From Words to Worlds: Transforming One-line Prompt into Immersive Multi-modal Digital Stories with Communicative LLM Agent
2406.10478

0
0
Abstract
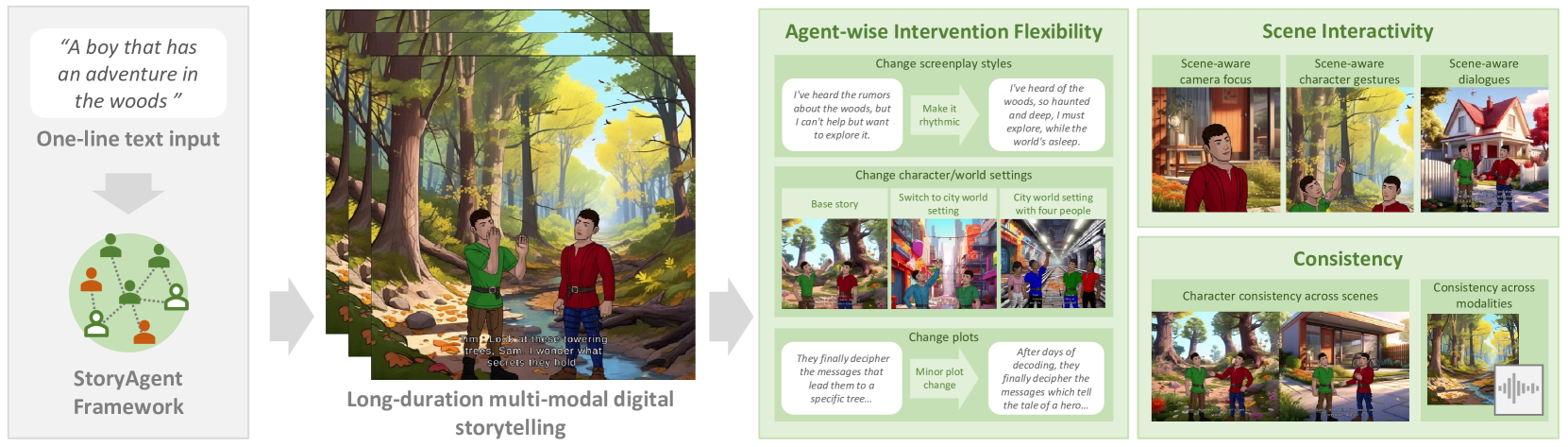
Digital storytelling, essential in entertainment, education, and marketing, faces challenges in production scalability and flexibility. The StoryAgent framework, introduced in this paper, utilizes Large Language Models and generative tools to automate and refine digital storytelling. Employing a top-down story drafting and bottom-up asset generation approach, StoryAgent tackles key issues such as manual intervention, interactive scene orchestration, and narrative consistency. This framework enables efficient production of interactive and consistent narratives across multiple modalities, democratizing content creation and enhancing engagement. Our results demonstrate the framework's capability to produce coherent digital stories without reference videos, marking a significant advancement in automated digital storytelling.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a novel approach to transforming one-line prompts into immersive, multi-modal digital stories using a communicative Large Language Model (LLM) agent.
- The proposed system, called "From Words to Worlds," aims to enable users to co-author dynamic plot lines and narratives that can be visualized in interactive 3D environments.
- The research builds on previous work in areas like Storyverse, Large Language User Interfaces, and Storypark.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a new system that can take a simple one-sentence prompt and turn it into an immersive, interactive digital story. The system uses a powerful language model to understand the prompt and then generate a detailed narrative, characters, and 3D environments to bring the story to life.
For example, if you typed in the prompt "A wizard embarks on a journey to save their village from an evil sorcerer," the system would automatically create a rich, visual world where you could explore the wizard's adventure, interact with characters, and even influence how the story unfolds.
This allows users to co-author dynamic, multi-modal stories in a way that goes beyond traditional text-based storytelling. Instead of just reading a story, you can immerse yourself in it and shape it through your own actions and choices.
The researchers build on previous work that has explored using large language models to generate stories and interactive environments. By combining language understanding, narrative generation, and 3D visualization, this new system aims to create a more seamless and engaging storytelling experience.
Technical Explanation
The key components of the "From Words to Worlds" system include:
-
Prompt Understanding: A large language model is used to analyze the one-line prompt and extract relevant entities, relationships, and narrative elements.
-
Story Generation: Based on the prompt understanding, the system generates a detailed narrative, including character development, plot points, and dialogue.
-
3D Environment Creation: The generated story is then used to procedurally build an interactive 3D environment, with visualizations of the characters, settings, and events.
-
Interactive Narrative: Users can explore the 3D world, interact with characters, and influence the unfolding of the story through their choices and actions.
The researchers evaluated their system through a series of user studies, demonstrating its ability to transform simple prompts into engaging, immersive digital stories. The results suggest that this approach can enable more accessible and collaborative storytelling experiences compared to traditional text-based or linear narrative formats.
Critical Analysis
The paper acknowledges several limitations and areas for future research. For example, the current system is limited to generating relatively short, self-contained stories, and the 3D environments may lack the level of detail and polish found in dedicated game engines.
Additionally, the researchers note that further work is needed to improve the coherence and consistency of the generated narratives, as well as to better understand how users' interactions and choices can shape the unfolding of the story in meaningful ways.
One potential concern raised by the research is the risk of perpetuating biases or stereotypes in the automatically generated characters and storylines. The researchers emphasize the importance of addressing these issues through careful prompt design, model training, and user testing.
Overall, the "From Words to Worlds" system represents a promising step towards more accessible and interactive storytelling platforms. By leveraging the power of large language models and 3D visualization, the researchers have demonstrated the potential to transform simple prompts into immersive digital experiences. However, continued refinement and exploration of the ethical implications will be crucial as this technology continues to evolve.
Conclusion
The "From Words to Worlds" paper presents an innovative approach to transforming one-line prompts into immersive, multi-modal digital stories. By combining language understanding, narrative generation, and 3D environment creation, the system aims to enable more accessible and collaborative storytelling experiences.
The research builds on previous work in the field and demonstrates the potential of large language models to power interactive, user-driven narratives. While the current system has some limitations, the authors highlight several areas for future improvement, such as enhancing narrative coherence and addressing potential biases.
Overall, the "From Words to Worlds" project represents an exciting step forward in the integration of language AI and interactive 3D experiences. As the technology continues to evolve, it may open up new avenues for creative expression, education, and entertainment, allowing users to co-author dynamic and immersive digital stories.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
👁️
StoryVerse: Towards Co-authoring Dynamic Plot with LLM-based Character Simulation via Narrative Planning
Yi Wang, Qian Zhou, David Ledo

0
0
Automated plot generation for games enhances the player's experience by providing rich and immersive narrative experience that adapts to the player's actions. Traditional approaches adopt a symbolic narrative planning method which limits the scale and complexity of the generated plot by requiring extensive knowledge engineering work. Recent advancements use Large Language Models (LLMs) to drive the behavior of virtual characters, allowing plots to emerge from interactions between characters and their environments. However, the emergent nature of such decentralized plot generation makes it difficult for authors to direct plot progression. We propose a novel plot creation workflow that mediates between a writer's authorial intent and the emergent behaviors from LLM-driven character simulation, through a novel authorial structure called abstract acts. The writers define high-level plot outlines that are later transformed into concrete character action sequences via an LLM-based narrative planning process, based on the game world state. The process creates living stories that dynamically adapt to various game world states, resulting in narratives co-created by the author, character simulation, and player. We present StoryVerse as a proof-of-concept system to demonstrate this plot creation workflow. We showcase the versatility of our approach with examples in different stories and game environments.
5/24/2024
💬
New!Improving Visual Storytelling with Multimodal Large Language Models
Xiaochuan Lin, Xiangyong Chen

0
0
Visual storytelling is an emerging field that combines images and narratives to create engaging and contextually rich stories. Despite its potential, generating coherent and emotionally resonant visual stories remains challenging due to the complexity of aligning visual and textual information. This paper presents a novel approach leveraging large language models (LLMs) and large vision-language models (LVLMs) combined with instruction tuning to address these challenges. We introduce a new dataset comprising diverse visual stories, annotated with detailed captions and multimodal elements. Our method employs a combination of supervised and reinforcement learning to fine-tune the model, enhancing its narrative generation capabilities. Quantitative evaluations using GPT-4 and qualitative human assessments demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing models, achieving higher scores in narrative coherence, relevance, emotional depth, and overall quality. The results underscore the effectiveness of instruction tuning and the potential of LLMs/LVLMs in advancing visual storytelling.
7/4/2024

Large Language User Interfaces: Voice Interactive User Interfaces powered by LLMs
Syed Mekael Wasti, Ken Q. Pu, Ali Neshati

0
0
The evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) has showcased remarkable capacities for logical reasoning and natural language comprehension. These capabilities can be leveraged in solutions that semantically and textually model complex problems. In this paper, we present our efforts toward constructing a framework that can serve as an intermediary between a user and their user interface (UI), enabling dynamic and real-time interactions. We employ a system that stands upon textual semantic mappings of UI components, in the form of annotations. These mappings are stored, parsed, and scaled in a custom data structure, supplementary to an agent-based prompting backend engine. Employing textual semantic mappings allows each component to not only explain its role to the engine but also provide expectations. By comprehending the needs of both the user and the components, our LLM engine can classify the most appropriate application, extract relevant parameters, and subsequently execute precise predictions of the user's expected actions. Such an integration evolves static user interfaces into highly dynamic and adaptable solutions, introducing a new frontier of intelligent and responsive user experiences.
4/17/2024
Storypark: Leveraging Large Language Models to Enhance Children Story Learning Through Child-AI collaboration Storytelling
Lyumanshan Ye, Jiandong Jiang, Danni Chang, Pengfei Liu

0
0
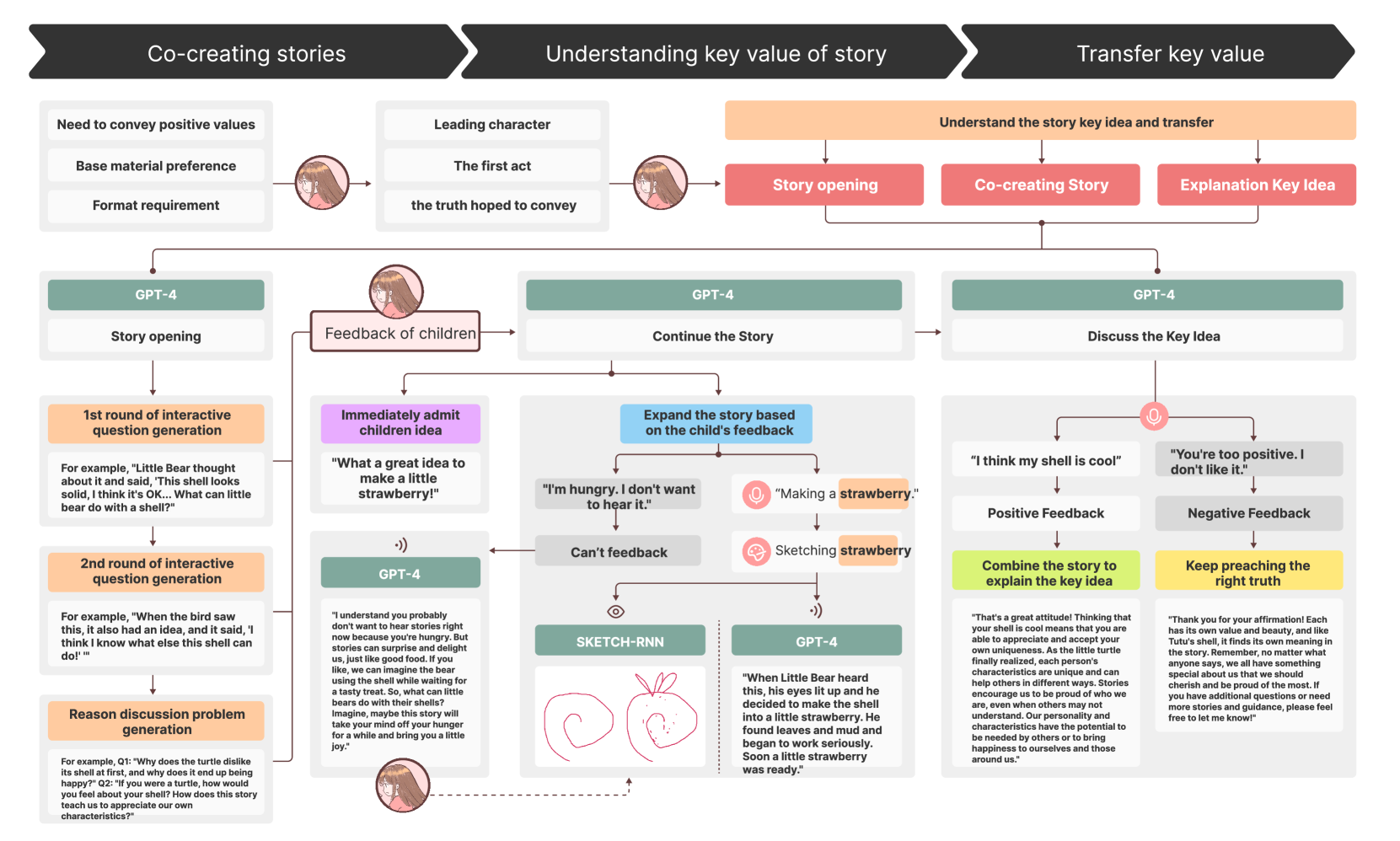
Interactive storytelling has been widely adopted by educators in teaching activities of young children. Such a teaching method combines storytelling with active child participation, benefiting their expressive abilities, creative thinking, and understanding of stories. Interactive storytelling requires facilitators to unidirectionally narrate the story content and encourage children's participation in story plot creation and interpretation of central themes through multi-sensory interactive methods such as questioning and drawing. However, providing tailored guidance based on diverse feedback from children during interactive storytelling poses challenges for most facilitators. These challenges include expanding story plot development based on children's ideas, using drawings to visualize children's thoughts, and interpreting the story's central themes based on children's thinking. This necessitates facilitators to possess strong imaginative, associative, domain knowledge, and drawing skills. Large language models have demonstrated their potential in facilitating responsive and participatory dialogues, offering new design possibilities to address the challenges faced by facilitators in interactive storytelling. In this study, our goal is to leverage large language models to design an interactive storytelling system that provides children with plot frameworks and interpretations of central themes during the interactive storytelling process. Through user experiments involving 20 child participants, we evaluate this interactive system's usability, learning effectiveness, and user experience. The user study shows that Storypark improves learning outcomes in understanding story key ideas, generalization, and transfer. And high engagement and willingness to use of participants demonstrate that StoryPark provides children with a positive learning experience.
5/14/2024