Large Language User Interfaces: Voice Interactive User Interfaces powered by LLMs
2402.07938

0
0

Abstract
The evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) has showcased remarkable capacities for logical reasoning and natural language comprehension. These capabilities can be leveraged in solutions that semantically and textually model complex problems. In this paper, we present our efforts toward constructing a framework that can serve as an intermediary between a user and their user interface (UI), enabling dynamic and real-time interactions. We employ a system that stands upon textual semantic mappings of UI components, in the form of annotations. These mappings are stored, parsed, and scaled in a custom data structure, supplementary to an agent-based prompting backend engine. Employing textual semantic mappings allows each component to not only explain its role to the engine but also provide expectations. By comprehending the needs of both the user and the components, our LLM engine can classify the most appropriate application, extract relevant parameters, and subsequently execute precise predictions of the user's expected actions. Such an integration evolves static user interfaces into highly dynamic and adaptable solutions, introducing a new frontier of intelligent and responsive user experiences.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Introduction
This paper explores the potential of using large language models (LLMs) to power voice-based user interfaces. The researchers investigate how LLMs can be leveraged to create interactive, natural language-driven experiences that go beyond traditional speech recognition and synthesis. The authors examine the motivations and challenges of this approach, as well as the technical details and potential applications.
Motivations of the Research
The researchers are motivated by the rapid advancements in LLMs and their ability to understand and generate human-like language. They believe that by integrating LLMs into voice-based interfaces, users can engage in more natural, conversational interactions, expanding the capabilities of traditional speech-based systems. This could lead to more intuitive and accessible interfaces for a wide range of applications, from virtual assistants to educational tools.
Challenges
The paper acknowledges several key challenges in developing voice-based interfaces powered by LLMs. These include issues related to natural language understanding, contextual awareness, multimodal integration, and ensuring safe and ethical deployment. The researchers highlight the need for careful design and testing to address these challenges and deliver reliable and trustworthy voice-based experiences.
Technical Explanation
The authors present a system architecture that leverages LLMs to enable voice-based interactions. This involves integrating speech recognition, language understanding, and language generation components to create a seamless conversational experience. The paper also discusses techniques for incorporating multimodal data, such as visual information, to enhance the user experience.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thoughtful analysis of the potential and limitations of using LLMs for voice-based interfaces. While the researchers highlight the promise of this approach, they also acknowledge the need for further research and development to address challenges related to robustness, safety, and ethical considerations. Ongoing work in areas such as VoicePilot, LAMI, and ComuniQA may help to address some of these challenges.
Conclusion
The paper presents a compelling vision for voice-based user interfaces powered by large language models. By harnessing the capabilities of LLMs, the researchers aim to create more natural, conversational, and multimodal experiences that could revolutionize how users interact with technology. While significant challenges remain, the insights and directions outlined in this work contribute to the ongoing exploration of autonomous agents through the lens of large language models and the potential of using LLMs to advance research.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
LaMI: Large Language Models for Multi-Modal Human-Robot Interaction
Chao Wang, Stephan Hasler, Daniel Tanneberg, Felix Ocker, Frank Joublin, Antonello Ceravola, Joerg Deigmoeller, Michael Gienger

0
0
This paper presents an innovative large language model (LLM)-based robotic system for enhancing multi-modal human-robot interaction (HRI). Traditional HRI systems relied on complex designs for intent estimation, reasoning, and behavior generation, which were resource-intensive. In contrast, our system empowers researchers and practitioners to regulate robot behavior through three key aspects: providing high-level linguistic guidance, creating atomic actions and expressions the robot can use, and offering a set of examples. Implemented on a physical robot, it demonstrates proficiency in adapting to multi-modal inputs and determining the appropriate manner of action to assist humans with its arms, following researchers' defined guidelines. Simultaneously, it coordinates the robot's lid, neck, and ear movements with speech output to produce dynamic, multi-modal expressions. This showcases the system's potential to revolutionize HRI by shifting from conventional, manual state-and-flow design methods to an intuitive, guidance-based, and example-driven approach. Supplementary material can be found at https://hri-eu.github.io/Lami/
4/12/2024
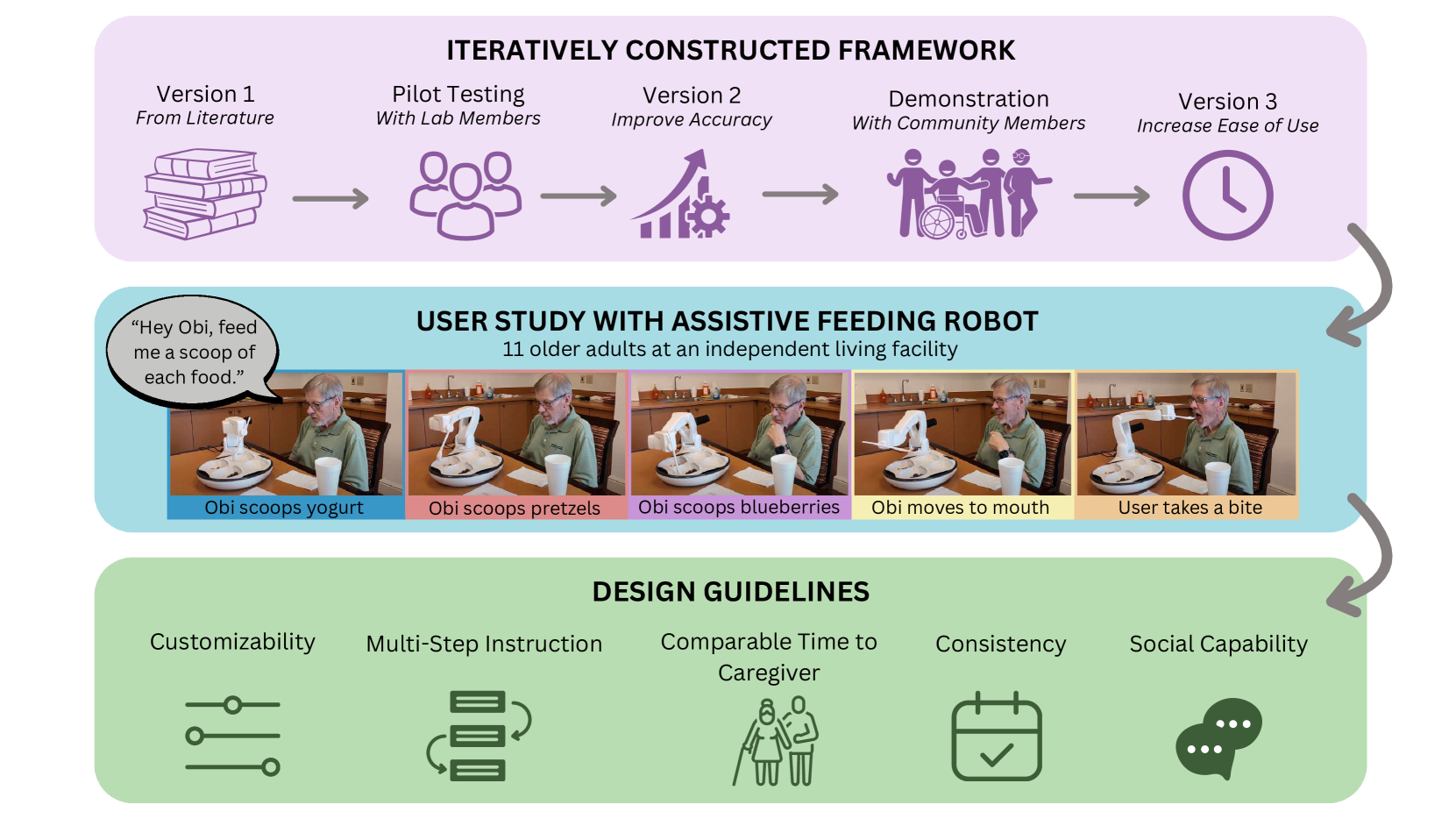
VoicePilot: Harnessing LLMs as Speech Interfaces for Physically Assistive Robots
Akhil Padmanabha, Jessie Yuan, Janavi Gupta, Zulekha Karachiwalla, Carmel Majidi, Henny Admoni, Zackory Erickson

0
0
Physically assistive robots present an opportunity to significantly increase the well-being and independence of individuals with motor impairments or other forms of disability who are unable to complete activities of daily living. Speech interfaces, especially ones that utilize Large Language Models (LLMs), can enable individuals to effectively and naturally communicate high-level commands and nuanced preferences to robots. Frameworks for integrating LLMs as interfaces to robots for high level task planning and code generation have been proposed, but fail to incorporate human-centric considerations which are essential while developing assistive interfaces. In this work, we present a framework for incorporating LLMs as speech interfaces for physically assistive robots, constructed iteratively with 3 stages of testing involving a feeding robot, culminating in an evaluation with 11 older adults at an independent living facility. We use both quantitative and qualitative data from the final study to validate our framework and additionally provide design guidelines for using LLMs as speech interfaces for assistive robots. Videos and supporting files are located on our project website: https://sites.google.com/andrew.cmu.edu/voicepilot/
4/8/2024
Exploring Autonomous Agents through the Lens of Large Language Models: A Review
Saikat Barua

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming artificial intelligence, enabling autonomous agents to perform diverse tasks across various domains. These agents, proficient in human-like text comprehension and generation, have the potential to revolutionize sectors from customer service to healthcare. However, they face challenges such as multimodality, human value alignment, hallucinations, and evaluation. Techniques like prompting, reasoning, tool utilization, and in-context learning are being explored to enhance their capabilities. Evaluation platforms like AgentBench, WebArena, and ToolLLM provide robust methods for assessing these agents in complex scenarios. These advancements are leading to the development of more resilient and capable autonomous agents, anticipated to become integral in our digital lives, assisting in tasks from email responses to disease diagnosis. The future of AI, with LLMs at the forefront, is promising.
4/9/2024
🤖
Predicting the usability of mobile applications using AI tools: the rise of large user interface models, opportunities, and challenges
Abdallah Namoun, Ahmed Alrehaili, Zaib Un Nisa, Hani Almoamari, Ali Tufail

0
0
This article proposes the so-called large user interface models (LUIMs) to enable the generation of user interfaces and prediction of usability using artificial intelligence in the context of mobile applications.
5/8/2024