LLM-SAP: Large Language Models Situational Awareness Based Planning

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
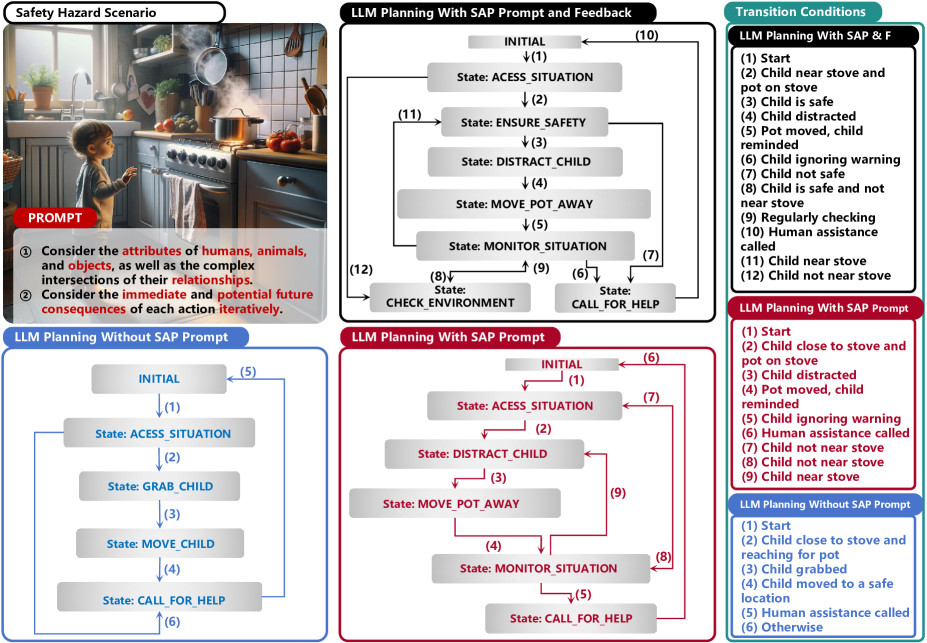
- This paper explores the use of large language models (LLMs) for situational awareness-based planning in various applications.
- The researchers investigate how LLMs can be leveraged to enhance planning capabilities, particularly in complex, dynamic environments.
- Key focus areas include task formulation, architectural design, and evaluation of LLM-based planning techniques.
Plain English Explanation
Large language models (LLMs) are powerful AI systems that can understand and generate human-like text. In this paper, the researchers explore how LLMs can be used to improve planning and decision-making, especially in complex real-world scenarios.
What's Plan? Evaluating and Developing Planning-Aware Techniques and CPS-LLM: Large Language Model-Based Safe and Reliable Cyber-Physical Systems have also looked at using LLMs for planning and decision-making in various contexts.
The researchers in this paper focus on leveraging LLMs' ability to understand context and situation to enhance planning capabilities. For example, an LLM could analyze the current state of a complex environment, such as a city, and use that understanding to plan more effective actions. This could be useful in applications like Autonomous Urban Activity Planning and Management with Large Language Models or Exploring Autonomous Agents through the Lens of Large Language Models.
By incorporating situational awareness into the planning process, the researchers aim to develop more flexible, adaptable, and intelligent planning systems that can better handle the uncertainties and complexities of real-world environments.
Technical Explanation
The paper begins by formulating the task of situational awareness-based planning and outlining key challenges, such as how to effectively capture and represent contextual information, and how to integrate this understanding into the planning process.
The researchers then propose a novel architectural design that leverages LLMs to address these challenges. The core idea is to use an LLM to first build a rich representation of the current situation, drawing on its deep understanding of language and context. This situational awareness is then used to inform and guide the planning process, helping the system make more informed and appropriate decisions.
The paper also describes various evaluation approaches to assess the performance of the LLM-based planning system, including both simulated and real-world experiments. The researchers analyze the system's ability to generate effective plans, adapt to changing circumstances, and handle complex, ambiguous situations.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a compelling approach to incorporating situational awareness into planning systems using large language models. By leveraging the contextual understanding of LLMs, the researchers demonstrate the potential for more flexible and adaptive planning capabilities, which could be valuable in a wide range of applications, from Autonomous Urban Activity Planning and Management with Large Language Models to Exploring Autonomous Agents through the Lens of Large Language Models.
However, the paper also acknowledges several limitations and areas for further research. For example, the researchers note the need to address potential biases and inconsistencies in LLM outputs, as well as the challenge of scaling the approach to handle extremely complex, real-world environments. Additionally, the paper suggests exploring ways to further improve the integration of situational awareness and planning, potentially through the development of more sophisticated architectures or learning algorithms.
Overall, the research represents an important step forward in the field of AI-based planning, and the findings could have significant implications for the development of more intelligent and adaptive decision-making systems, as highlighted in Large Language Models for Synthetic Participatory Planning and Synergistic Urbanism.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel approach to incorporating situational awareness into planning systems using large language models. By leveraging the contextual understanding of LLMs, the researchers demonstrate the potential for more flexible and adaptive planning capabilities, which could have far-reaching implications for a wide range of applications, from autonomous decision-making to urban planning and management.
While the research has some limitations and areas for further exploration, the findings represent an important step forward in the development of more intelligent and adaptable planning systems. As LLMs continue to advance and become more widely integrated into various domains, the insights and techniques outlined in this paper could pave the way for a new generation of planning-aware technologies that can better handle the complexities and uncertainties of the real world.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!