Immersive Rover Control and Obstacle Detection based on Extended Reality and Artificial Intelligence
2404.14095

0
0

Abstract
Lunar exploration has become a key focus, driving scientific and technological advances. Ongoing missions are deploying rovers to the surface of the Moon, targeting the far side and south pole. However, these terrains pose challenges, emphasizing the need for precise obstacles and resource detection to avoid mission risks. This work proposes a novel system that integrates eXtended Reality (XR) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to teleoperate lunar rovers. It is capable of autonomously detecting rocks and recreating an immersive 3D virtual environment of the location of the robot. This system has been validated in a lunar laboratory to observe its advantages over traditional 2D-based teleoperation approaches
Create account to get full access
Overview
- The paper presents a system for immersive teleoperation of a rover using extended reality (XR) and artificial intelligence (AI) for autonomous object detection and localization.
- The system allows a human operator to control a rover remotely while receiving real-time video and sensor data in an immersive XR environment.
- The AI component provides autonomous object detection and localization to assist the operator in navigating the rover and avoiding obstacles.
Plain English Explanation
The researchers have developed a system that allows a human operator to control a remote rover, or a robotic vehicle, using extended reality (XR) technology. XR refers to a range of technologies, including virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), that can create immersive digital environments.
In this system, the human operator wears an XR headset, which displays a live video feed from the rover's cameras. The operator can then use hand gestures or other controls to steer the rover and navigate it through the environment. The key innovation is the inclusion of an AI-powered object detection and localization system.
This AI component continuously scans the video feed from the rover's cameras and automatically identifies any obstacles or objects in the rover's path. It then relays this information to the operator in the XR environment, highlighting the detected objects and their locations. This allows the operator to more easily navigate the rover and avoid collisions or other hazards.
The researchers believe this system could be particularly useful for remote exploration and inspection tasks, such as in autonomous vision-based algorithm for interplanetary navigation or multi-robot system for detection of explosive devices, where human operators need to control a rover in an unfamiliar or potentially dangerous environment.
Technical Explanation
The proposed system consists of two main components: an immersive XR interface for the human operator and an AI-powered object detection and localization module.
The XR interface provides the operator with a first-person view of the rover's environment, displayed on a virtual reality headset. The operator can then use hand gestures or other controllers to steer the rover and navigate through the environment. The system also provides the operator with additional sensor data, such as the rover's position, orientation, and environmental conditions.
The AI object detection and localization module continuously processes the video feed from the rover's cameras. It uses deep learning algorithms, similar to those used in spatial-assisted human-drone collaborative navigation interaction, to identify and locate any obstacles or objects of interest in the rover's path. This information is then overlaid onto the operator's XR view, allowing them to more easily navigate the rover and avoid collisions.
The researchers tested the system in a series of experiments, where participants were tasked with navigating a simulated rover through an environment with various obstacles. The results showed that the AI-assisted XR interface significantly improved the operators' ability to detect and avoid obstacles, compared to a traditional joystick-based control system.
Critical Analysis
The researchers have presented a promising approach for improving the efficiency and safety of remote rover teleoperation. The integration of XR technology and AI-powered object detection provides the operator with a more intuitive and informative control interface, which could be particularly useful in embodied agents for efficient exploration and smart scene description or dynamics of spherical telescopic linear-driven rotation robots.
However, the paper does not address several important limitations and potential issues. For example, the system's performance in real-world, outdoor environments with varying lighting and weather conditions is not evaluated. Additionally, the researchers do not discuss the computational resources required to run the AI object detection module on-board the rover, which could be a significant constraint, especially for spatial-assisted human-drone collaborative navigation interaction.
Further research is needed to address these challenges and explore the practical applications of this technology, particularly in more complex and unpredictable environments.
Conclusion
The presented system demonstrates the potential of integrating XR and AI technologies to improve the efficiency and safety of remote rover teleoperation. By providing the operator with an immersive, AI-assisted control interface, the system can enhance the operator's situational awareness and decision-making, which could be valuable for a wide range of applications, from autonomous vision-based algorithm for interplanetary navigation to multi-robot system for detection of explosive devices. However, further research is needed to address the system's limitations and explore its feasibility in real-world scenarios.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🧪
A Novel Methodology for Autonomous Planetary Exploration Using Multi-Robot Teams
Sarah Swinton, Jan-Hendrik Ewers, Euan McGookin, David Anderson, Douglas Thomson

0
0
One of the fundamental limiting factors in planetary exploration is the autonomous capabilities of planetary exploration rovers. This study proposes a novel methodology for trustworthy autonomous multi-robot teams which incorporates data from multiple sources (HiRISE orbiter imaging, probability distribution maps, and on-board rover sensors) to find efficient exploration routes in Jezero crater. A map is generated, consisting of a 3D terrain model, traversability analysis, and probability distribution map of points of scientific interest. A three-stage mission planner generates an efficient route, which maximises the accumulated probability of identifying points of interest. A 4D RRT* algorithm is used to determine smooth, flat paths, and prioritised planning is used to coordinate a safe set of paths. The above methodology is shown to coordinate safe and efficient rover paths, which ensure the rovers remain within their nominal pitch and roll limits throughout operation.
5/22/2024
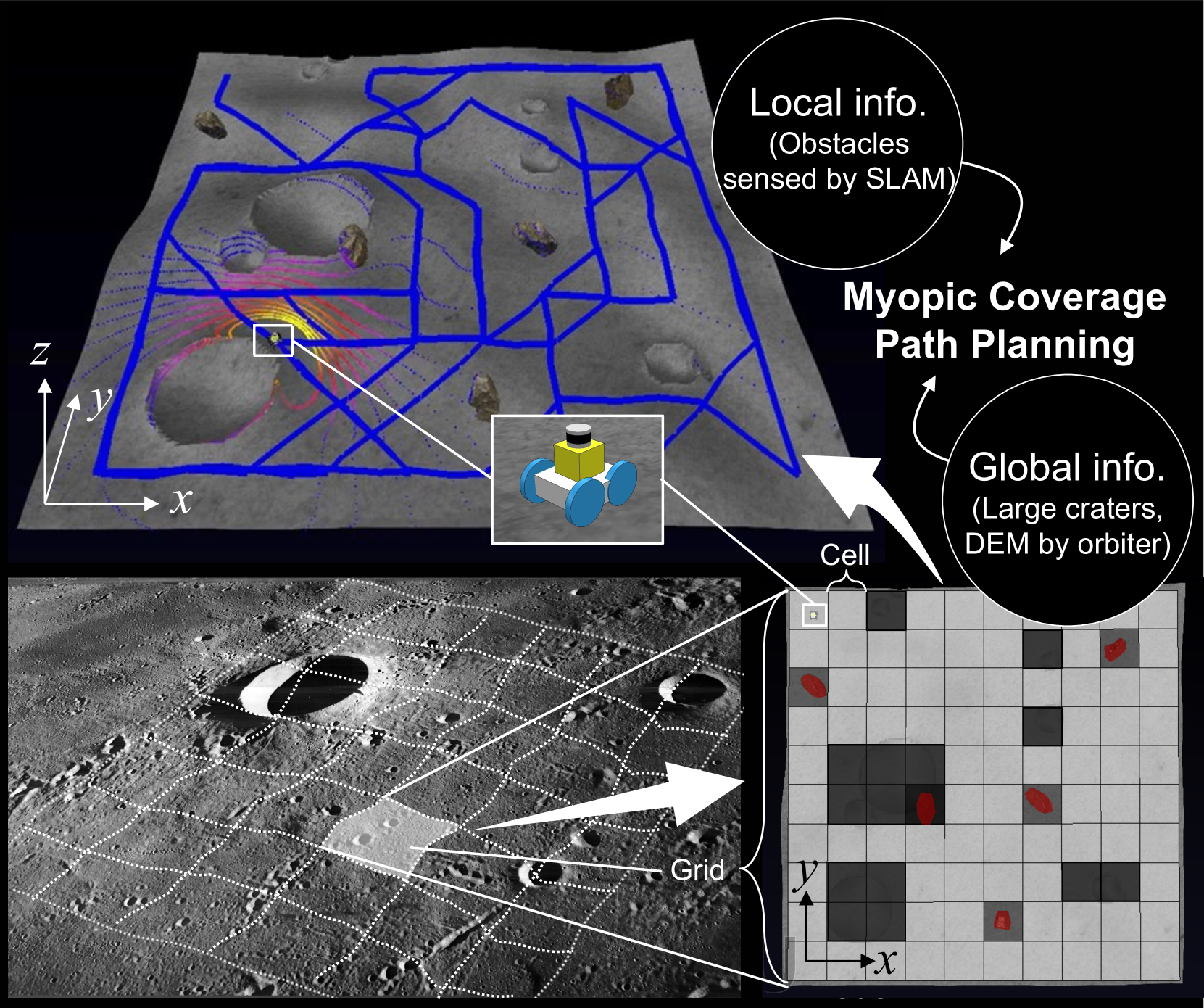
Risk-Aware Coverage Path Planning for Lunar Micro-Rovers Leveraging Global and Local Environmental Data
Shreya Santra, Kentaro Uno, Gen Kudo, Kazuya Yoshida

0
0
This paper presents a novel 3D myopic coverage path planning algorithm for lunar micro-rovers that can explore unknown environments with limited sensing and computational capabilities. The algorithm expands upon traditional non-graph path planning methods to accommodate the complexities of lunar terrain, utilizing global data with local topographic features into motion cost calculations. The algorithm also integrates localization and mapping to update the rover's pose and map the environment. The resulting environment map's accuracy is evaluated and tested in a 3D simulator. Outdoor field tests were conducted to validate the algorithm's efficacy in sim-to-real scenarios. The results showed that the algorithm could achieve high coverage with low energy consumption and computational cost, while incrementally exploring the terrain and avoiding obstacles. This study contributes to the advancement of path planning methodologies for space exploration, paving the way for efficient, scalable and autonomous exploration of lunar environments by small rovers.
4/30/2024
Quadruped robot traversing 3D complex environments with limited perception
Yi Cheng, Hang Liu, Guoping Pan, Linqi Ye, Houde Liu, Bin Liang

0
0
Traversing 3-D complex environments has always been a significant challenge for legged locomotion. Existing methods typically rely on external sensors such as vision and lidar to preemptively react to obstacles by acquiring environmental information. However, in scenarios like nighttime or dense forests, external sensors often fail to function properly, necessitating robots to rely on proprioceptive sensors to perceive diverse obstacles in the environment and respond promptly. This task is undeniably challenging. Our research finds that methods based on collision detection can enhance a robot's perception of environmental obstacles. In this work, we propose an end-to-end learning-based quadruped robot motion controller that relies solely on proprioceptive sensing. This controller can accurately detect, localize, and agilely respond to collisions in unknown and complex 3D environments, thereby improving the robot's traversability in complex environments. We demonstrate in both simulation and real-world experiments that our method enables quadruped robots to successfully traverse challenging obstacles in various complex environments.
5/1/2024
⛏️
Spatial Assisted Human-Drone Collaborative Navigation and Interaction through Immersive Mixed Reality
Luca Morando, Giuseppe Loianno

0
0
Aerial robots have the potential to play a crucial role in assisting humans with complex and dangerous tasks. Nevertheless, the future industry demands innovative solutions to streamline the interaction process between humans and drones to enable seamless collaboration and efficient co-working. In this paper, we present a novel tele-immersive framework that promotes cognitive and physical collaboration between humans and robots through Mixed Reality (MR). This framework incorporates a novel bi-directional spatial awareness and a multi-modal virtual-physical interaction approaches. The former seamlessly integrates the physical and virtual worlds, offering bidirectional egocentric and exocentric environmental representations. The latter, leveraging the proposed spatial representation, further enhances the collaboration combining a robot planning algorithm for obstacle avoidance with a variable admittance control. This allows users to issue commands based on virtual forces while maintaining compatibility with the environment map. We validate the proposed approach by performing several collaborative planning and exploration tasks involving a drone and an user equipped with a MR headset.
4/9/2024