Knowledge Boundary and Persona Dynamic Shape A Better Social Media Agent
2403.19275

0
0
Abstract
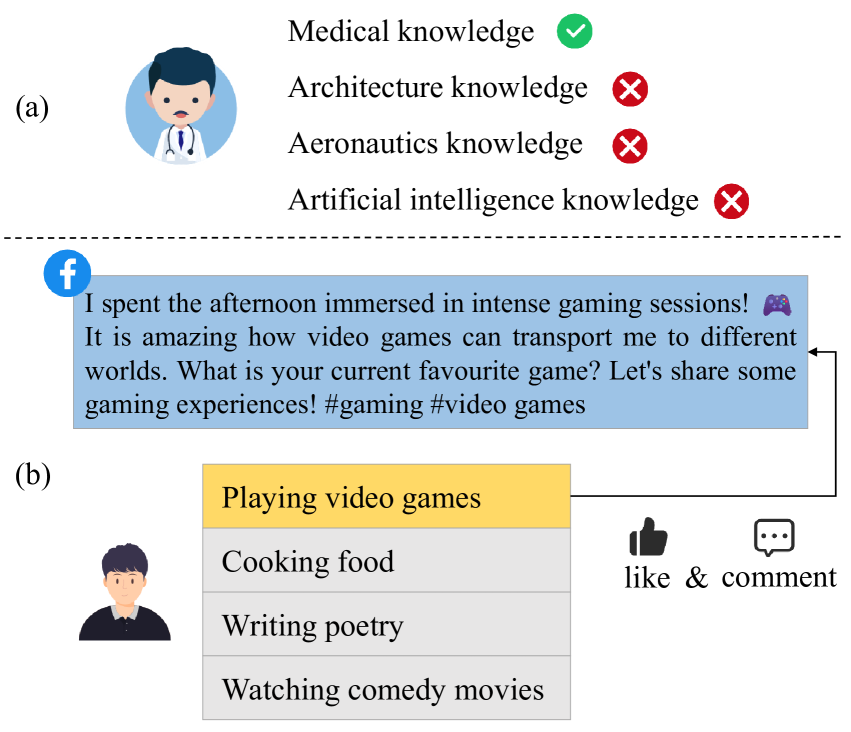
Constructing personalized and anthropomorphic agents holds significant importance in the simulation of social networks. However, there are still two key problems in existing works: the agent possesses world knowledge that does not belong to its personas, and it cannot eliminate the interference of diverse persona information on current actions, which reduces the personalization and anthropomorphism of the agent. To solve the above problems, we construct the social media agent based on personalized knowledge and dynamic persona information. For personalized knowledge, we add external knowledge sources and match them with the persona information of agents, thereby giving the agent personalized world knowledge. For dynamic persona information, we use current action information to internally retrieve the persona information of the agent, thereby reducing the interference of diverse persona information on the current action. To make the agent suitable for social media, we design five basic modules for it: persona, planning, action, memory and reflection. To provide an interaction and verification environment for the agent, we build a social media simulation sandbox. In the experimental verification, automatic and human evaluations demonstrated the effectiveness of the agent we constructed.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- The paper explores how the knowledge boundaries and persona dynamics of a social media agent can be leveraged to improve its performance.
- It proposes an approach that dynamically shapes the agent's persona based on the user's needs and preferences.
- The authors conduct experiments to evaluate the effectiveness of their approach compared to a baseline agent.
Plain English Explanation
The paper looks at how a social media agent, like a chatbot or virtual assistant, can become more helpful and engaging by adapting its persona to the user. The key idea is that the agent should have a flexible identity that changes based on the user's needs and preferences.
Imagine you're talking to a digital assistant. Typically, it has a fixed personality - it might be formal and serious, or friendly and casual. But what if the assistant could sense what kind of interaction you're looking for and adjust its persona accordingly? If you want quick, practical information, it could be more direct. If you're in a playful mood, it could be more lighthearted and engaging.
The researchers tested this concept by developing an agent that can dynamically shift its persona. They found that this approach led to better user experiences compared to a more rigid, one-size-fits-all assistant. By being responsive to the user's needs, the agent was able to build a stronger connection and provide more valuable assistance.
Technical Explanation
The paper introduces the concept of "knowledge boundary" - the scope of information and skills an agent possesses. The authors propose that dynamically shaping an agent's knowledge boundary, along with its persona, can lead to more effective social interactions.
Their approach involves two key components:
-
Persona modeling: The agent maintains a model of its own persona, including traits, interests, and communication style. This model is updated based on user feedback and interactions.
-
Persona-aware knowledge retrieval: When responding to a user's query, the agent selects relevant information from its knowledge base in a way that aligns with its current persona. This helps ensure the response is tailored to the user's needs.
The researchers conducted experiments where participants interacted with either their persona-adaptive agent or a baseline agent with a fixed persona. The results showed the persona-adaptive agent was rated higher in terms of engagement, trustworthiness, and overall user satisfaction.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach for enhancing the capabilities of social media agents. By dynamically adjusting the agent's persona and knowledge scope, the system is able to provide more personalized and engaging interactions.
However, the authors acknowledge that further research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of this approach. For example, it's unclear how users would respond to an agent whose persona shifts dramatically over time. There may be a need to maintain a sense of consistency or authenticity in the agent's identity.
Additionally, the paper does not address potential privacy and ethical concerns around an agent closely tailoring its persona to individual users. There could be risks around exploitation or manipulation if the agent's persona is overly responsive to user preferences.
Overall, the work demonstrates the value of adaptive persona modeling for social media agents, but more investigation is needed to ensure the approach is implemented responsibly and effectively.
Conclusion
This paper proposes an innovative way to improve social media agents by dynamically shaping their persona and knowledge scope based on user needs. By adapting its identity and expertise, the agent is able to foster more engaging and valuable interactions.
The research highlights the importance of flexibility and responsiveness in artificial social agents. As these technologies become increasingly prevalent, finding ways to make them more personalized and user-centric will be crucial. The insights from this work suggest a promising direction for enhancing the user experience and capabilities of social media agents.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Evolving Agents: Interactive Simulation of Dynamic and Diverse Human Personalities
Jiale Li, Jiayang Li, Jiahao Chen, Yifan Li, Shijie Wang, Hugo Zhou, Minjun Ye, Yunsheng Su

0
0
Human-like Agents with diverse and dynamic personality could serve as an important design probe in the process of user-centered design, thereby enabling designers to enhance the user experience of interactive application.In this article, we introduce Evolving Agents, a novel agent architecture that consists of two systems: Personality and Behavior. The Personality system includes three modules: Cognition, Emotion and Character Growth. The Behavior system comprises two modules: Planning and Action. We also build a simulation platform that enables agents to interact with the environment and other agents. Evolving Agents can simulate the human personality evolution process. Compared to its initial state, agents' personality and behavior patterns undergo believable development after several days of simulation. Agents reflect on their behavior to reason and develop new personality traits. These traits, in turn, generate new behavior patterns, forming a feedback loop-like personality evolution.In our experiment, we utilized simulation platform with 10 agents for evaluation. During the evaluation, these agents experienced believable and inspirational personality evolution. Through ablation and control experiments, we demonstrated the outstanding effectiveness of agent personality evolution and all modules of our agent architecture contribute to creating believable human-like agents with diverse and dynamic personalities. We also demonstrated through workshops how Evolving Agents could inspire designers.
4/4/2024
🤯
Social Life Simulation for Non-Cognitive Skills Learning
Zihan Yan, Yaohong Xiang, Yun Huang

0
0
Non-cognitive skills are crucial for personal and social life well-being, and such skill development can be supported by narrative-based (e.g., storytelling) technologies. While generative AI enables interactive and role-playing storytelling, little is known about how users engage with and perceive the use of AI in social life simulation for non-cognitive skills learning. To this end, we introduced SimuLife++, an interactive platform enabled by a large language model (LLM). The system allows users to act as protagonists, creating stories with one or multiple AI-based characters in diverse social scenarios. In particular, we expanded the Human-AI interaction to a Human-AI-AI collaboration by including a sage agent, who acts as a bystander to provide users with more insightful perspectives on their choices and conversations. Through a within-subject user study, we found that the inclusion of the sage agent significantly enhanced narrative immersion, according to the narrative transportation scale, leading to more messages, particularly in group chats. Participants' interactions with the sage agent were also associated with significantly higher scores in their perceived motivation, self-perceptions, and resilience and coping, indicating positive impacts on non-cognitive skills reflection. Participants' interview results further explained the sage agent's aid in decision-making, solving ethical dilemmas, and problem-solving; on the other hand, they suggested improvements in user control and balanced responses from multiple characters. We provide design implications on the application of generative AI in narrative solutions for non-cognitive skill development in broader social contexts.
5/2/2024
🤔
Designing for Human-Agent Alignment: Understanding what humans want from their agents
Nitesh Goyal, Minsuk Chang, Michael Terry

0
0
Our ability to build autonomous agents that leverage Generative AI continues to increase by the day. As builders and users of such agents it is unclear what parameters we need to align on before the agents start performing tasks on our behalf. To discover these parameters, we ran a qualitative empirical research study about designing agents that can negotiate during a fictional yet relatable task of selling a camera online. We found that for an agent to perform the task successfully, humans/users and agents need to align over 6 dimensions: 1) Knowledge Schema Alignment 2) Autonomy and Agency Alignment 3) Operational Alignment and Training 4) Reputational Heuristics Alignment 5) Ethics Alignment and 6) Human Engagement Alignment. These empirical findings expand previous work related to process and specification alignment and the need for values and safety in Human-AI interactions. Subsequently we discuss three design directions for designers who are imagining a world filled with Human-Agent collaborations.
4/9/2024
⛏️
An Embodied Generalist Agent in 3D World
Jiangyong Huang, Silong Yong, Xiaojian Ma, Xiongkun Linghu, Puhao Li, Yan Wang, Qing Li, Song-Chun Zhu, Baoxiong Jia, Siyuan Huang

0
0
Leveraging massive knowledge from large language models (LLMs), recent machine learning models show notable successes in general-purpose task solving in diverse domains such as computer vision and robotics. However, several significant challenges remain: (i) most of these models rely on 2D images yet exhibit a limited capacity for 3D input; (ii) these models rarely explore the tasks inherently defined in 3D world, e.g., 3D grounding, embodied reasoning and acting. We argue these limitations significantly hinder current models from performing real-world tasks and approaching general intelligence. To this end, we introduce LEO, an embodied multi-modal generalist agent that excels in perceiving, grounding, reasoning, planning, and acting in the 3D world. LEO is trained with a unified task interface, model architecture, and objective in two stages: (i) 3D vision-language (VL) alignment and (ii) 3D vision-language-action (VLA) instruction tuning. We collect large-scale datasets comprising diverse object-level and scene-level tasks, which require considerable understanding of and interaction with the 3D world. Moreover, we meticulously design an LLM-assisted pipeline to produce high-quality 3D VL data. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate LEO's remarkable proficiency across a wide spectrum of tasks, including 3D captioning, question answering, embodied reasoning, navigation and manipulation. Our ablative studies and scaling analyses further provide valuable insights for developing future embodied generalist agents. Code and data are available on project page.
5/10/2024