LaMI: Large Language Models for Multi-Modal Human-Robot Interaction
2401.15174

0
0
Abstract
This paper presents an innovative large language model (LLM)-based robotic system for enhancing multi-modal human-robot interaction (HRI). Traditional HRI systems relied on complex designs for intent estimation, reasoning, and behavior generation, which were resource-intensive. In contrast, our system empowers researchers and practitioners to regulate robot behavior through three key aspects: providing high-level linguistic guidance, creating atomic actions and expressions the robot can use, and offering a set of examples. Implemented on a physical robot, it demonstrates proficiency in adapting to multi-modal inputs and determining the appropriate manner of action to assist humans with its arms, following researchers' defined guidelines. Simultaneously, it coordinates the robot's lid, neck, and ear movements with speech output to produce dynamic, multi-modal expressions. This showcases the system's potential to revolutionize HRI by shifting from conventional, manual state-and-flow design methods to an intuitive, guidance-based, and example-driven approach. Supplementary material can be found at https://hri-eu.github.io/Lami/
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper explores the use of large language models (LLMs) as a foundation for building speech interfaces and enabling better human-computer interaction.
- The researchers investigate how LLMs can be leveraged to facilitate voice-based control and interaction with physical systems, such as robots.
- The paper also reviews the potential of multi-modal LLMs that can process and generate speech, text, and other modalities like images and videos.
- Additionally, the research examines how LLMs can be used to orchestrate the actions of bimanual (two-armed) robots for complex manipulation tasks.
- The paper discusses the implications of using LLMs for long-horizon locomotion and manipulation tasks with quadrupedal (four-legged) robots.
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores how large language models (LLMs) can be used to build better speech interfaces and enable more natural human-computer interaction. The researchers investigate using LLMs as the foundation for voice-based control and interaction with physical systems, like robots.
The paper also looks at multi-modal LLMs that can process and generate speech, text, images, and videos. This could allow for more seamless and intuitive interactions with computers and robots.
Additionally, the research examines how LLMs can be used to coordinate the actions of two-armed (bimanual) robots to perform complex manipulation tasks. The paper also discusses using LLMs for long-horizon locomotion and manipulation tasks with four-legged (quadrupedal) robots.
Overall, the paper explores how advances in LLM technology can enable more natural and capable speech interfaces, as well as more sophisticated control and coordination of physical systems like robots.
Technical Explanation
The paper investigates the use of large language models (LLMs) as a foundation for building speech interfaces and facilitating better human-computer interaction. The researchers explore how LLMs can be leveraged to enable voice-based control and interaction with physical systems, such as robots.
The paper also examines the potential of multi-modal LLMs that can process and generate speech, text, images, and videos. This could enable more seamless and intuitive interactions with computers and robots, as the models can understand and respond to different types of input and output.
Additionally, the research investigates how LLMs can be used to orchestrate the actions of two-armed (bimanual) robots for complex manipulation tasks. The paper also discusses the implications of using LLMs for long-horizon locomotion and manipulation tasks with four-legged (quadrupedal) robots.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive overview of the potential applications of LLMs in enabling more natural and capable speech interfaces, as well as for controlling and coordinating physical systems like robots. However, the researchers acknowledge some caveats and limitations of the current approaches.
One potential issue is the reliance on large, pre-trained language models, which can be resource-intensive and have high computational requirements. This may limit the deployment of such systems in resource-constrained environments, such as on-device applications or embedded systems.
The paper also notes that the integration of LLMs with physical systems, such as robots, presents challenges in terms of ensuring safe and reliable operation, especially in complex, real-world scenarios. Further research may be needed to address these challenges and enable the seamless deployment of LLM-powered speech interfaces and robot control systems.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the ethical considerations and potential societal implications of widespread deployment of LLM-based technologies, such as privacy concerns, bias, and transparency issues. These are important aspects that warrant further exploration and discussion.
Conclusion
This paper presents a compelling vision for the use of large language models (LLMs) as a foundation for building more natural and capable speech interfaces, as well as for enabling more sophisticated control and coordination of physical systems like robots.
The researchers demonstrate the potential of LLMs to facilitate voice-based interaction, process multi-modal input and output, and orchestrate the actions of complex robotic systems. This could lead to significant advancements in human-computer interaction and the development of more intelligent and adaptable physical systems.
However, the paper also highlights the need to address challenges related to computational requirements, safety, and ethical considerations. Continued research and development in these areas will be crucial to unlocking the full potential of LLM-powered technologies and ensuring their responsible and beneficial deployment.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
Large Language Models for Human-Robot Interaction: Opportunities and Risks
Jesse Atuhurra

0
0
The tremendous development in large language models (LLM) has led to a new wave of innovations and applications and yielded research results that were initially forecast to take longer. In this work, we tap into these recent developments and present a meta-study about the potential of large language models if deployed in social robots. We place particular emphasis on the applications of social robots: education, healthcare, and entertainment. Before being deployed in social robots, we also study how these language models could be safely trained to ``understand'' societal norms and issues, such as trust, bias, ethics, cognition, and teamwork. We hope this study provides a resourceful guide to other robotics researchers interested in incorporating language models in their robots.
5/3/2024
💬
A Survey on Integration of Large Language Models with Intelligent Robots
Yeseung Kim, Dohyun Kim, Jieun Choi, Jisang Park, Nayoung Oh, Daehyung Park

0
0
In recent years, the integration of large language models (LLMs) has revolutionized the field of robotics, enabling robots to communicate, understand, and reason with human-like proficiency. This paper explores the multifaceted impact of LLMs on robotics, addressing key challenges and opportunities for leveraging these models across various domains. By categorizing and analyzing LLM applications within core robotics elements -- communication, perception, planning, and control -- we aim to provide actionable insights for researchers seeking to integrate LLMs into their robotic systems. Our investigation focuses on LLMs developed post-GPT-3.5, primarily in text-based modalities while also considering multimodal approaches for perception and control. We offer comprehensive guidelines and examples for prompt engineering, facilitating beginners' access to LLM-based robotics solutions. Through tutorial-level examples and structured prompt construction, we illustrate how LLM-guided enhancements can be seamlessly integrated into robotics applications. This survey serves as a roadmap for researchers navigating the evolving landscape of LLM-driven robotics, offering a comprehensive overview and practical guidance for harnessing the power of language models in robotics development.
4/16/2024
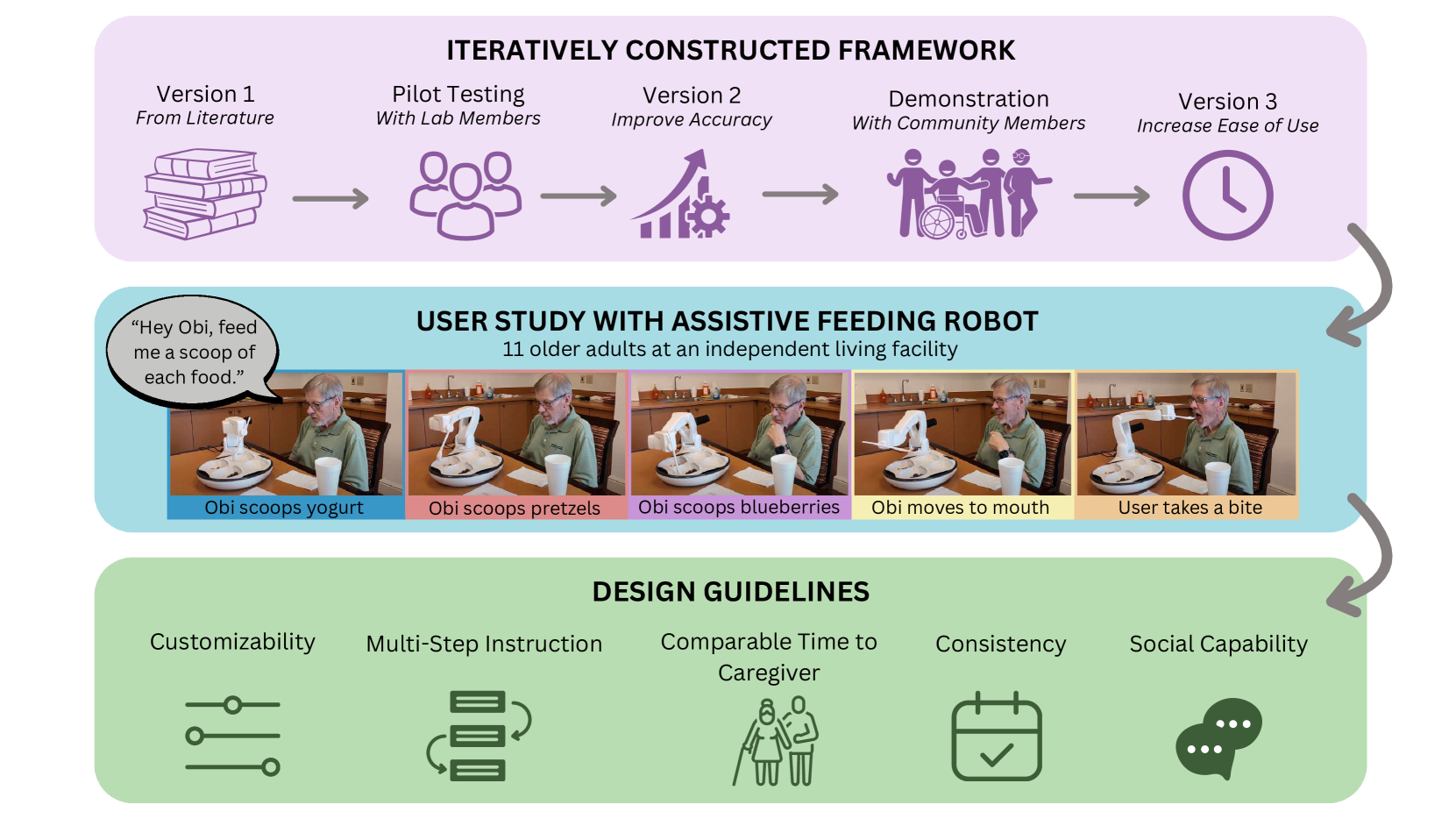
VoicePilot: Harnessing LLMs as Speech Interfaces for Physically Assistive Robots
Akhil Padmanabha, Jessie Yuan, Janavi Gupta, Zulekha Karachiwalla, Carmel Majidi, Henny Admoni, Zackory Erickson

0
0
Physically assistive robots present an opportunity to significantly increase the well-being and independence of individuals with motor impairments or other forms of disability who are unable to complete activities of daily living. Speech interfaces, especially ones that utilize Large Language Models (LLMs), can enable individuals to effectively and naturally communicate high-level commands and nuanced preferences to robots. Frameworks for integrating LLMs as interfaces to robots for high level task planning and code generation have been proposed, but fail to incorporate human-centric considerations which are essential while developing assistive interfaces. In this work, we present a framework for incorporating LLMs as speech interfaces for physically assistive robots, constructed iteratively with 3 stages of testing involving a feeding robot, culminating in an evaluation with 11 older adults at an independent living facility. We use both quantitative and qualitative data from the final study to validate our framework and additionally provide design guidelines for using LLMs as speech interfaces for assistive robots. Videos and supporting files are located on our project website: https://sites.google.com/andrew.cmu.edu/voicepilot/
4/8/2024
🌿
New!Incremental Learning of Humanoid Robot Behavior from Natural Interaction and Large Language Models
Leonard Barmann, Rainer Kartmann, Fabian Peller-Konrad, Jan Niehues, Alex Waibel, Tamim Asfour

0
0
Natural-language dialog is key for intuitive human-robot interaction. It can be used not only to express humans' intents, but also to communicate instructions for improvement if a robot does not understand a command correctly. Of great importance is to endow robots with the ability to learn from such interaction experience in an incremental way to allow them to improve their behaviors or avoid mistakes in the future. In this paper, we propose a system to achieve incremental learning of complex behavior from natural interaction, and demonstrate its implementation on a humanoid robot. Building on recent advances, we present a system that deploys Large Language Models (LLMs) for high-level orchestration of the robot's behavior, based on the idea of enabling the LLM to generate Python statements in an interactive console to invoke both robot perception and action. The interaction loop is closed by feeding back human instructions, environment observations, and execution results to the LLM, thus informing the generation of the next statement. Specifically, we introduce incremental prompt learning, which enables the system to interactively learn from its mistakes. For that purpose, the LLM can call another LLM responsible for code-level improvements of the current interaction based on human feedback. The improved interaction is then saved in the robot's memory, and thus retrieved on similar requests. We integrate the system in the robot cognitive architecture of the humanoid robot ARMAR-6 and evaluate our methods both quantitatively (in simulation) and qualitatively (in simulation and real-world) by demonstrating generalized incrementally-learned knowledge.
5/17/2024