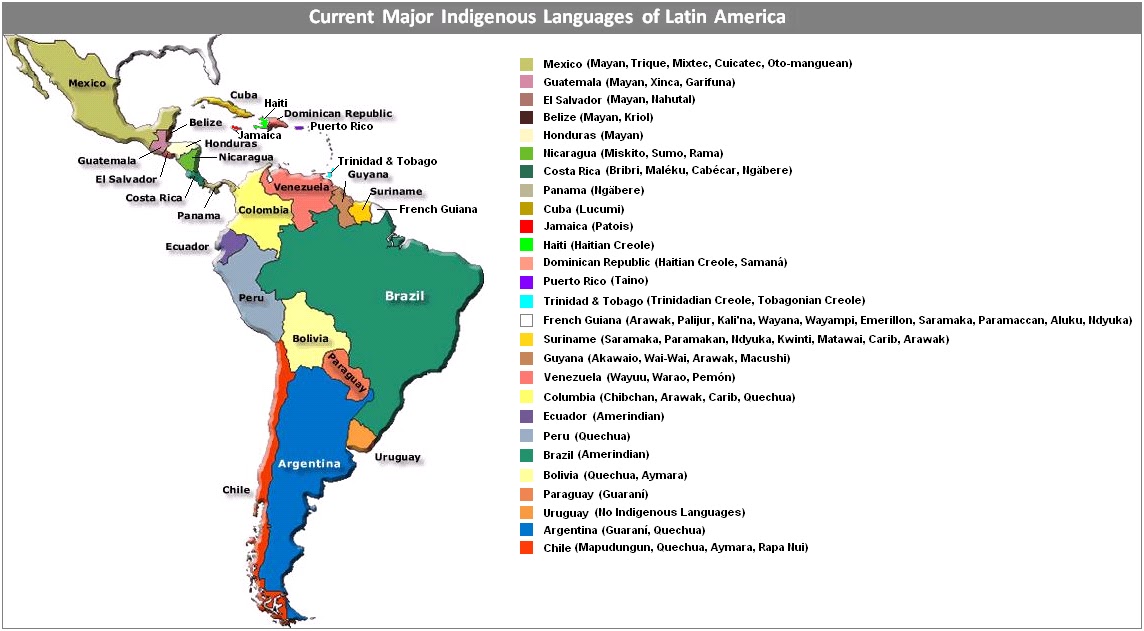
NLP Progress in Indigenous Latin American Languages
Atnafu Lambebo Tonja, Fazlourrahman Balouchzahi, Sabur Butt, Olga Kolesnikova, Hector Ceballos, Alexander Gelbukh, Thamar Solorio
The paper focuses on the marginalization of indigenous language communities in the face of rapid technological advancements. We highlight the cultural richness of these languages and the risk they face of being overlooked in the realm of Natural Language Processing (NLP). We aim to bridge the gap between these communities and researchers, emphasizing the need for inclusive technological advancements that respect indigenous community perspectives. We show the NLP progress of indigenous Latin American languages and the survey that covers the status of indigenous languages in Latin America, their representation in NLP, and the challenges and innovations required for their preservation and development. The paper contributes to the current literature in understanding the need and progress of NLP for indigenous communities of Latin America, specifically low-resource and indigenous communities in general.
Read more5/14/2024
➖

0
The Ghanaian NLP Landscape: A First Look
Sheriff Issaka, Zhaoyi Zhang, Mihir Heda, Keyi Wang, Yinka Ajibola, Ryan DeMar, Xuefeng Du
Despite comprising one-third of global languages, African languages are critically underrepresented in Artificial Intelligence (AI), threatening linguistic diversity and cultural heritage. Ghanaian languages, in particular, face an alarming decline, with documented extinction and several at risk. This study pioneers a comprehensive survey of Natural Language Processing (NLP) research focused on Ghanaian languages, identifying methodologies, datasets, and techniques employed. Additionally, we create a detailed roadmap outlining challenges, best practices, and future directions, aiming to improve accessibility for researchers. This work serves as a foundational resource for Ghanaian NLP research and underscores the critical need for integrating global linguistic diversity into AI development.
Read more5/14/2024

0
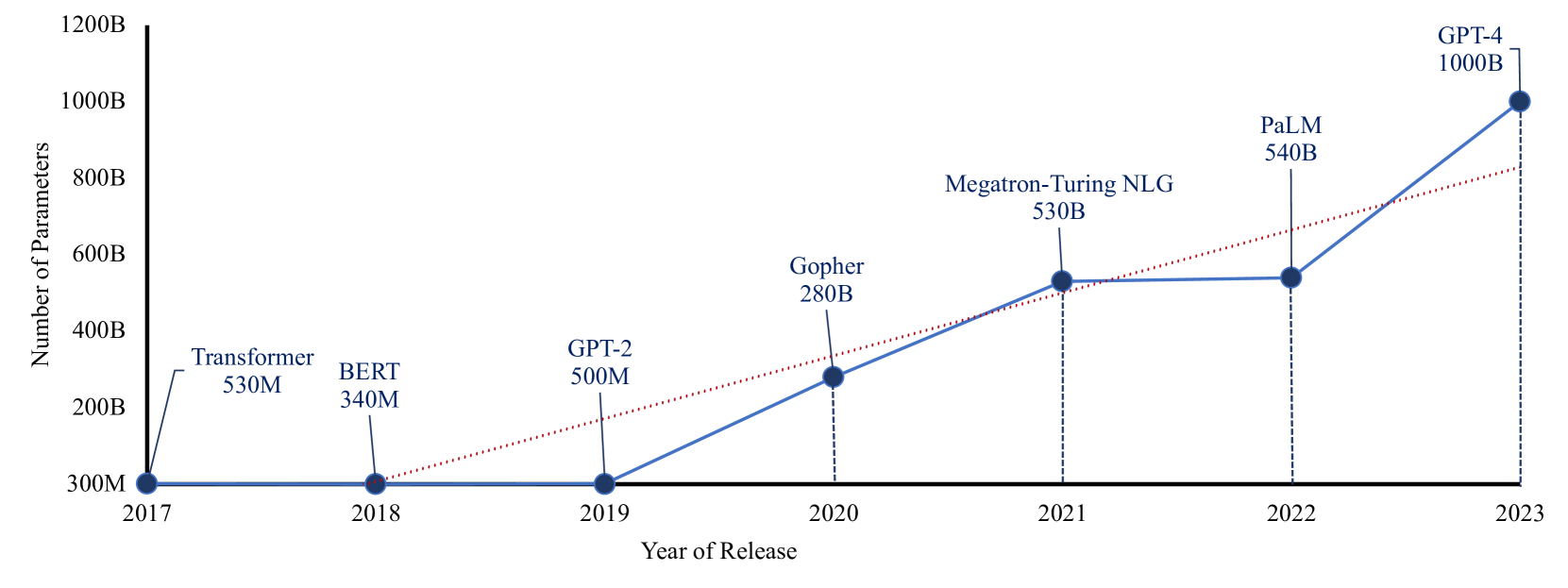
Recent Advances in Generative AI and Large Language Models: Current Status, Challenges, and Perspectives
Desta Haileselassie Hagos, Rick Battle, Danda B. Rawat
The emergence of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) has marked a new era of Natural Language Processing (NLP), introducing unprecedented capabilities that are revolutionizing various domains. This paper explores the current state of these cutting-edge technologies, demonstrating their remarkable advancements and wide-ranging applications. Our paper contributes to providing a holistic perspective on the technical foundations, practical applications, and emerging challenges within the evolving landscape of Generative AI and LLMs. We believe that understanding the generative capabilities of AI systems and the specific context of LLMs is crucial for researchers, practitioners, and policymakers to collaboratively shape the responsible and ethical integration of these technologies into various domains. Furthermore, we identify and address main research gaps, providing valuable insights to guide future research endeavors within the AI research community.
Read more8/26/2024