VoicePilot: Harnessing LLMs as Speech Interfaces for Physically Assistive Robots
2404.04066

0
0
Abstract
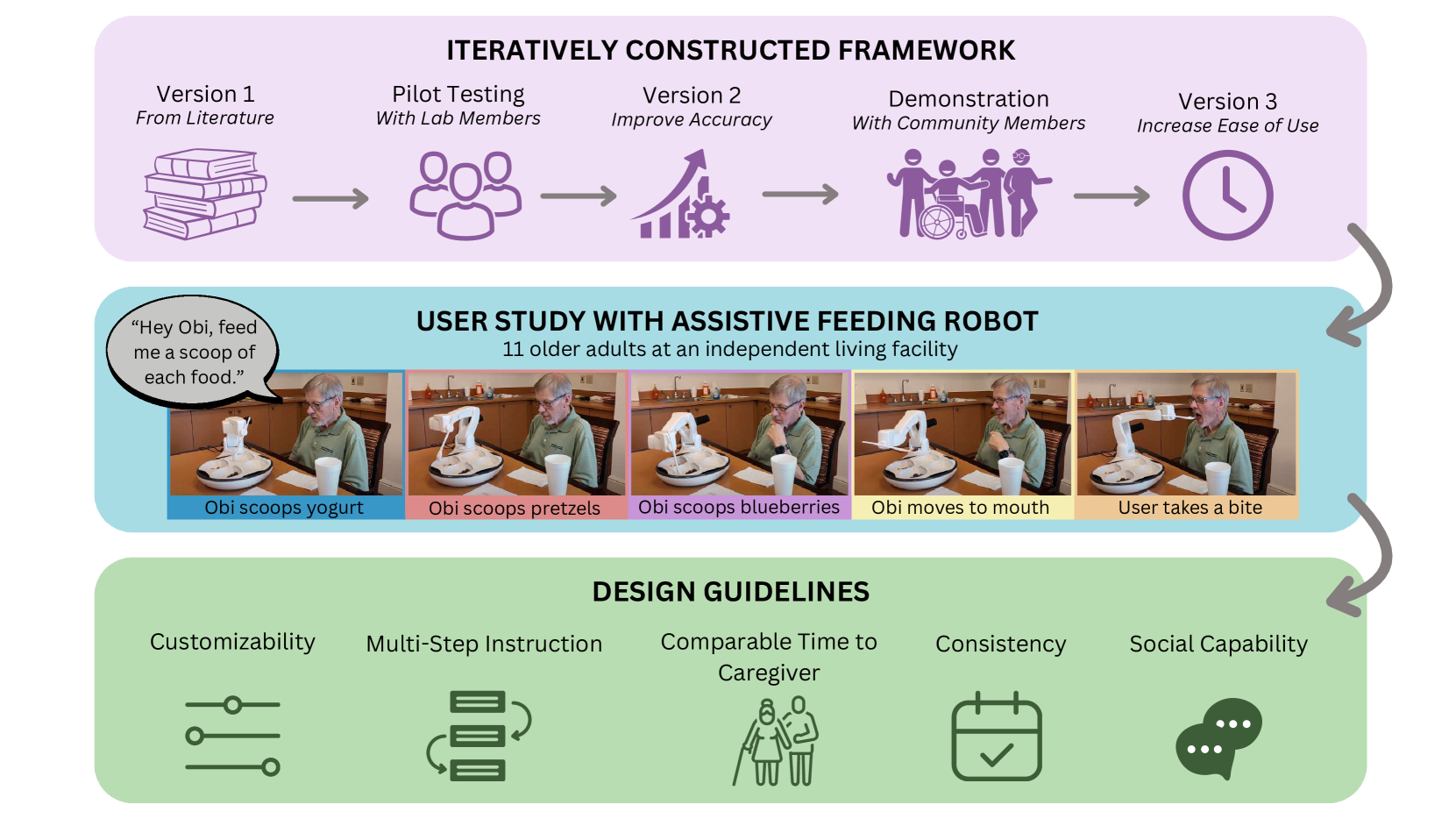
Physically assistive robots present an opportunity to significantly increase the well-being and independence of individuals with motor impairments or other forms of disability who are unable to complete activities of daily living. Speech interfaces, especially ones that utilize Large Language Models (LLMs), can enable individuals to effectively and naturally communicate high-level commands and nuanced preferences to robots. Frameworks for integrating LLMs as interfaces to robots for high level task planning and code generation have been proposed, but fail to incorporate human-centric considerations which are essential while developing assistive interfaces. In this work, we present a framework for incorporating LLMs as speech interfaces for physically assistive robots, constructed iteratively with 3 stages of testing involving a feeding robot, culminating in an evaluation with 11 older adults at an independent living facility. We use both quantitative and qualitative data from the final study to validate our framework and additionally provide design guidelines for using LLMs as speech interfaces for assistive robots. Videos and supporting files are located on our project website: https://sites.google.com/andrew.cmu.edu/voicepilot/
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper introduces VoicePilot, a system that leverages large language models (LLMs) to enable speech-based control of physically assistive robots.
- The researchers developed a framework that integrates LLMs with robot control systems, allowing users to issue voice commands to control the robot's movements and actions.
- The goal is to improve accessibility and usability of physically assistive robots for individuals with limited mobility or dexterity.
Plain English Explanation
The paper discusses a new system called VoicePilot that uses advanced language AI, known as large language models (LLMs), to allow people to control physical robots just by speaking to them. This could make it much easier for people with disabilities or limited mobility to use assistive robots to help with everyday tasks.
Traditionally, controlling robots has required complex programming or specialized controllers. But by tapping into the power of LLMs, which are trained on massive amounts of natural language data, VoicePilot enables users to simply speak instructions and have the robot understand and execute them. This could open up the use of assistive robots to a much wider audience.
The researchers developed a framework that seamlessly integrates the LLM speech recognition and natural language processing capabilities with the robot's control systems. This allows the robot to respond directly to voice commands, rather than requiring the user to use a separate interface.
The goal of VoicePilot is to enhance the accessibility and usability of physically assistive robots, empowering those with limited mobility or dexterity to more easily leverage the capabilities of such robotic systems to improve their independence and quality of life.
Technical Explanation
The core of the VoicePilot system is the integration of a large language model (LLM) with the robot control system. The researchers used a state-of-the-art LLM [<a href="https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/integrating-large-language-models-multimodal-virtual-reality">1</a>] to enable robust speech recognition and natural language understanding. This LLM was then connected to the robot's actuation and navigation modules, allowing voice commands to directly control the robot's movements and actions.
To evaluate the effectiveness of VoicePilot, the researchers conducted experiments in which participants with various mobility impairments used the system to control a physically assistive robot. The results showed significant improvements in the users' ability to command the robot and complete tasks compared to traditional control interfaces [<a href="https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/survey-large-language-model-based-autonomous-agents">2</a>], [<a href="https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/large-language-models-orchestrating-bimanual-robots">3</a>].
The VoicePilot framework also demonstrated the ability to handle complex, multi-step instructions, going beyond simple single-action commands [<a href="https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/dialogbench-evaluating-llms-as-human-like-dialogue">4</a>]. This highlights the potential of LLMs to enable more natural, conversational control of assistive robots [<a href="https://aimodels.fyi/papers/arxiv/comuniqa-exploring-large-language-models-improving-speaking">5</a>].
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge that VoicePilot is a prototype system and that further development and testing is needed to fully realize its potential. Integrating LLMs with physical robot systems introduces several technical challenges, such as ensuring reliable and low-latency responses, maintaining safety and security, and handling diverse user preferences and abilities.
Additionally, the evaluation in the paper was limited to a relatively small number of participants, and it would be important to conduct larger-scale studies to better understand the system's performance and usability across a more diverse user population.
While the results are promising, the researchers also note that social and ethical considerations around the use of such speech-controlled robot systems will need to be carefully addressed, particularly around issues of privacy, autonomy, and potential displacement of human caregivers.
Conclusion
The VoicePilot system demonstrates the exciting potential of leveraging large language models to enhance the accessibility and usability of physically assistive robots. By enabling natural, voice-based control, the researchers have taken an important step towards making these technologies more widely available and empowering for individuals with limited mobility.
As the field of robotics and AI continues to advance, it will be crucial to consider not just the technical capabilities, but also the societal impact and ethical implications of these systems. The VoicePilot project highlights the importance of designing assistive technologies that prioritize user needs, autonomy, and inclusive accessibility.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
LaMI: Large Language Models for Multi-Modal Human-Robot Interaction
Chao Wang, Stephan Hasler, Daniel Tanneberg, Felix Ocker, Frank Joublin, Antonello Ceravola, Joerg Deigmoeller, Michael Gienger

0
0
This paper presents an innovative large language model (LLM)-based robotic system for enhancing multi-modal human-robot interaction (HRI). Traditional HRI systems relied on complex designs for intent estimation, reasoning, and behavior generation, which were resource-intensive. In contrast, our system empowers researchers and practitioners to regulate robot behavior through three key aspects: providing high-level linguistic guidance, creating atomic actions and expressions the robot can use, and offering a set of examples. Implemented on a physical robot, it demonstrates proficiency in adapting to multi-modal inputs and determining the appropriate manner of action to assist humans with its arms, following researchers' defined guidelines. Simultaneously, it coordinates the robot's lid, neck, and ear movements with speech output to produce dynamic, multi-modal expressions. This showcases the system's potential to revolutionize HRI by shifting from conventional, manual state-and-flow design methods to an intuitive, guidance-based, and example-driven approach. Supplementary material can be found at https://hri-eu.github.io/Lami/
4/12/2024

Large Language User Interfaces: Voice Interactive User Interfaces powered by LLMs
Syed Mekael Wasti, Ken Q. Pu, Ali Neshati

0
0
The evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) has showcased remarkable capacities for logical reasoning and natural language comprehension. These capabilities can be leveraged in solutions that semantically and textually model complex problems. In this paper, we present our efforts toward constructing a framework that can serve as an intermediary between a user and their user interface (UI), enabling dynamic and real-time interactions. We employ a system that stands upon textual semantic mappings of UI components, in the form of annotations. These mappings are stored, parsed, and scaled in a custom data structure, supplementary to an agent-based prompting backend engine. Employing textual semantic mappings allows each component to not only explain its role to the engine but also provide expectations. By comprehending the needs of both the user and the components, our LLM engine can classify the most appropriate application, extract relevant parameters, and subsequently execute precise predictions of the user's expected actions. Such an integration evolves static user interfaces into highly dynamic and adaptable solutions, introducing a new frontier of intelligent and responsive user experiences.
4/17/2024
💬
A Survey on Integration of Large Language Models with Intelligent Robots
Yeseung Kim, Dohyun Kim, Jieun Choi, Jisang Park, Nayoung Oh, Daehyung Park

0
0
In recent years, the integration of large language models (LLMs) has revolutionized the field of robotics, enabling robots to communicate, understand, and reason with human-like proficiency. This paper explores the multifaceted impact of LLMs on robotics, addressing key challenges and opportunities for leveraging these models across various domains. By categorizing and analyzing LLM applications within core robotics elements -- communication, perception, planning, and control -- we aim to provide actionable insights for researchers seeking to integrate LLMs into their robotic systems. Our investigation focuses on LLMs developed post-GPT-3.5, primarily in text-based modalities while also considering multimodal approaches for perception and control. We offer comprehensive guidelines and examples for prompt engineering, facilitating beginners' access to LLM-based robotics solutions. Through tutorial-level examples and structured prompt construction, we illustrate how LLM-guided enhancements can be seamlessly integrated into robotics applications. This survey serves as a roadmap for researchers navigating the evolving landscape of LLM-driven robotics, offering a comprehensive overview and practical guidance for harnessing the power of language models in robotics development.
4/16/2024
💬
How Can Large Language Models Enable Better Socially Assistive Human-Robot Interaction: A Brief Survey
Zhonghao Shi, Ellen Landrum, Amy O' Connell, Mina Kian, Leticia Pinto-Alva, Kaleen Shrestha, Xiaoyuan Zhu, Maja J Matari'c

0
0
Socially assistive robots (SARs) have shown great success in providing personalized cognitive-affective support for user populations with special needs such as older adults, children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and individuals with mental health challenges. The large body of work on SAR demonstrates its potential to provide at-home support that complements clinic-based interventions delivered by mental health professionals, making these interventions more effective and accessible. However, there are still several major technical challenges that hinder SAR-mediated interactions and interventions from reaching human-level social intelligence and efficacy. With the recent advances in large language models (LLMs), there is an increased potential for novel applications within the field of SAR that can significantly expand the current capabilities of SARs. However, incorporating LLMs introduces new risks and ethical concerns that have not yet been encountered, and must be carefully be addressed to safely deploy these more advanced systems. In this work, we aim to conduct a brief survey on the use of LLMs in SAR technologies, and discuss the potentials and risks of applying LLMs to the following three major technical challenges of SAR: 1) natural language dialog; 2) multimodal understanding; 3) LLMs as robot policies.
4/9/2024