Low-Latency Video Conferencing via Optimized Packet Routing and Reordering

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents a low-latency video conferencing system designed for geo-distributed data centers.
- The system leverages optimized packet scheduling and cross-layer quality optimization to minimize end-to-end latency and provide high-quality video experiences.
- Key features include efficient data transmission, intelligent routing, and digital twin-based data processing.
Plain English Explanation
The paper describes a new video conferencing system that is designed to work well in situations where the people participating in the call are located in different geographic areas, with the video and audio data being processed in distributed data centers. The main goal of the system is to minimize the delay or "latency" that users experience, so that the video and audio feel smooth and responsive, even when the participants are far apart.
To achieve this, the system uses a technique called "packet scheduling" to carefully manage the flow of video and audio data, optimizing it to reduce delays. It also employs cross-layer quality optimization to ensure the video and audio quality remains high, even as it minimizes latency.
Other key features of the system include efficient data transmission, intelligent routing, and digital twin-based data processing. These techniques work together to create a video conferencing system that can provide a high-quality, low-latency experience, even when the participants are distributed across different geographic regions.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a low-latency video conferencing system designed for geo-distributed data centers. The system leverages several key techniques to minimize end-to-end latency and optimize video quality:
-
Tile-weighted rate-distortion optimized packet scheduling: The system uses a packet scheduling algorithm that prioritizes the most important video tiles, ensuring the most critical visual information is delivered first.
-
Quality-experience oriented cross-layer optimization: The system jointly optimizes multiple layers of the network stack, including video encoding, transport, and playout, to provide the best overall quality of experience for users.
-
Efficient data transmission: The system utilizes techniques like adaptive bit rate adjustment and intelligent bandwidth management to ensure data is transmitted efficiently across the geo-distributed network.
-
Intelligent routing: The system employs routing algorithms that consider factors like network load and workload interference to minimize latency and optimize data flow.
-
Efficient digital twin-based data processing: The system leverages digital twin models to enable low-latency data processing at the edge, reducing the need for data to travel long distances to centralized data centers.
Through the combination of these techniques, the proposed video conferencing system is able to provide a high-quality, low-latency experience for users, even in the context of geo-distributed data centers.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a comprehensive approach to addressing the challenges of low-latency video conferencing in geo-distributed environments. The authors have clearly identified the key pain points, such as network latency, bandwidth constraints, and workload interference, and have designed a system that effectively mitigates these issues.
One potential limitation of the research is the lack of detailed evaluation of the system's performance in real-world scenarios. While the authors have provided simulation-based results, it would be beneficial to see how the system performs in actual deployments, especially in terms of scalability and robustness to various network conditions and user loads.
Additionally, the paper could have explored the potential trade-offs between latency optimization and other quality-of-service metrics, such as video resolution or frame rate. It would be interesting to understand how the system's performance and resource utilization might change when prioritizing different aspects of the user experience.
Further research could also investigate the applicability of the proposed techniques to other real-time communication services, such as online gaming or remote healthcare, where low-latency is equally critical. Exploring the dynamics of data transmission in 5G networks and studying workload interference in intelligent routing could provide valuable insights in this direction.
Conclusion
The paper presents a innovative video conferencing system designed for geo-distributed data centers. By leveraging techniques like optimized packet scheduling, cross-layer quality optimization, and efficient digital twin-based data processing, the system is able to provide low-latency, high-quality video experiences, even when participants are distributed across different geographic regions.
The proposed system represents a significant advancement in the field of real-time communication, addressing a critical challenge faced by many modern applications. As remote work, telehealth, and other distributed services continue to grow, the importance of low-latency, high-quality video conferencing will only increase. The insights and techniques presented in this paper could have far-reaching implications for the development of next-generation communication technologies.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Low-Latency Video Conferencing via Optimized Packet Routing and Reordering
Yao Xiao, Sitian Chen, Amelie Chi Zhou, Shuhao Zhang, Yi Wang, Rui Mao, Xuan Yang
In the face of rising global demand for video meetings, managing traffic across geographically distributed (geo-distributed) data centers presents a significant challenge due to the dynamic and limited nature of inter-DC network performance. Facing these issues, this paper introduces two novel techniques, VCRoute and WMJitter, to optimize the performance of geo-distributed video conferencing systems. VCRoute is a routing method designed for audio data packets of video conferences. It treats the routing problem as a Multi-Armed Bandit issue, and utilizes a tailored Thompson Sampling algorithm for resolution. Unlike traditional approaches, VCRoute considers transmitting latency and its variance simultaneously by using Thompson Sampling algorithm, which leads to effective end-to-end latency optimization. In conjunction with VCRoute, we present WMJitter, a watermark-based mechanism for managing network jitter, which can further reduce the end-to-end delay and keep an improved balance between latency and loss rate. Evaluations based on real geo-distributed network performance demonstrate the effectiveness and scalability of VCRoute and WMJitter, offering robust solutions for optimizing video conferencing systems in geo-distributed settings.
Read more4/26/2024
📶

0
Tile-Weighted Rate-Distortion Optimized Packet Scheduling for 360$^circ$ VR Video Streaming
Haopeng Wang, Haiwei Dong, Abdulmotaleb El Saddik
A key challenge of 360$^circ$ VR video streaming is ensuring high quality with limited network bandwidth. Currently, most studies focus on tile-based adaptive bitrate streaming to reduce bandwidth consumption, where resources in network nodes are not fully utilized. This article proposes a tile-weighted rate-distortion (TWRD) packet scheduling optimization system to reduce data volume and improve video quality. A multimodal spatial-temporal attention transformer is proposed to predict viewpoint with probability that is used to dynamically weight tiles and corresponding packets. The packet scheduling problem of determining which packets should be dropped is formulated as an optimization problem solved by a dynamic programming solution. Experiment results demonstrate the proposed method outperforms the existing methods under various conditions.
Read more4/24/2024
➖

0
Enhancing Video Transmission with Machine Learning based Routing in Software-Defined Networks
An{i}l Dursun .Ipek, Murtaza Ciciou{g}lu, Ali c{C}alhan
Our study uses the centralized, flexible, dynamic, and programmable structure of Software-Defined networks (SDN) to overcome the problems. Although SDN effectively addresses the challenges present in traditional networks, it still requires further enhancements to achieve a more optimized network architecture. The Floodlight controller utilized in this study employs metrics such as hop count, which provides limited information for routing. In scenarios such as video transmission, this situation is insufficient and the need for optimization arises. For this purpose, an artificial intelligence (AI) based routing algorithm is proposed between the server and the client in the scenario based on NSFNET topology. The topology designed with the Floodlight controller in the Mininet simulation environment includes a client, a server, and 14 switches. A realistic network environment is provided by adding different receivers and creating TCP traffic between these receivers using the iperf3 tool. In three scenarios, video streaming is performed using the FFmpeg tool, and 49 path metrics such as RTT, throughput, and loss are recorded. In these scenarios, PSNR and SSIM calculations are made to observe the differences between the transmitted and the original video in congested and uncongested environments. Due to the lack of a dataset suitable for the proposed network environment in the literature, a new dataset consisting of 876 records is created using continuously transmitted video traffic. Low and high traffic levels are created within the dataset, and different machine learning techniques such as KNN, Random Forest, SVM, AdaBoost, Logistic Regression and XGBoost are applied using the features that affect the traffic levels.
Read more9/17/2024

0
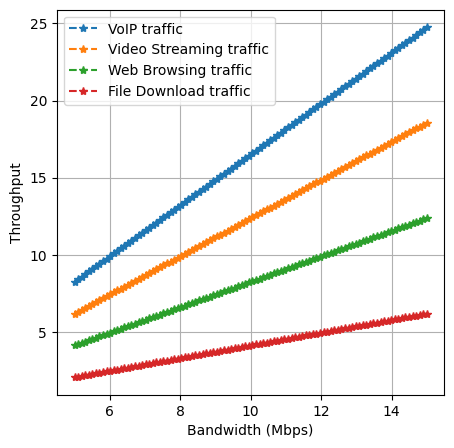
Maximization of Communication Network Throughput using Dynamic Traffic Allocation Scheme
Md. Arquam, Suchi Kumari
Optimizing network throughput in real-world dynamic systems is critical, especially for diverse and delay-sensitive multimedia data types such as VoIP and video streaming. Traditional routing protocols, which rely on static metrics and single shortest-path algorithms, were unable in managing this complex information. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach that enhances resource utilization while maintaining Quality of Service (QoS). Our dynamic traffic allocation model prioritizes different data types based on their delay sensitivity and allocates traffic by considering factors such as bandwidth, latency, and network failures. This approach is shown to significantly improve network throughput compared to static load balancing, especially for multimedia applications. Simulation results confirm the effectiveness of this dynamic method in maximizing network throughput and maintaining QoS across various data types.
Read more9/10/2024