Joint Training and Reflection Pattern Optimization for Non-Ideal RIS-Aided Multiuser Systems
2403.19955

0
0

Abstract
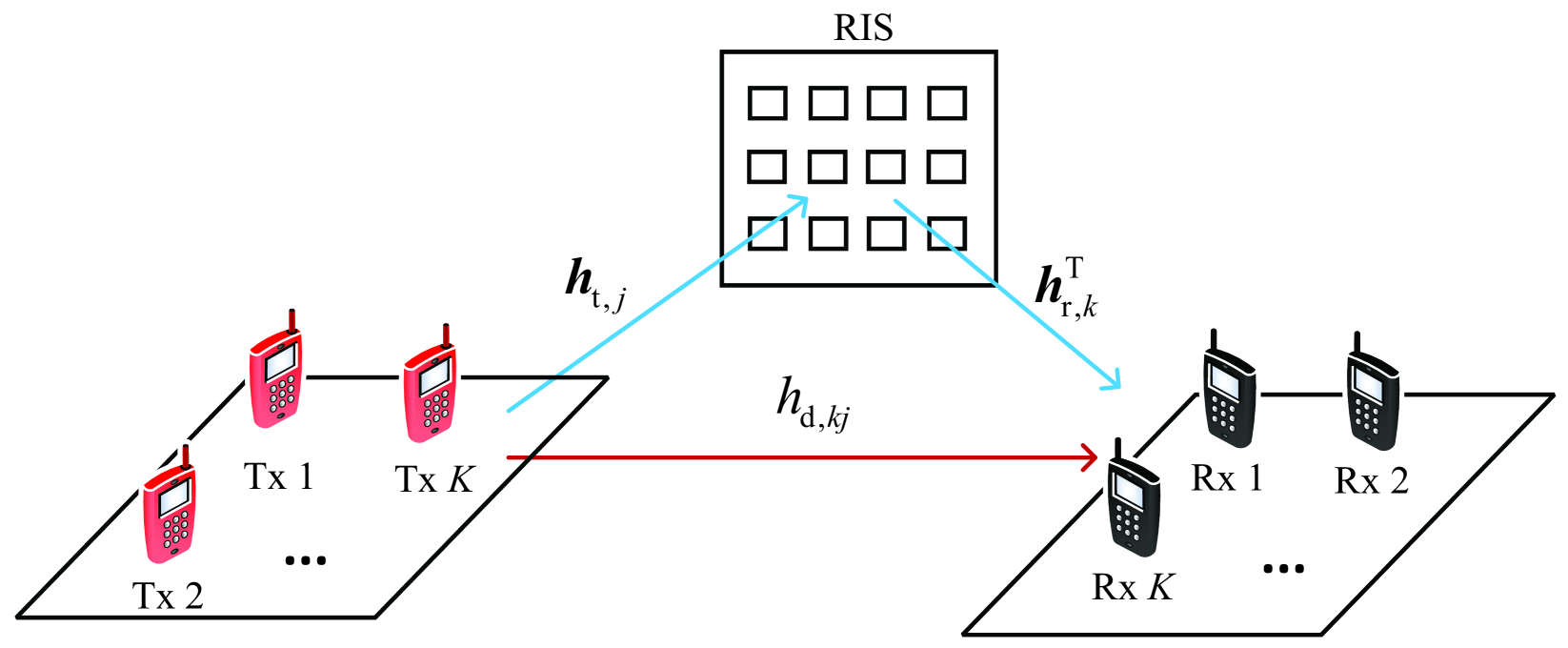
Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is a promising technique to improve the performance of future wireless communication systems at low energy consumption. To reap the potential benefits of RIS-aided beamforming, it is vital to enhance the accuracy of channel estimation. In this paper, we consider an RIS-aided multiuser system with non-ideal reflecting elements, each of which has a phase-dependent reflecting amplitude, and we aim to minimize the mean-squared error (MSE) of the channel estimation by jointly optimizing the training signals at the user equipments (UEs) and the reflection pattern at the RIS. As examples the least squares (LS) and linear minimum MSE (LMMSE) estimators are considered. The considered problems do not admit simple solution mainly due to the complicated constraints pertaining to the non-ideal RIS reflecting elements. As far as the LS criterion is concerned, we tackle this difficulty by first proving the optimality of orthogonal training symbols and then propose a majorization-minimization (MM)-based iterative method to design the reflection pattern, where a semi-closed form solution is obtained in each iteration. As for the LMMSE criterion, we address the joint training and reflection pattern optimization problem with an MM-based alternating algorithm, where a closed-form solution to the training symbols and a semi-closed form solution to the RIS reflecting coefficients are derived, respectively. Furthermore, an acceleration scheme is proposed to improve the convergence rate of the proposed MM algorithms. Finally, simulation results demonstrate the performance advantages of our proposed joint training and reflection pattern designs.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper investigates optimizing the reflection pattern of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) in multiuser communications systems.
- It proposes joint training of the RIS reflection pattern and channel estimation to improve overall system performance.
- The paper considers non-ideal RIS elements with imperfections that impact performance.
- Experiments are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach compared to existing methods.
Plain English Explanation
Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) are a emerging technology for wireless communications. RISs are metasurfaces that can dynamically control the reflection of wireless signals. This allows them to improve signal coverage and strength for users.
In a typical multiuser communications system with RISs, there are several users trying to receive signals from a base station. The RIS can be programmed to reflect the signals in a way that benefits all the users. However, the RIS elements may not be perfect, introducing distortions that degrade performance.
This paper presents a new method to jointly optimize the RIS reflection pattern and estimate the wireless channels. By training these two components together, the system can account for the non-ideal RIS elements and maximize the overall performance for the multiple users. The authors demonstrate through simulations that their approach outperforms existing techniques that do not consider the RIS imperfections.
The key idea is to have the RIS reflection pattern and channel estimation work in harmony, rather than treating them separately. This allows the system to adapt to the real-world limitations of the RIS hardware and deliver better results for the users.
Technical Explanation
The paper formulates the joint optimization problem for the RIS reflection pattern and channel estimation. It considers a multiuser downlink scenario where a base station communicates with multiple users assisted by a RIS.
The channel estimation is performed using either least squares (LS) or linear minimum mean-squared error (LMMSE) methods. The RIS reflection pattern is optimized using a majorization-minimization (MM) approach. The authors derive the optimal solutions for both components and show how to alternate between updating them.
Experiments are conducted to compare the proposed joint optimization approach against independent optimization of the RIS pattern and channel estimation. The results demonstrate significant performance gains, especially in scenarios with more severe RIS element impairments.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough analysis of the joint optimization problem and presents a practical solution. The consideration of non-ideal RIS elements is an important aspect, as real-world RISs are likely to have some level of hardware imperfections.
One potential limitation is the assumption of perfect knowledge of the RIS element impairments. In practice, accurately modeling and estimating these impairments may be challenging. The paper could have discussed strategies for handling uncertainty in the RIS element characteristics.
Additionally, the paper focuses on a downlink multiuser scenario. Extending the analysis to uplink or more general multipoint-to-multipoint setups could broaden the applicability of the proposed techniques.
Overall, the paper makes a valuable contribution by demonstrating the benefits of jointly optimizing the RIS reflection pattern and channel estimation in the presence of non-ideal RIS elements. Further research could explore more realistic system models and explore the trade-offs involved in practical deployments.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel approach for optimizing the reflection pattern of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) in multiuser communications systems. By jointly training the RIS reflection pattern and channel estimation, the proposed method can effectively account for non-ideal RIS elements and deliver superior performance compared to existing techniques.
The key insights are the importance of considering RIS imperfections and the advantages of a holistic optimization approach that tightly couples the RIS configuration and channel estimation. These findings have important implications for the practical deployment of RIS-aided wireless systems, as they highlight the need to design robust algorithms that can adapt to real-world hardware limitations.
As RIS technology continues to evolve, this research provides a valuable foundation for developing advanced signal processing and optimization techniques to fully harness the potential of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces in future wireless networks.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
✅
Multi-hop Multi-RIS Wireless Communication Systems: Multi-reflection Path Scheduling and Beamforming
Xiaoyan Ma, Haixia Zhang, Xianhao Chen, Yuguang Fangmand Dongfeng Yuan

0
0
Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) provides a promising way to proactively augment propagation environments for better transmission performance in wireless communications. Existing multi-RIS works mainly focus on link-level optimization with predetermined transmission paths, which cannot be directly extended to system-level management, since they neither consider the interference caused by undesired scattering of RISs, nor the performance balancing between different transmission paths. To address this, we study an innovative multi-hop multi-RIS communication system, where a base station (BS) transmits information to a set of distributed users over multi-RIS configuration space in a multi-hop manner. The signals for each user are subsequently reflected by the selected RISs via multi-reflection line-of-sight (LoS) links. To ensure that all users have fair access to the system to avoid excessive number of RISs serving one user, we aim to find the optimal beam reflecting path for each user, while judiciously determining the path scheduling strategies with the corresponding beamforming design to ensure the fairness. Due to the presence of interference caused by undesired scattering of RISs, it is highly challenging to solve the formulated multi-RIS multi-path beamforming optimization problem. To solve it, we first derive the optimal RISs' phase shifts and the corresponding reflecting path selection for each user based on its practical deployment location. With the optimized multi-reflection paths, we obtain a feasible user grouping pattern for effective interference mitigation by constructing the maximum independent sets (MISs). Finally, we propose a joint heuristic algorithm to iteratively update the beamforming vectors and the group scheduling policies to maximize the minimum equivalent data rate of all users.
5/22/2024

Physically-Consistent Modeling and Optimization of Non-local RIS-Assisted Multi-User MIMO Communication Systems
Dilki Wijekoon, Amine Mezghani, George C. Alexandropoulos, Ekram Hossain

0
0
Mutual Coupling (MC) emerges as an inherent feature in Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs), particularly, when they are fabricated with sub-wavelength inter-element spacing. Hence, any physically-consistent model of the RIS operation needs to accurately describe MC-induced effects. In addition, the design of the ElectroMagnetic (EM) transmit/receive radiation patterns constitutes another critical factor for efficient RIS operation. The latter two factors lead naturally to the emergence of non-local RIS structures, whose operation can be effectively described via non-diagonal phase shift matrices. In this paper, we focus on jointly optimizing MC and the radiation patterns in multi-user MIMO communication systems assisted by non-local RISs, which are modeled via the scattering parameters. We particularly present a novel problem formulation for the joint optimization of MC, radiation patterns, and the active and passive beamforming in a physically-consistent manner, considering either reflective or transmissive RIS setups. Differently from the current approaches that design the former two parameters on the fly, we present an offline optimization method which is solved for both considered RIS functionalities. Our extensive simulation results, using both parametric and geometric channel models, showcase the validity of the proposed optimization framework over benchmark schemes, indicating that improved performance is achievable without the need for optimizing MC and the radiation patterns of the RIS on the fly, which can be rather cumbersome.
6/11/2024
Power-Aware Sparse Reflect Beamforming in Active RIS-aided Interference Channels
Ruizhe Long, Hu Zhou, Ying-Chang Liang

0
0
Active reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) has attracted significant attention in wireless communications, due to its reflecting elements (REs) capable of reflecting incident signals with not only phase shifts but also amplitude amplifications. In this paper, we are interested in active RIS-aided interference channels in which $K$ user pairs share the same time and frequency resources with the aid of active RIS. Thanks to the promising amplitude amplification capability, activating a moderate number of REs, rather than all of them, is sufficient for the active RIS to mitigate cross-channel interferences. Motivated by this, we propose a power-aware sparse reflect beamforming design for the active RIS-aided interference channels, which allows the active RIS to flexibly adjust the number of activated REs for the sake of reducing hardware and power costs. Specifically, we establish the power consumption model in which only those activated REs consume the biasing and operation power that supports the amplitude amplification, yielding an $ell_0$-norm power consumption function. Based on the proposed model, we investigate a sum-rate maximization problem and an active RIS power minimization problem by carefully designing the sparse reflect beamforming vector. To solve these problems, we first replace the nonconvex $ell_0$-norm function with an iterative reweighted $ell_1$-norm function. Then, fractional programming is used to solve the sum-rate maximization, while semidefinite programming together with the difference-of-convex algorithm (DCA) is used to solve the active RIS power minimization. Numerical results show that the proposed sparse designs can notably increase the sum rate of user pairs and decrease the power consumption of active RIS in interference channels.
4/1/2024

Heuristic Solution to Joint Deployment and Beamforming Design for STAR-RIS Aided Networks
Bai Yan, Qi Zhao, Jin Zhang, J. Andrew Zhang

0
0
This paper tackles the deployment challenges of Simultaneous Transmitting and Reflecting Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (STAR-RIS) in communication systems. Unlike existing works that use fixed deployment setups or solely optimize the location, this paper emphasizes the joint optimization of the location and orientation of STAR-RIS. This enables searching across all user grouping possibilities and fully boosting the system's performance. We consider a sum rate maximization problem with joint optimization and hybrid beamforming design. An offline heuristic solution is proposed for the problem, developed based on differential evolution and semi-definite programming methods. In particular, a point-point representation is proposed for characterizing and exploiting the user-grouping. A balanced grouping method is designed to achieve a desired user grouping with low complexity. Numerical results demonstrate the substantial performance gains achievable through optimal deployment design.
4/16/2024