Minimizing Power Consumption under SINR Constraints for Cell-Free Massive MIMO in O-RAN

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Explores minimizing power consumption in cell-free massive MIMO systems for Open RAN (O-RAN) networks
- Proposes an optimization framework to minimize power under signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) constraints
- Considers both analog and digital beamforming to optimize power allocation
Plain English Explanation
The paper examines how to reduce power usage in a type of 5G network called cell-free massive MIMO. In traditional cellular networks, each user connects to a single cell tower. In a cell-free system, users can connect to multiple distributed access points, which can improve coverage and performance.
The researchers develop an optimization framework to minimize the total power consumption in the cell-free network, while ensuring that each user has a minimum required signal quality (SINR). This involves carefully allocating the power between the analog and digital parts of the beamforming process. Beamforming is a technique that focuses the wireless signal in a specific direction to improve performance.
By optimizing the power allocation, the system can reduce overall energy usage without compromising the user experience. This is important for environmental sustainability and battery life in mobile devices. The proposed approach could help enable more efficient and widespread deployment of cell-free 5G networks.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents an optimization framework to minimize the total power consumption in a cell-free massive MIMO system operating in an Open RAN (O-RAN) architecture. The authors consider both analog and digital beamforming to optimize the power allocation, subject to constraints on the minimum required signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR) for each user.
The system model includes a set of distributed access points (APs) that serve a number of user equipments (UEs) in a cell-free environment. The optimization problem aims to find the power allocation that minimizes the total power consumption while ensuring each UE achieves its target SINR. The problem is formulated as a non-convex quadratically constrained quadratic program (QCQP), which the authors solve using an efficient semidefinite relaxation technique.
The proposed approach is evaluated through simulations, demonstrating significant power savings compared to baseline schemes that do not optimize the power allocation. The results show the tradeoffs between power consumption, SINR, and the choice of analog versus digital beamforming. The authors also discuss the practical considerations for implementing the proposed solution in an O-RAN system.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a practical optimization framework for minimizing power consumption in cell-free massive MIMO systems, which is an important consideration for the deployment of 5G and beyond networks. The authors acknowledge several limitations and areas for future work, such as the need to incorporate more realistic channel and hardware models, as well as the potential impact of user mobility and imperfect channel state information.
One aspect that could be further explored is the interplay between power optimization and other system-level objectives, such as spectral efficiency, fairness, and latency. Additionally, the proposed solution assumes perfect coordination among the distributed access points, which may not always be the case in real-world deployments. Investigating decentralized optimization approaches could be a valuable direction for future research.
Overall, the paper presents a solid contribution to the field of energy-efficient cell-free massive MIMO, and the insights and techniques developed could be useful for researchers and practitioners working on optimizing the performance and sustainability of next-generation wireless networks.
Conclusion
This paper develops an optimization framework to minimize power consumption in cell-free massive MIMO systems for Open RAN (O-RAN) networks. The proposed approach optimizes the power allocation between analog and digital beamforming while ensuring each user meets a minimum SINR requirement. Simulation results demonstrate significant power savings compared to baseline schemes, highlighting the potential of this approach to enable more energy-efficient and sustainable 5G and beyond deployments. The authors also discuss practical considerations and areas for future research, such as incorporating more realistic system models and exploring the interplay between power optimization and other performance metrics.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Minimizing Power Consumption under SINR Constraints for Cell-Free Massive MIMO in O-RAN
Vaishnavi Kasuluru, Luis Blanco, Miguel Angel Vazquez, Cristian J. Vaca-Rubio, Engin Zeydan
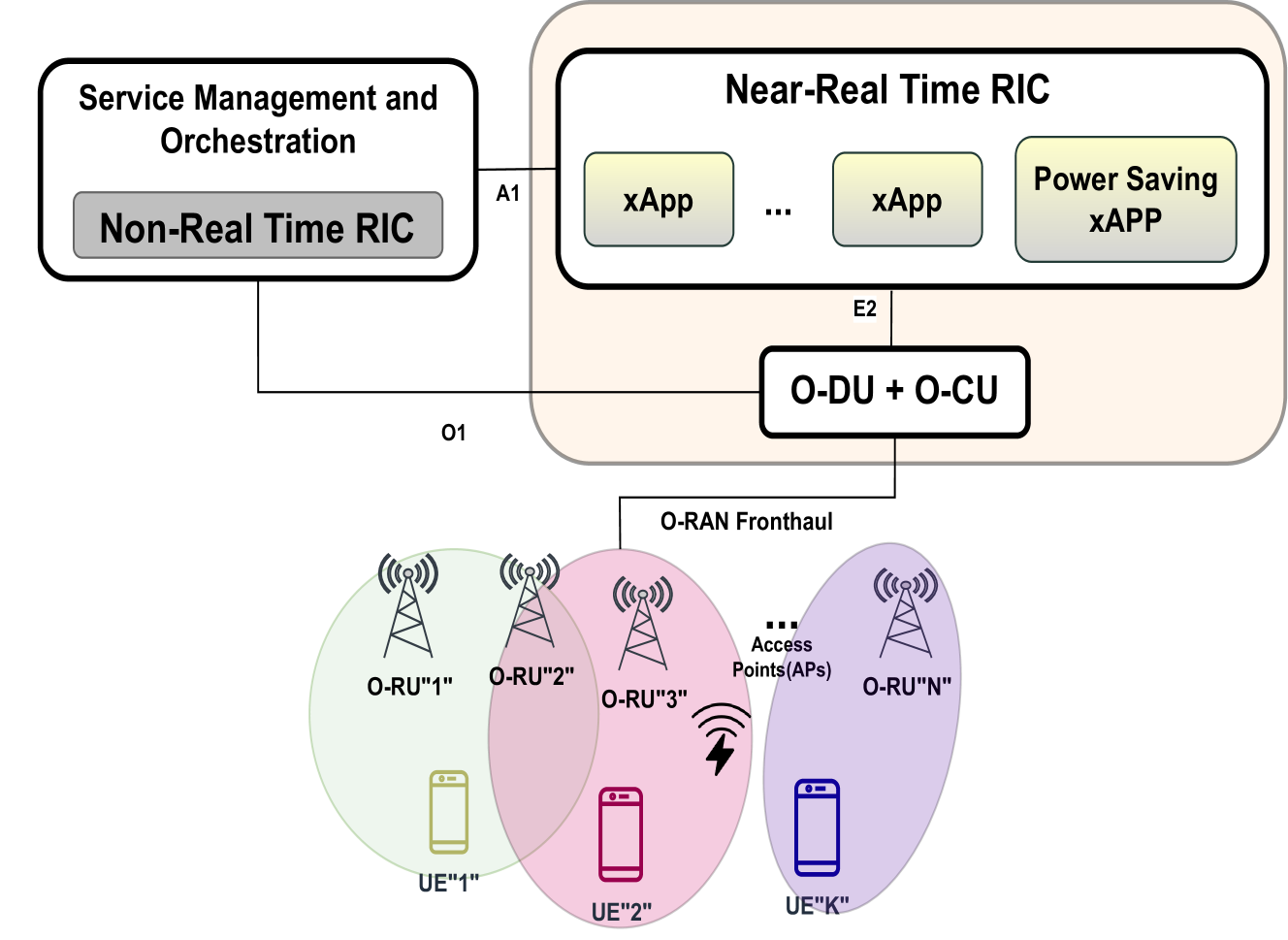
This paper deals with the problem of energy consumption minimization in Open RAN cell-free (CF) massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (mMIMO) systems under minimum per-user signal-to-noise-plus-interference ratio (SINR) constraints. Considering that several access points (APs) are deployed with multiple antennas, and they jointly serve multiple users on the same time-frequency resources, we design the precoding vectors that minimize the system power consumption, while preserving a minimum SINR for each user. We use a simple, yet representative, power consumption model, which consists of a fixed term that models the power consumption due to activation of the AP and a variable one that depends on the transmitted power. The mentioned problem boils down to a binary-constrained quadratic optimization problem, which is strongly non-convex. In order to solve this problem, we resort to a novel approach, which is based on the penalized convex-concave procedure. The proposed approach can be implemented in an O-RAN cell-free mMIMO system as an xApp in the near-real time RIC (RAN intelligent Controller). Numerical results show the potential of this approach for dealing with joint precoding optimization and AP selection.
Read more9/9/2024


0
Physically-consistent Multi-band Massive MIMO Systems: A Radio Resource Management Model
Nuwan Balasuriya, Amine Mezghani, Ekram Hossain
Massive multiple-input multiple-output (mMIMO) antenna systems and inter-band carrier aggregation (CA)-enabled multi-band communication are two key technologies to achieve very high data rates in beyond fifth generation (B5G) wireless systems. We propose a joint optimization framework for such systems where the mMIMO antenna spacing selection, precoder optimization, optimum sub-carrier selection and optimum power allocation are carried out simultaneously. We harness the bandwidth gain existing in a tightly coupled base station mMIMO antenna system to avoid sophisticated, non-practical antenna systems for multi-band operation. In particular, we analyze a multi-band communication system using a circuit-theoretic model to consider physical characteristics of a tightly coupled antenna array, and formulate a joint optimization problem to maximize the sum-rate. As part of the optimization, we also propose a novel block iterative water-filling-based sub-carrier selection and power allocation optimization algorithm for the multi-band mMIMO system. A novel sub-carrier windowing-based sub-carrier selection scheme is also proposed which considers the physical constraints (hardware limitation) at the mobile user devices. We carryout the optimizations in two ways: (i) to optimize the antenna spacing selection in an offline manner, and (ii) to select antenna elements from a dense array dynamically. Via computer simulations, we illustrate superior bandwidth gains present in the tightly-coupled colinear and rectangular planar antenna arrays, compared to the loosely-coupled or tightly-coupled parallel arrays. We further show the optimum sum-rate performance of the proposed optimization-based framework under various power allocation schemes and various user capability scenarios.
Read more7/31/2024

0
Joint AP-UE Association and Power Factor Optimization for Distributed Massive MIMO
Mohd Saif Ali Khan, Samar Agnihotri, Karthik R. M
The uplink sum-throughput of distributed massive multiple-input-multiple-output (mMIMO) networks depends majorly on Access point (AP)-User Equipment (UE) association and power control. The AP-UE association and power control both are important problems in their own right in distributed mMIMO networks to improve scalability and reduce front-haul load of the network, and to enhance the system performance by mitigating the interference and boosting the desired signals, respectively. Unlike previous studies, which focused primarily on addressing these two problems separately, this work addresses the uplink sum-throughput maximization problem in distributed mMIMO networks by solving the joint AP-UE association and power control problem, while maintaining Quality-of-Service (QoS) requirements for each UE. To improve scalability, we present an l1-penalty function that delicately balances the trade-off between spectral efficiency (SE) and front-haul signaling load. Our proposed methodology leverages fractional programming, Lagrangian dual formation, and penalty functions to provide an elegant and effective iterative solution with guaranteed convergence. Extensive numerical simulations validate the efficacy of the proposed technique for maximizing sum-throughput while considering the joint AP-UE association and power control problem, demonstrating its superiority over approaches that address these problems individually. Furthermore, the results show that the introduced penalty function can help us effectively control the maximum front-haul load.
Read more5/14/2024
🧪

0
Cell-Free Massive MIMO with Multi-Antenna Users and Phase Misalignments: A Novel Partially Coherent Transmission Framework
Unnikrishnan Kunnath Ganesan, Tung Thanh Vu, Erik G. Larsson
Cell-free massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) is a promising technology for next-generation communication systems. This work proposes a novel partially coherent (PC) transmission framework to cope with the challenge of phase misalignment among the access points (APs), which is important for unlocking the full potential of cell-free massive MIMO technology. With the PC operation, the APs are only required to be phase-aligned within clusters. Each cluster transmits the same data stream towards each user equipment (UE), while different clusters send different data streams. We first propose a novel algorithm to group APs into clusters such that the distance between two APs is always smaller than a reference distance ensuring the phase alignment of these APs. Then, we propose new algorithms that optimize the combining at UEs and precoding at APs to maximize the downlink sum data rates. We also propose a novel algorithm for data stream allocation to further improve the sum data rate of the PC operation. Numerical results show that the PC operation using the proposed framework with a sufficiently small reference distance can offer a sum rate close to the sum rate of the ideal fully coherent (FC) operation that requires network-wide phase alignment. This demonstrates the potential of PC operation in practical deployments of cell-free massive MIMO networks.
Read more4/4/2024