Large Language Models for Cyber Security: A Systematic Literature Review
2405.04760

0
0
Abstract
The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has opened up new opportunities for leveraging artificial intelligence in various domains, including cybersecurity. As the volume and sophistication of cyber threats continue to grow, there is an increasing need for intelligent systems that can automatically detect vulnerabilities, analyze malware, and respond to attacks. In this survey, we conduct a comprehensive review of the literature on the application of LLMs in cybersecurity (LLM4Security). By comprehensively collecting over 30K relevant papers and systematically analyzing 127 papers from top security and software engineering venues, we aim to provide a holistic view of how LLMs are being used to solve diverse problems across the cybersecurity domain. Through our analysis, we identify several key findings. First, we observe that LLMs are being applied to a wide range of cybersecurity tasks, including vulnerability detection, malware analysis, network intrusion detection, and phishing detection. Second, we find that the datasets used for training and evaluating LLMs in these tasks are often limited in size and diversity, highlighting the need for more comprehensive and representative datasets. Third, we identify several promising techniques for adapting LLMs to specific cybersecurity domains, such as fine-tuning, transfer learning, and domain-specific pre-training. Finally, we discuss the main challenges and opportunities for future research in LLM4Security, including the need for more interpretable and explainable models, the importance of addressing data privacy and security concerns, and the potential for leveraging LLMs for proactive defense and threat hunting. Overall, our survey provides a comprehensive overview of the current state-of-the-art in LLM4Security and identifies several promising directions for future research.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper provides a systematic literature review of how large language models (LLMs) are being applied to the field of cybersecurity.
- The authors examine the current state of research on using LLMs for tasks like vulnerability detection and repair, education and training, and assisting cybersecurity researchers.
- The review covers the key techniques and architectures being explored, as well as the potential benefits and challenges of leveraging LLMs in the cybersecurity domain.
Plain English Explanation
This paper looks at how powerful AI language models, known as large language models (LLMs), are being used to help with cybersecurity tasks. Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting computer systems and networks from unauthorized access or harm.
The researchers reviewed a lot of previous studies to see how LLMs are currently being applied in this field. They found that LLMs are being explored for things like automatically detecting security vulnerabilities in software and training people on cybersecurity concepts. LLMs are also being used to assist cybersecurity researchers in their work.
The key idea is that LLMs, which are very skilled at understanding and generating human language, could be valuable tools for tackling complex cybersecurity challenges. By automating certain tasks or augmenting human experts, LLMs have the potential to make cybersecurity more efficient and effective.
However, the researchers also note that there are still challenges and limitations to using LLMs in this domain. More research is needed to fully understand how to best leverage these powerful AI models for cybersecurity applications.
Technical Explanation
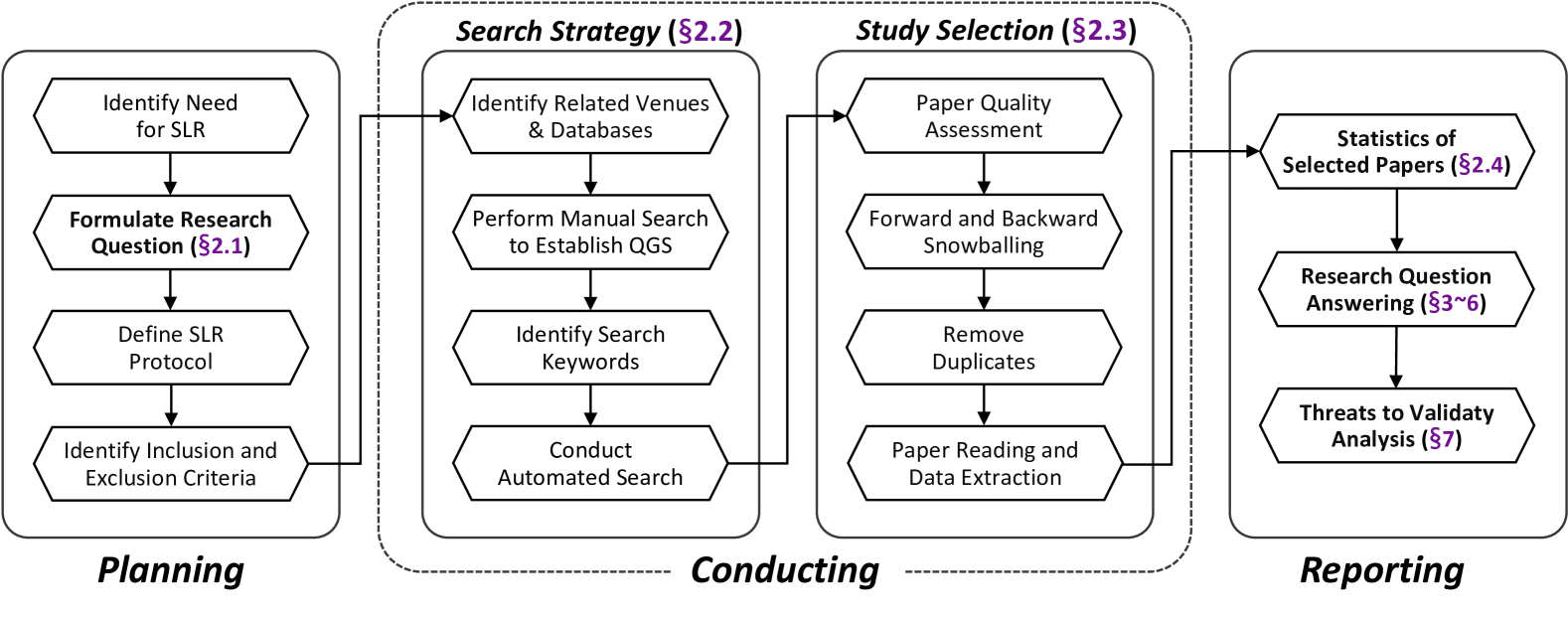
The paper conducts a systematic literature review to investigate how large language models (LLMs) are being applied to cybersecurity tasks. The authors searched academic databases to identify relevant studies, which they then carefully analyzed and synthesized.
Key areas where LLMs are being explored include:
-
Vulnerability Detection and Repair: Researchers are investigating how LLMs can be used to automatically identify security vulnerabilities in software code and even propose patches to fix those issues.
-
Education and Training: LLMs are being leveraged to enhance cybersecurity education and training, by generating realistic practice scenarios or providing personalized feedback to learners.
-
Assisting Cybersecurity Researchers: LLMs are being explored as research assistants to help cybersecurity experts analyze data, generate hypotheses, and more.
The review also covers the various LLM architectures and techniques being applied, such as fine-tuning models on domain-specific data or using LLMs in combination with other AI/ML approaches.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of research on using LLMs for cybersecurity applications. However, it also acknowledges several key limitations and areas for further study:
-
Data Biases: The authors note that the performance of LLMs in cybersecurity tasks may be affected by biases in the training data, which could lead to blind spots or inconsistencies.
-
Interpretability: While LLMs can be powerful, their inner workings are often opaque, which can make it challenging to fully understand and trust their outputs in high-stakes cybersecurity scenarios.
-
Adversarial Attacks: The review briefly discusses the potential vulnerability of LLMs to adversarial attacks, where malicious actors could try to fool the models and undermine their security applications.
Overall, the paper provides a solid foundation for understanding the current state of LLM research in cybersecurity. However, it also highlights the need for continued efforts to address the technical and ethical challenges of deploying these powerful AI models in real-world security contexts.
Conclusion
This systematic literature review examines how large language models (LLMs) are being leveraged to address a variety of cybersecurity challenges. The research covers a range of applications, from automated vulnerability detection and repair to enhancing cybersecurity education and training to assisting cybersecurity researchers.
While the potential benefits of using LLMs in the cybersecurity domain are significant, the review also highlights important limitations and areas for further research. Addressing challenges related to data biases, model interpretability, and adversarial attacks will be crucial as these powerful AI technologies continue to be adopted in high-stakes security contexts.
Overall, this paper provides a valuable synthesis of the current state of LLM research in cybersecurity, offering both researchers and practitioners a comprehensive understanding of the key trends, techniques, and open questions in this rapidly evolving field.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🔎
When LLMs Meet Cybersecurity: A Systematic Literature Review
Jie Zhang, Haoyu Bu, Hui Wen, Yu Chen, Lun Li, Hongsong Zhu

0
0
The rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs) have opened new avenues across various fields, including cybersecurity, which faces an ever-evolving threat landscape and need for innovative technologies. Despite initial explorations into the application of LLMs in cybersecurity, there is a lack of a comprehensive overview of this research area. This paper bridge this gap by providing a systematic literature review, encompassing an analysis of over 180 works, spanning across 25 LLMs and more than 10 downstream scenarios. Our comprehensive overview addresses three critical research questions: the construction of cybersecurity-oriented LLMs, LLMs' applications in various cybersecurity tasks, and the existing challenges and further research in this area. This study aims to shed light on the extensive potential of LLMs in enhancing cybersecurity practices, and serve as a valuable resource for applying LLMs in this doamin. We also maintain and regularly updated list of practical guides on LLMs for cybersecurity at https://github.com/tmylla/Awesome-LLM4Cybersecurity.
5/7/2024
Large Language Model for Vulnerability Detection and Repair: Literature Review and Roadmap
Xin Zhou, Sicong Cao, Xiaobing Sun, David Lo

0
0
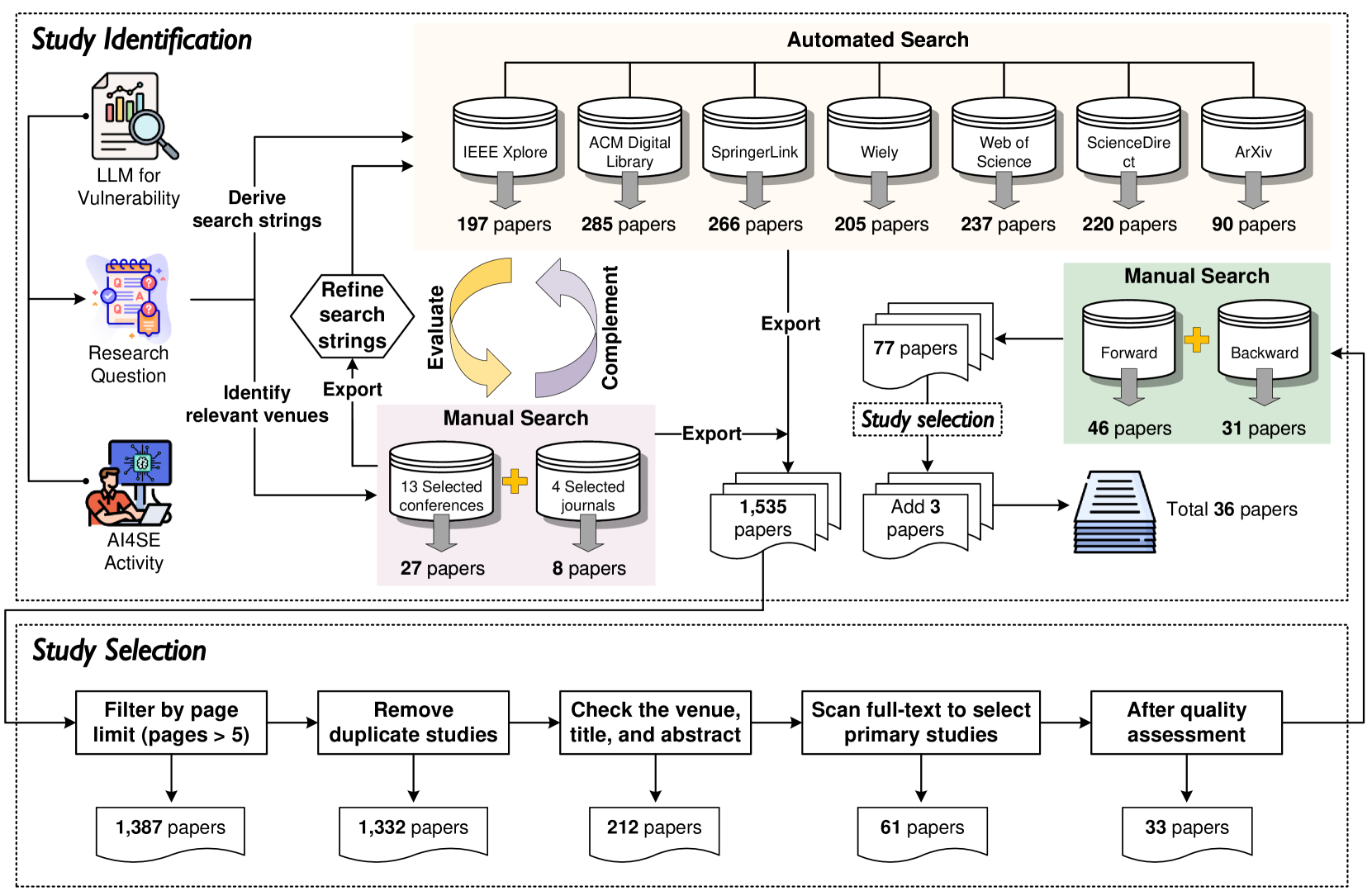
The significant advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have resulted in their widespread adoption across various tasks within Software Engineering (SE), including vulnerability detection and repair. Numerous recent studies have investigated the application of LLMs to enhance vulnerability detection and repair tasks. Despite the increasing research interest, there is currently no existing survey that focuses on the utilization of LLMs for vulnerability detection and repair. In this paper, we aim to bridge this gap by offering a systematic literature review of approaches aimed at improving vulnerability detection and repair through the utilization of LLMs. The review encompasses research work from leading SE, AI, and Security conferences and journals, covering 36 papers published at 21 distinct venues. By answering three key research questions, we aim to (1) summarize the LLMs employed in the relevant literature, (2) categorize various LLM adaptation techniques in vulnerability detection, and (3) classify various LLM adaptation techniques in vulnerability repair. Based on our findings, we have identified a series of challenges that still need to be tackled considering existing studies. Additionally, we have outlined a roadmap highlighting potential opportunities that we believe are pertinent and crucial for future research endeavors.
4/4/2024
Large Language Models for Education: A Survey and Outlook
Shen Wang, Tianlong Xu, Hang Li, Chaoli Zhang, Joleen Liang, Jiliang Tang, Philip S. Yu, Qingsong Wen

0
0
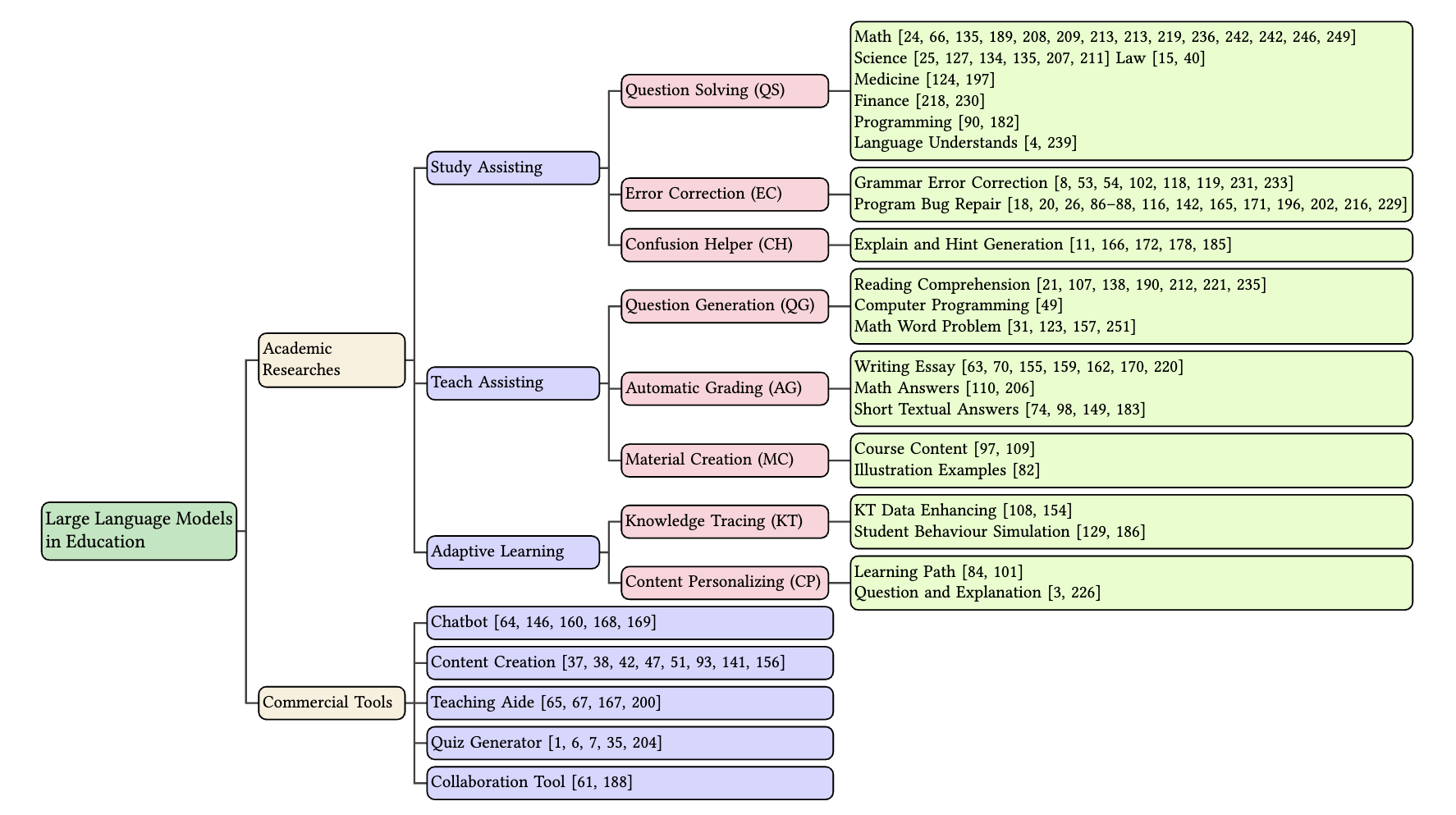
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has brought in a new era of possibilities in the realm of education. This survey paper summarizes the various technologies of LLMs in educational settings from multifaceted perspectives, encompassing student and teacher assistance, adaptive learning, and commercial tools. We systematically review the technological advancements in each perspective, organize related datasets and benchmarks, and identify the risks and challenges associated with deploying LLMs in education. Furthermore, we outline future research opportunities, highlighting the potential promising directions. Our survey aims to provide a comprehensive technological picture for educators, researchers, and policymakers to harness the power of LLMs to revolutionize educational practices and foster a more effective personalized learning environment.
4/3/2024
💬
Exploring the landscape of large language models: Foundations, techniques, and challenges
Milad Moradi, Ke Yan, David Colwell, Matthias Samwald, Rhona Asgari

0
0
In this review paper, we delve into the realm of Large Language Models (LLMs), covering their foundational principles, diverse applications, and nuanced training processes. The article sheds light on the mechanics of in-context learning and a spectrum of fine-tuning approaches, with a special focus on methods that optimize efficiency in parameter usage. Additionally, it explores how LLMs can be more closely aligned with human preferences through innovative reinforcement learning frameworks and other novel methods that incorporate human feedback. The article also examines the emerging technique of retrieval augmented generation, integrating external knowledge into LLMs. The ethical dimensions of LLM deployment are discussed, underscoring the need for mindful and responsible application. Concluding with a perspective on future research trajectories, this review offers a succinct yet comprehensive overview of the current state and emerging trends in the evolving landscape of LLMs, serving as an insightful guide for both researchers and practitioners in artificial intelligence.
4/19/2024