When LLMs Meet Cybersecurity: A Systematic Literature Review
2405.03644

0
0
🔎
Abstract
The rapid advancements in large language models (LLMs) have opened new avenues across various fields, including cybersecurity, which faces an ever-evolving threat landscape and need for innovative technologies. Despite initial explorations into the application of LLMs in cybersecurity, there is a lack of a comprehensive overview of this research area. This paper bridge this gap by providing a systematic literature review, encompassing an analysis of over 180 works, spanning across 25 LLMs and more than 10 downstream scenarios. Our comprehensive overview addresses three critical research questions: the construction of cybersecurity-oriented LLMs, LLMs' applications in various cybersecurity tasks, and the existing challenges and further research in this area. This study aims to shed light on the extensive potential of LLMs in enhancing cybersecurity practices, and serve as a valuable resource for applying LLMs in this doamin. We also maintain and regularly updated list of practical guides on LLMs for cybersecurity at https://github.com/tmylla/Awesome-LLM4Cybersecurity.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper provides a comprehensive review of research on the application of large language models (LLMs) in the field of cybersecurity.
- The review covers the construction of cybersecurity-oriented LLMs, their applications in various cybersecurity tasks, and the existing challenges and future research directions in this area.
- The authors analyze over 180 research works spanning 25 LLMs and more than 10 downstream cybersecurity scenarios.
Plain English Explanation
Large language models (LLMs) are powerful artificial intelligence systems that can understand and generate human-like text. Recent advancements in LLMs have opened up new possibilities for their use in various fields, including cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity is an important and constantly evolving field that deals with protecting digital systems and information from various threats, such as cyber attacks. Researchers have started exploring ways to apply LLMs in cybersecurity, but there was a lack of a comprehensive overview of this research area.
This paper aims to bridge that gap by providing a detailed review of the existing research on using LLMs in cybersecurity. The authors looked at over 180 research papers to understand how LLMs are being developed and used for cybersecurity tasks, as well as the challenges and future directions in this field.
The review covers a wide range of topics, including how LLMs can be specially designed for cybersecurity applications, how they can be used for tasks like vulnerability detection and repair, code generation and analysis, and even detecting and understanding cybercrime. The authors also provide a list of practical guides on using LLMs for cybersecurity.
Technical Explanation
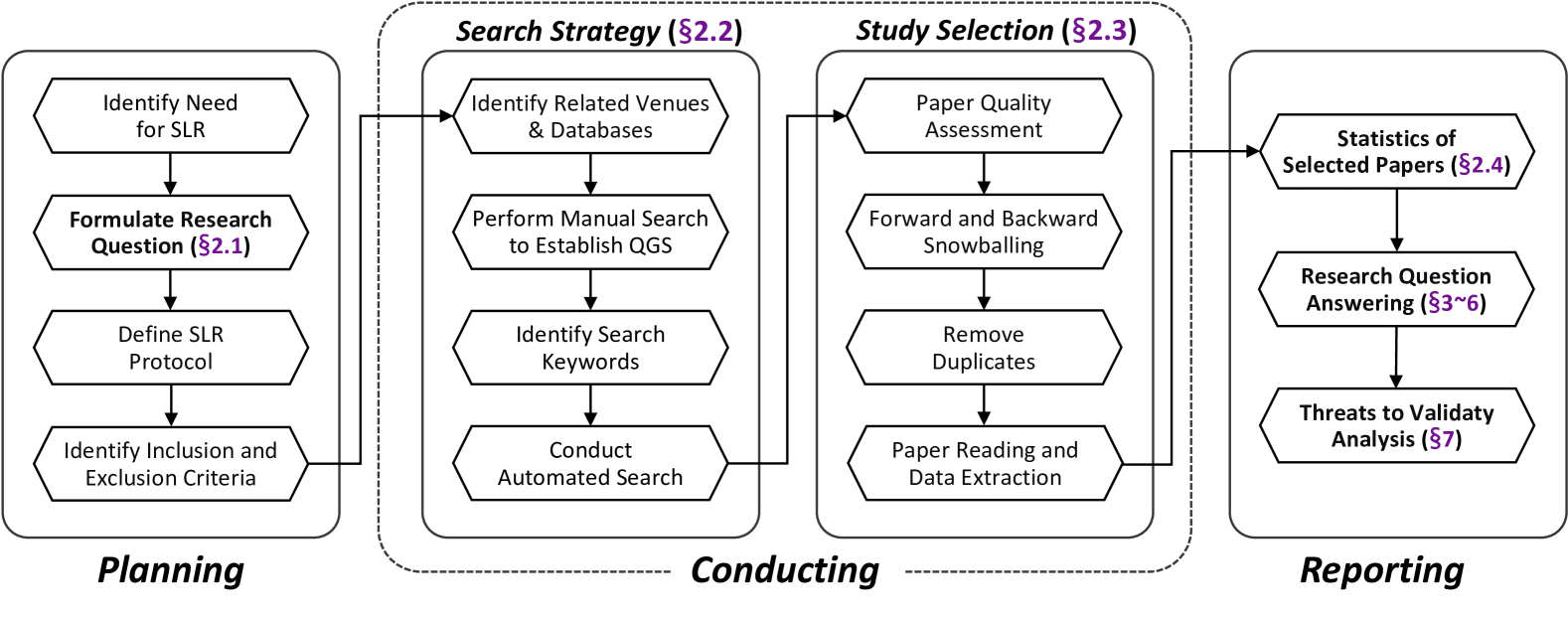
The paper presents a systematic literature review on the use of large language models (LLMs) in cybersecurity. The authors analyzed over 180 research works, spanning 25 LLMs and more than 10 downstream cybersecurity scenarios.
The review addresses three key research questions:
- How are cybersecurity-oriented LLMs constructed?
- What are the applications of LLMs in various cybersecurity tasks?
- What are the existing challenges and future research directions in this area?
To answer these questions, the authors conducted a comprehensive search and selection process, followed by a thorough analysis of the identified literature. They categorized the research works based on the specific cybersecurity tasks, such as vulnerability detection and repair, code generation and analysis, and cybercrime understanding.
The review also covers the various techniques used to adapt and fine-tune LLMs for cybersecurity applications, including pretraining on cybersecurity-related data and developing specialized architectures.
Additionally, the paper discusses the challenges and limitations of using LLMs in cybersecurity, such as the need for further research on robustness and security of these models, and the potential for adversarial attacks targeting LLMs.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive and valuable overview of the research on the application of LLMs in cybersecurity. The authors have conducted a thorough literature review and addressed the key aspects of this emerging field, including the construction of cybersecurity-oriented LLMs, their diverse applications, and the existing challenges.
One potential limitation of the review is that it may not capture the most recent developments in this rapidly evolving field, as the review period likely extended only up to the paper's publication. Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific technical details and performance metrics of the various LLM-based cybersecurity approaches, which could be of interest to more technical readers.
Furthermore, the paper could have benefited from a more critical analysis of the reviewed studies, highlighting potential biases, methodological limitations, or areas where further research is needed to validate the findings. This would have provided a more nuanced understanding of the current state of the field and the need for additional exploration.
Conclusion
This paper provides a comprehensive and valuable overview of the research on the application of large language models (LLMs) in the field of cybersecurity. By analyzing over 180 research works spanning various LLMs and cybersecurity scenarios, the authors have shed light on the extensive potential of LLMs in enhancing cybersecurity practices.
The review covers the construction of cybersecurity-oriented LLMs, their applications in diverse cybersecurity tasks, and the existing challenges and future research directions in this area. The authors also maintain a regularly updated list of practical guides on using LLMs for cybersecurity, making this paper a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners in the field.
As LLMs continue to advance and their capabilities expand, the insights and findings presented in this paper will be instrumental in guiding future research and development efforts to harness the power of these models for strengthening cybersecurity defenses against the ever-evolving threat landscape.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Large Language Models for Cyber Security: A Systematic Literature Review
HanXiang Xu, ShenAo Wang, NingKe Li, KaiLong Wang, YanJie Zhao, Kai Chen, Ting Yu, Yang Liu, HaoYu Wang

0
0
The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has opened up new opportunities for leveraging artificial intelligence in various domains, including cybersecurity. As the volume and sophistication of cyber threats continue to grow, there is an increasing need for intelligent systems that can automatically detect vulnerabilities, analyze malware, and respond to attacks. In this survey, we conduct a comprehensive review of the literature on the application of LLMs in cybersecurity (LLM4Security). By comprehensively collecting over 30K relevant papers and systematically analyzing 127 papers from top security and software engineering venues, we aim to provide a holistic view of how LLMs are being used to solve diverse problems across the cybersecurity domain. Through our analysis, we identify several key findings. First, we observe that LLMs are being applied to a wide range of cybersecurity tasks, including vulnerability detection, malware analysis, network intrusion detection, and phishing detection. Second, we find that the datasets used for training and evaluating LLMs in these tasks are often limited in size and diversity, highlighting the need for more comprehensive and representative datasets. Third, we identify several promising techniques for adapting LLMs to specific cybersecurity domains, such as fine-tuning, transfer learning, and domain-specific pre-training. Finally, we discuss the main challenges and opportunities for future research in LLM4Security, including the need for more interpretable and explainable models, the importance of addressing data privacy and security concerns, and the potential for leveraging LLMs for proactive defense and threat hunting. Overall, our survey provides a comprehensive overview of the current state-of-the-art in LLM4Security and identifies several promising directions for future research.
5/10/2024
🤖
Generative AI and Large Language Models for Cyber Security: All Insights You Need
Mohamed Amine Ferrag, Fatima Alwahedi, Ammar Battah, Bilel Cherif, Abdechakour Mechri, Norbert Tihanyi

0
0
This paper provides a comprehensive review of the future of cybersecurity through Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs). We explore LLM applications across various domains, including hardware design security, intrusion detection, software engineering, design verification, cyber threat intelligence, malware detection, and phishing detection. We present an overview of LLM evolution and its current state, focusing on advancements in models such as GPT-4, GPT-3.5, Mixtral-8x7B, BERT, Falcon2, and LLaMA. Our analysis extends to LLM vulnerabilities, such as prompt injection, insecure output handling, data poisoning, DDoS attacks, and adversarial instructions. We delve into mitigation strategies to protect these models, providing a comprehensive look at potential attack scenarios and prevention techniques. Furthermore, we evaluate the performance of 42 LLM models in cybersecurity knowledge and hardware security, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. We thoroughly evaluate cybersecurity datasets for LLM training and testing, covering the lifecycle from data creation to usage and identifying gaps for future research. In addition, we review new strategies for leveraging LLMs, including techniques like Half-Quadratic Quantization (HQQ), Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF), Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), Quantized Low-Rank Adapters (QLoRA), and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). These insights aim to enhance real-time cybersecurity defenses and improve the sophistication of LLM applications in threat detection and response. Our paper provides a foundational understanding and strategic direction for integrating LLMs into future cybersecurity frameworks, emphasizing innovation and robust model deployment to safeguard against evolving cyber threats.
5/22/2024
🏅
New!Psychological Profiling in Cybersecurity: A Look at LLMs and Psycholinguistic Features
Jean Marie Tshimula, D'Jeff K. Nkashama, Jean Tshibangu Muabila, Ren'e Manass'e Galekwa, Hugues Kanda, Maximilien V. Dialufuma, Mbuyi Mukendi Didier, Kalala Kalonji, Serge Mundele, Patience Kinshie Lenye, Tighana Wenge Basele, Aristarque Ilunga, Christian N. Mayemba, Nathanael M. Kasoro, Selain K. Kasereka, Hardy Mikese, Pierre-Martin Tardif, Marc Frappier, Froduald Kabanza, Belkacem Chikhaoui, Shengrui Wang, Ali Mulenda Sumbu, Xavier Ndona, Raoul Kienge-Kienge Intudi

0
0
The increasing sophistication of cyber threats necessitates innovative approaches to cybersecurity. In this paper, we explore the potential of psychological profiling techniques, particularly focusing on the utilization of Large Language Models (LLMs) and psycholinguistic features. We investigate the intersection of psychology and cybersecurity, discussing how LLMs can be employed to analyze textual data for identifying psychological traits of threat actors. We explore the incorporation of psycholinguistic features, such as linguistic patterns and emotional cues, into cybersecurity frameworks. iffalse Through case studies and experiments, we discuss the effectiveness of these methods in enhancing threat detection and mitigation strategies.fi Our research underscores the importance of integrating psychological perspectives into cybersecurity practices to bolster defense mechanisms against evolving threats.
6/28/2024
A Reality check of the benefits of LLM in business
Ming Cheung

0
0
Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable performance in language understanding and generation tasks by leveraging vast amounts of online texts. Unlike conventional models, LLMs can adapt to new domains through prompt engineering without the need for retraining, making them suitable for various business functions, such as strategic planning, project implementation, and data-driven decision-making. However, their limitations in terms of bias, contextual understanding, and sensitivity to prompts raise concerns about their readiness for real-world applications. This paper thoroughly examines the usefulness and readiness of LLMs for business processes. The limitations and capacities of LLMs are evaluated through experiments conducted on four accessible LLMs using real-world data. The findings have significant implications for organizations seeking to leverage generative AI and provide valuable insights into future research directions. To the best of our knowledge, this represents the first quantified study of LLMs applied to core business operations and challenges.
6/18/2024