Imagining from Images with an AI Storytelling Tool

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper introduces ImageTeller, an AI-based storytelling tool that generates narratives from visual inputs.
- The authors explore the use of large language models to generate stories inspired by images, drawing on the narrative art tradition.
- The paper describes the ImageTeller prototype and its key components, including the image encoding, story generation, and story refinement modules.
- The authors also discuss the potential benefits and limitations of this approach, as well as areas for future research.
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses an AI system called ImageTeller that can create stories inspired by images. The researchers wanted to explore how large language models, which are trained on vast amounts of text data, can be used to generate narratives based on visual inputs.
The narrative art tradition is a long-standing practice in visual arts, where artists create paintings or illustrations that tell a story. The authors of this paper were interested in how an AI system could be used to create similar narrative experiences, but starting from a visual input instead of a written prompt.
The ImageTeller prototype they developed has several key components:
- An image encoding module that processes the input image and extracts relevant visual features
- A story generation module that uses a large language model to generate a narrative based on the encoded image
- A story refinement module that further polishes and refines the generated story
By combining these elements, the ImageTeller system can take an image as input and produce an original story inspired by that visual information.
The authors discuss the potential benefits of this approach, such as enabling new forms of interactive storytelling and creative expression. They also acknowledge the limitations, such as the challenge of ensuring the generated stories are coherent, meaningful, and aligned with the original visual input.
Overall, this research explores an interesting intersection between visual arts, language models, and computational creativity, with the goal of developing AI-powered tools that can help humans expand their storytelling abilities.
Technical Explanation
The ImageTeller prototype consists of three main components:
-
Image Encoding Module: This module takes an input image and encodes it into a compact, high-dimensional vector representation. The authors experimented with different image encoding architectures, including convolutional neural networks and vision transformers, to find the most effective approach for their storytelling task.
-
Story Generation Module: This module uses a large language model, such as GPT-3, to generate a story based on the encoded image features. The language model is fine-tuned on a dataset of image-caption pairs to learn the association between visual inputs and textual narratives.
-
Story Refinement Module: After the initial story generation, this module further refines and polishes the output to improve its coherence, fluency, and alignment with the original visual input. The authors explored various techniques for this refinement process, including iterative prompting and multi-pass generation.
The authors conducted experiments to evaluate the performance of the ImageTeller prototype. They assessed the generated stories in terms of their narrative quality, coherence, and relevance to the input images, using both human evaluation and automated metrics.
The results suggest that the ImageTeller system can generate plausible and engaging stories from visual inputs, outperforming baseline approaches. However, the authors also acknowledge the limitations of the current prototype, such as the potential for factual inconsistencies or imaginative biases in the generated narratives.
Critical Analysis
The authors of this paper have made a commendable effort to explore the intersection of visual arts, language models, and computational creativity. The ImageTeller prototype represents an interesting step forward in the development of AI-powered storytelling tools.
One of the key strengths of this research is the authors' grounding in the narrative art tradition, which provides a solid foundation for their work. By understanding the principles and techniques used by human artists and storytellers, the authors have been able to design an AI system that can generate narratives in a more thoughtful and meaningful way.
However, the authors also acknowledge several limitations and areas for further research. For example, they note the challenge of ensuring the generated stories are coherent, meaningful, and aligned with the original visual input. There is also the potential for the language model to introduce biases or factual inconsistencies into the narratives.
Additionally, the authors do not explore the potential ethical implications of this technology, such as the risk of AI-generated content being used to spread misinformation or manipulate emotions. As this field continues to develop, it will be important for researchers to consider these broader societal impacts.
Overall, this paper represents a valuable contribution to the field of AI-powered storytelling. The ImageTeller prototype demonstrates the potential of large language models to assist and augment human creativity, but also highlights the need for further research and refinement to address the remaining challenges.
Conclusion
The paper introduces the ImageTeller system, an AI-based storytelling tool that generates narratives inspired by visual inputs. The authors explore the use of large language models to create stories that draw on the narrative art tradition, leveraging the power of these models to translate visual information into textual narratives.
The ImageTeller prototype showcases the potential of this approach, with its ability to generate plausible and engaging stories from images. However, the authors also acknowledge the limitations of the current system, such as the need to ensure the generated narratives are coherent, meaningful, and aligned with the original visual input.
As the field of AI-powered storytelling continues to evolve, this research represents an important step forward. By combining advances in language models, computer vision, and narrative theory, the authors have developed a novel tool that could enable new forms of interactive storytelling and creative expression. Moving forward, it will be crucial to further refine these systems and address the ethical implications of this technology, ensuring it is developed and deployed responsibly.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Imagining from Images with an AI Storytelling Tool
Edirlei Soares de Lima, Marco A. Casanova, Antonio L. Furtado
A method for generating narratives by analyzing single images or image sequences is presented, inspired by the time immemorial tradition of Narrative Art. The proposed method explores the multimodal capabilities of GPT-4o to interpret visual content and create engaging stories, which are illustrated by a Stable Diffusion XL model. The method is supported by a fully implemented tool, called ImageTeller, which accepts images from diverse sources as input. Users can guide the narrative's development according to the conventions of fundamental genres - such as Comedy, Romance, Tragedy, Satire or Mystery -, opt to generate data-driven stories, or to leave the prototype free to decide how to handle the narrative structure. User interaction is provided along the generation process, allowing the user to request alternative chapters or illustrations, and even reject and restart the story generation based on the same input. Additionally, users can attach captions to the input images, influencing the system's interpretation of the visual content. Examples of generated stories are provided, along with details on how to access the prototype.
Read more8/22/2024
🤖

0
ID.8: Co-Creating Visual Stories with Generative AI
Victor Nikhil Antony, Chien-Ming Huang
Storytelling is an integral part of human culture and significantly impacts cognitive and socio-emotional development and connection. Despite the importance of interactive visual storytelling, the process of creating such content requires specialized skills and is labor-intensive. This paper introduces ID.8, an open-source system designed for the co-creation of visual stories with generative AI. We focus on enabling an inclusive storytelling experience by simplifying the content creation process and allowing for customization. Our user evaluation confirms a generally positive user experience in domains such as enjoyment and exploration, while highlighting areas for improvement, particularly in immersiveness, alignment, and partnership between the user and the AI system. Overall, our findings indicate promising possibilities for empowering people to create visual stories with generative AI. This work contributes a novel content authoring system, ID.8, and insights into the challenges and potential of using generative AI for multimedia content creation.
Read more6/4/2024


0
New!The Art of Storytelling: Multi-Agent Generative AI for Dynamic Multimodal Narratives
Samee Arif, Taimoor Arif, Aamina Jamal Khan, Muhammad Saad Haroon, Agha Ali Raza, Awais Athar
This paper introduces the concept of an education tool that utilizes Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) to enhance storytelling for children. The system combines GenAI-driven narrative co-creation, text-to-speech conversion, and text-to-video generation to produce an engaging experience for learners. We describe the co-creation process, the adaptation of narratives into spoken words using text-to-speech models, and the transformation of these narratives into contextually relevant visuals through text-to-video technology. Our evaluation covers the linguistics of the generated stories, the text-to-speech conversion quality, and the accuracy of the generated visuals.
Read more9/19/2024
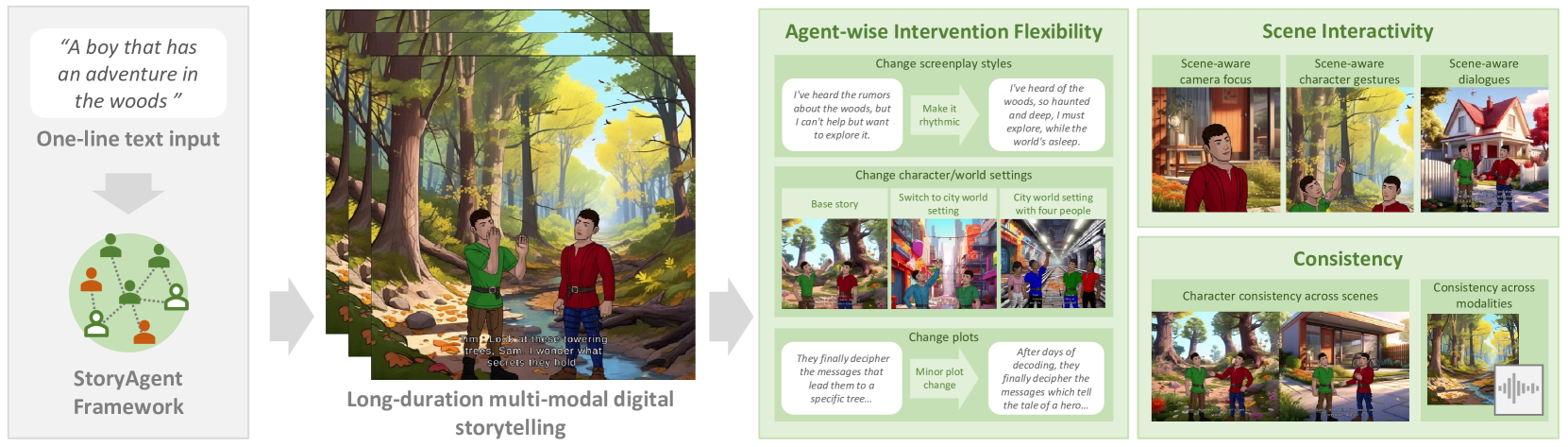

0
From Words to Worlds: Transforming One-line Prompt into Immersive Multi-modal Digital Stories with Communicative LLM Agent
Samuel S. Sohn, Danrui Li, Sen Zhang, Che-Jui Chang, Mubbasir Kapadia
Digital storytelling, essential in entertainment, education, and marketing, faces challenges in production scalability and flexibility. The StoryAgent framework, introduced in this paper, utilizes Large Language Models and generative tools to automate and refine digital storytelling. Employing a top-down story drafting and bottom-up asset generation approach, StoryAgent tackles key issues such as manual intervention, interactive scene orchestration, and narrative consistency. This framework enables efficient production of interactive and consistent narratives across multiple modalities, democratizing content creation and enhancing engagement. Our results demonstrate the framework's capability to produce coherent digital stories without reference videos, marking a significant advancement in automated digital storytelling.
Read more6/24/2024