An investigation into the scientific landscape of the conversational and generative artificial intelligence, and human-chatbot interaction in education and research

0
❗
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Artificial intelligence (AI) has been a disruptive technology for some time, but its recent evolution, driven by technological advancements, big data analytics, and quantum computing, has produced conversational and generative AI (CGAI/GenAI) and human-like chatbots that are disrupting conventional operations and methods in various fields.
- This study investigates the scientific landscape of CGAI and human-chatbot interaction/collaboration, evaluating use cases, benefits, challenges, and policy implications for multidisciplinary education and allied industry operations.
- The research found a significant increase in CGAI-related publications, with 96% occurring between 2019 and 2023, and identified prominent use cases in computer science, medical/healthcare, engineering, and business fields.
Plain English Explanation
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been around for a while, but it's undergone some major changes recently. Advances in technology, data analysis, and quantum computing have led to the development of conversational and generative AI (CGAI/GenAI) and human-like chatbots. These new AI systems are starting to disrupt the way things are done in different fields, like education and healthcare.
This study looked at how CGAI and human-chatbot interactions are being used and what the benefits and challenges are. It found that there's been a huge increase in CGAI-related research, with most of it happening in the last few years. The researchers saw a lot of CGAI being used in computer science, medicine, engineering, and business.
For example, teachers and researchers are using CGAI to generate course content and help with academic writing. But there are also concerns about CGAI being misused, like for plagiarism or spreading misinformation, especially in medical applications. The study suggests that we need to develop policies and strategies to address these potential challenges as CGAI becomes more widely used.
Technical Explanation
The study analyzed the scientific landscape of conversational and generative AI (CGAI/GenAI) and human-chatbot interaction/collaboration. The researchers used bibliometric analysis to examine publication trends, prominent use cases, intellectual structure, and thematic focus.
The publication trend analysis showed a significant increase in CGAI-related publications, with just 4% occurring during 2006-2018 and a massive 96% growth during 2019-2023. The prominent use cases of CGAI (e.g., ChatGPT) were found in computer science [multidisciplinary and AI] (32%), medical/healthcare (17%), engineering (7%), and business fields (6%).
The intellectual structure analysis revealed strong collaboration among eminent multidisciplinary sources in business, information systems, and other areas. The thematic structure highlighted key CGAI use cases, such as improved user experience in human-computer interaction, computer program/code generation, and system creation.
The study also identified widespread CGAI usefulness for teachers, researchers, and learners, including syllabus/course content generation, testing aids, and academic writing assistance. However, it also raised concerns about potential abuse and misuse, such as plagiarism, privacy violations, and the spread of misinformation, especially in medical/healthcare applications.
Critical Analysis
The study provides valuable insights into the rapidly evolving landscape of conversational and generative AI, but it also highlights several areas that warrant further investigation and consideration.
While the study identifies a range of use cases for CGAI across different disciplines, it does not delve deeply into the nuances and potential limitations of these applications. For example, the use of CGAI in language learning and teaching may face challenges related to the quality and appropriateness of the generated content, as well as the potential impact on student autonomy and critical thinking.
The study also acknowledges the concerns around the abuse and misuse of CGAI, but it does not offer detailed solutions or recommendations for addressing these issues. As CGAI becomes more prevalent, it will be crucial to develop robust policies and safeguards to mitigate the risks of plagiarism, privacy violations, and the spread of misinformation.
Additionally, the study focuses primarily on the current state of CGAI research and applications, but it does not delve into the long-term implications of these technologies. As CGAI systems become more advanced and integrated into various sectors, it will be important to consider the potential societal and ethical implications, such as the impact on employment, the exacerbation of biases, and the overall effect on human-machine interactions.
Conclusion
This study provides a comprehensive overview of the rapid evolution of conversational and generative AI (CGAI/GenAI) and its growing impact on various fields, including education, healthcare, and industry. The findings highlight the significant increase in CGAI-related research, the prominent use cases, and the potential benefits and challenges associated with these technologies.
As CGAI systems continue to advance and become more widely adopted, it will be crucial for policymakers, educators, and industry leaders to collaborate in developing effective strategies and policies to address the potential risks and ensure the responsible and ethical use of these technologies. By doing so, we can harness the power of CGAI to enhance learning, improve healthcare outcomes, and drive innovation, while mitigating the risks of abuse and misuse.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
❗

0
An investigation into the scientific landscape of the conversational and generative artificial intelligence, and human-chatbot interaction in education and research
Ikpe Justice Akpan, Yawo M. Kobara, Josiah Owolabi, Asuama Akpam, Onyebuchi Felix Offodile
Artificial intelligence (AI) as a disruptive technology is not new. However, its recent evolution, engineered by technological transformation, big data analytics, and quantum computing, produces conversational and generative AI (CGAI/GenAI) and human-like chatbots that disrupt conventional operations and methods in different fields. This study investigates the scientific landscape of CGAI and human-chatbot interaction/collaboration and evaluates use cases, benefits, challenges, and policy implications for multidisciplinary education and allied industry operations. The publications trend showed that just 4% (n=75) occurred during 2006-2018, while 2019-2023 experienced astronomical growth (n=1763 or 96%). The prominent use cases of CGAI (e.g., ChatGPT) for teaching, learning, and research activities occurred in computer science [multidisciplinary and AI] (32%), medical/healthcare (17%), engineering (7%), and business fields (6%). The intellectual structure shows strong collaboration among eminent multidisciplinary sources in business, Information Systems, and other areas. The thematic structure of SLP highlights prominent CGAI use cases, including improved user experience in human-computer interaction, computer programs/code generation, and systems creation. Widespread CGAI usefulness for teachers, researchers, and learners includes syllabi/course content generation, testing aids, and academic writing. The concerns about abuse and misuse (plagiarism, academic integrity, privacy violations) and issues about misinformation, danger of self-diagnoses, and patient privacy in medical/healthcare applications are prominent. Formulating strategies and policies to address potential CGAI challenges in teaching/learning and practice are priorities. Developing discipline-based automatic detection of GenAI contents to check abuse is proposed.
Read more7/18/2024
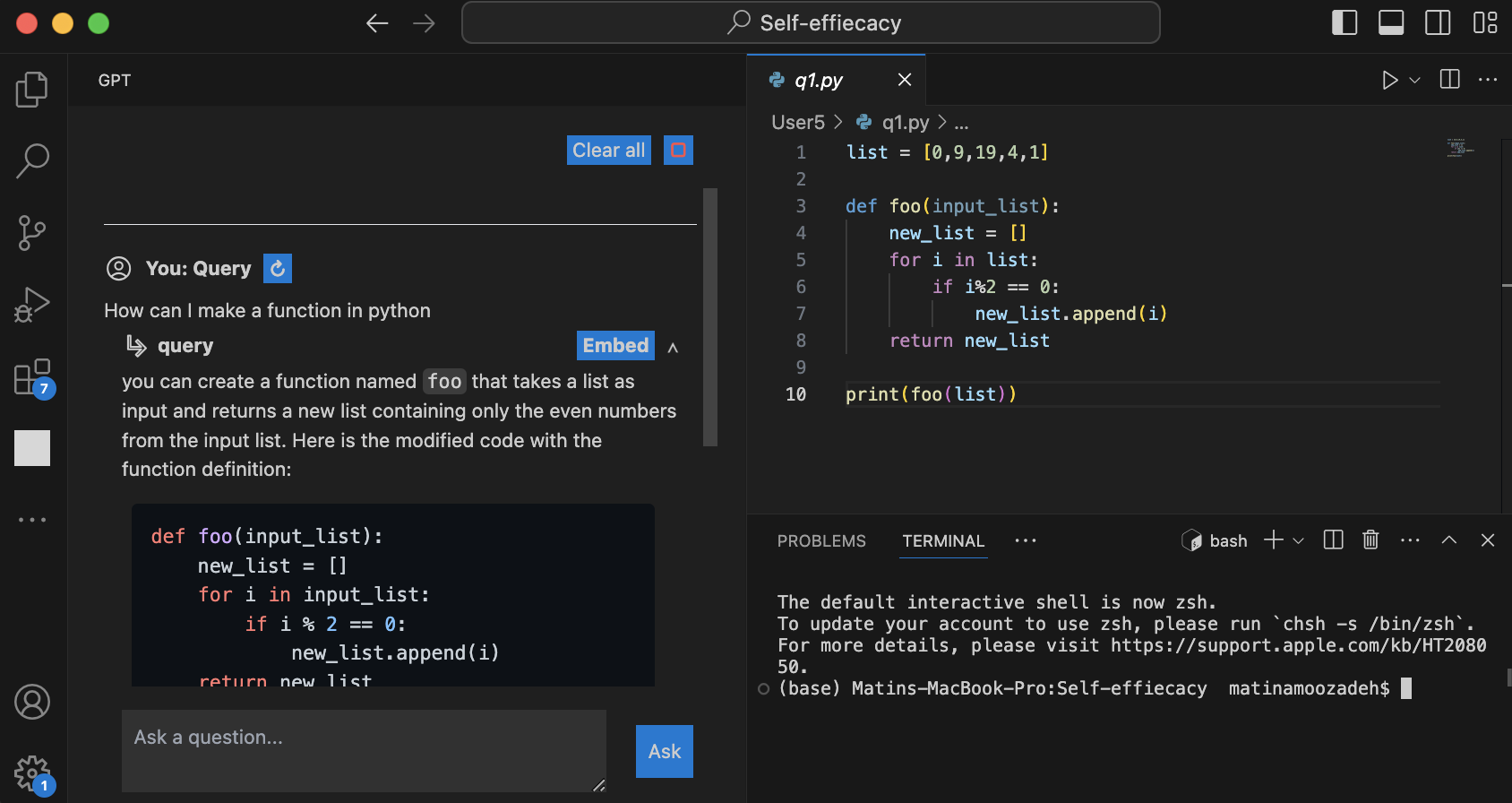

0
Student-AI Interaction: A Case Study of CS1 students
Matin Amoozadeh, Daye Nam, Daniel Prol, Ali Alfageeh, James Prather, Michael Hilton, Sruti Srinivasa Ragavan, Mohammad Amin Alipour
The new capabilities of generative artificial intelligence tools Generative AI, such as ChatGPT, allow users to interact with the system in intuitive ways, such as simple conversations, and receive (mostly) good-quality answers. These systems can support students' learning objectives by providing accessible explanations and examples even with vague queries. At the same time, they can encourage undesired help-seeking behaviors by providing solutions to the students' homework. Therefore, it is important to better understand how students approach such tools and the potential issues such approaches might present for the learners. In this paper, we present a case study for understanding student-AI collaboration to solve programming tasks in the CS1 introductory programming course. To this end, we recruited a gender-balanced majority non-white set of 15 CS1 students at a large public university in the US. We observed them solving programming tasks. We used a mixed-method approach to study their interactions as they tackled Python programming tasks, focusing on when and why they used ChatGPT for problem-solving. We analyze and classify the questions submitted by the 15 participants to ChatGPT. Additionally, we analyzed user interaction patterns, their reactions to ChatGPT's responses, and the potential impacts of Generative AI on their perception of self-efficacy. Our results suggest that in about a third of the cases, the student attempted to complete the task by submitting the full description of the tasks to ChatGPT without making any effort on their own. We also observed that few students verified their solutions. We discuss the results and their potential implications.
Read more7/2/2024
🤖

0
Developing generative AI chatbots conceptual framework for higher education
Joshua Ebere Chukwuere
This research explores the quickly changing field of generative artificial intelligence (GAI) chatbots in higher education, an industry that is undergoing major technological changes. AI chatbots, such as ChatGPT, HuggingChat, and Google Bard, are becoming more and more common in a variety of sectors, including education. Their acceptance is still in its early phases, with a variety of prospects and obstacles. However, their potential in higher education is particularly noteworthy, providing lecturers and students with affordable, individualized support. Creating a comprehensive framework to aid the usage of generative AI chatbots in higher education institutions (HEIs) is the aim of this project. The Generative AI Chatbots Acceptance Model (GAICAM) is the result of this study's synthesis of elements from well-known frameworks, including the TAM, UTAUT2, TPB, and others along with variables like optimism, innovativeness, discomfort, insecurity, and others. Using a research method that encompasses a comprehensive analysis of extant literature from databases such as IEEE, ACM, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar, the study aims to comprehend the implications of AI Chatbots on higher education and pinpoint critical elements for their efficacious implementation. Peer-reviewed English-language publications published between 2020 and 2023 with a focus on the use of AI chatbots in higher education were the main focus of the search criteria. The results demonstrate how much AI chatbots can do to improve student engagement, streamline the educational process, and support administrative and research duties. But there are also clear difficulties, such as unfavorable student sentiments, doubts about the veracity of material produced by AI, and unease and nervousness with new technologies.
Read more5/14/2024


0
Generative Artificial Intelligence and Human Learning
Lixiang Yan, Samuel Greiff, Ziwen Teuber, Dragan Gav{s}evi'c
Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) holds the potential to transform the delivery, cultivation, and evaluation of human learning. This Perspective examines the integration of GenAI as a tool for human learning, addressing its promises and challenges from a holistic viewpoint that integrates insights from learning sciences, educational technology, and human-computer interaction. GenAI promises to enhance learning experiences by scaling personalised support, diversifying learning materials, enabling timely feedback, and innovating assessment methods. However, it also presents critical issues such as model imperfections, ethical dilemmas, and the disruption of traditional assessments. Cultivating AI literacy and adaptive skills is imperative for facilitating informed engagement with GenAI technologies. Rigorous research across learning contexts is essential to evaluate GenAI's impact on human cognition, metacognition, and creativity. Humanity must learn with and about GenAI, ensuring it becomes a powerful ally in the pursuit of knowledge and innovation, rather than a crutch that undermines our intellectual abilities.
Read more9/6/2024