Improving Arithmetic Reasoning Ability of Large Language Models through Relation Tuples, Verification and Dynamic Feedback

0
Sign in to get full access
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Improving Arithmetic Reasoning Ability of Large Language Models through Relation Tuples, Verification and Dynamic Feedback
Zhongtao Miao, Kaiyan Zhao, Yoshimasa Tsuruoka
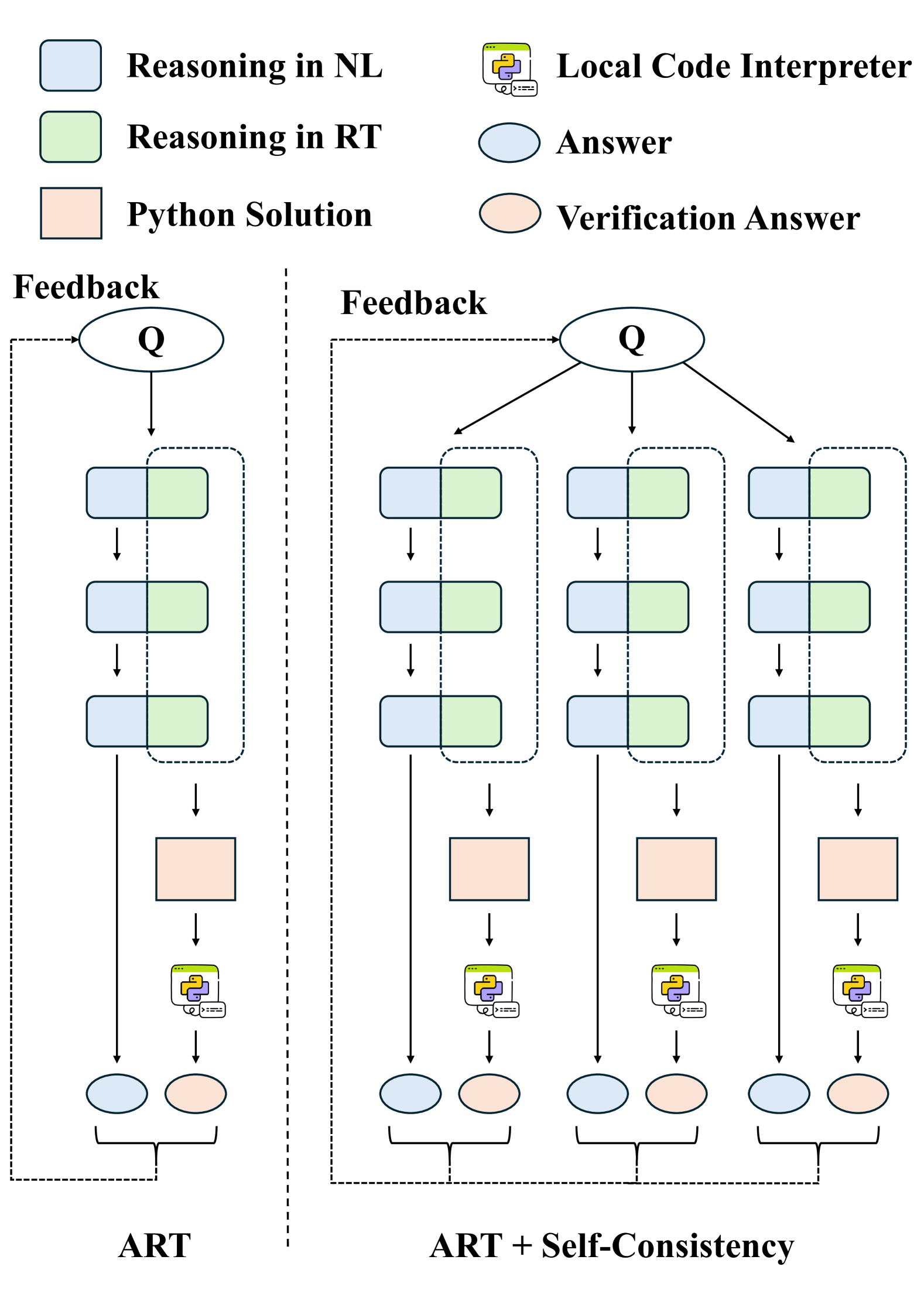
Current representations used in reasoning steps of large language models can mostly be categorized into two main types: (1) natural language, which is difficult to verify; and (2) non-natural language, usually programming code, which is difficult for people who are unfamiliar with coding to read. In this paper, we propose to use a semi-structured form to represent reasoning steps of large language models. Specifically, we use relation tuples, which are not only human-readable but also machine-friendly and easier to verify than natural language. We implement a framework that includes three main components: (1) introducing relation tuples into the reasoning steps of large language models; (2) implementing an automatic verification process of reasoning steps with a local code interpreter based on relation tuples; and (3) integrating a simple and effective dynamic feedback mechanism, which we found helpful for self-improvement of large language models. The experimental results on various arithmetic datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in improving the arithmetic reasoning ability of large language models. The source code is available at https://github.com/gpgg/art.
Read more6/27/2024
💬

0
Logic Contrastive Reasoning with Lightweight Large Language Model for Math Word Problems
Ding Kai, Ma Zhenguo, Yan Xiaoran
This study focuses on improving the performance of lightweight Large Language Models (LLMs) in mathematical reasoning tasks. We introduce a novel method for measuring mathematical logic similarity and design an automatic screening mechanism to construct a set of reference problems that integrate both semantic and logical similarity. By employing carefully crafted positive and negative example prompts, we guide the model towards adopting sound reasoning logic. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to utilize retrieval-enhanced generation for mathematical problem-solving. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves a 15.8% improvement over the Chain of Thought approach on the SVAMP dataset and a 21.5 % improvement on the GSM8K dataset. Further application of this method to a large-scale model with 175 billion parameters yields performance comparable to the best results on both aforementioned datasets. Finally, we conduct an analysis of errors during the reasoning process, providing valuable insights and directions for future research on reasoning tasks using large language models.
Read more9/4/2024
💬

0
Can Large Language Models put 2 and 2 together? Probing for Entailed Arithmetical Relationships
D. Panas, S. Seth, V. Belle
Two major areas of interest in the era of Large Language Models regard questions of what do LLMs know, and if and how they may be able to reason (or rather, approximately reason). Since to date these lines of work progressed largely in parallel (with notable exceptions), we are interested in investigating the intersection: probing for reasoning about the implicitly-held knowledge. Suspecting the performance to be lacking in this area, we use a very simple set-up of comparisons between cardinalities associated with elements of various subjects (e.g. the number of legs a bird has versus the number of wheels on a tricycle). We empirically demonstrate that although LLMs make steady progress in knowledge acquisition and (pseudo)reasoning with each new GPT release, their capabilities are limited to statistical inference only. It is difficult to argue that pure statistical learning can cope with the combinatorial explosion inherent in many commonsense reasoning tasks, especially once arithmetical notions are involved. Further, we argue that bigger is not always better and chasing purely statistical improvements is flawed at the core, since it only exacerbates the dangerous conflation of the production of correct answers with genuine reasoning ability.
Read more5/1/2024


0
Self-training Language Models for Arithmetic Reasoning
Marek Kadlv{c}'ik, Michal v{S}tef'anik
Language models achieve impressive results in tasks involving complex multistep reasoning, but scaling these capabilities further traditionally requires expensive collection of more annotated data. In this work, we explore the potential of improving the capabilities of language models without new data, merely using automated feedback to the validity of their predictions in arithmetic reasoning (self-training). We find that models can substantially improve in both single-round (offline) and online self-training. In the offline setting, supervised methods are able to deliver gains comparable to preference optimization, but in online self-training, preference optimization shows to largely outperform supervised training thanks to superior stability and robustness on unseen types of problems.
Read more7/12/2024