Physically-consistent Multi-band Massive MIMO Systems: A Radio Resource Management Model

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Examines a physically-consistent model for multi-user, multi-band massive MIMO systems with carrier aggregation
- Presents a joint optimization framework for radio resource management
- Proposes a block iterative water-filling algorithm for efficient optimization
Plain English Explanation
This research paper explores a new way to manage and optimize the use of radio resources in advanced wireless communication systems known as "multi-user, multi-band massive MIMO". These systems use many antennas at the base station to serve multiple users simultaneously across different frequency bands.
The key innovation is a "physically-consistent" model that takes into account the real-world physics and constraints of these complex systems. This allows the researchers to develop a sophisticated joint optimization framework to efficiently allocate resources like transmit power and bandwidth.
The optimization problem is solved using a novel "block iterative water-filling" algorithm, which iteratively adjusts the resource allocation to find the best overall performance. This is more efficient than previous approaches and helps ensure the system operates in a physically-realistic manner.
The end result is a more reliable and high-performing wireless network that can better support the growing demand for mobile data and connectivity. The techniques described could be applied to emerging 5G and 6G cellular networks, as well as other applications of massive MIMO technology.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a physically-consistent model for a multi-user, multi-band massive MIMO system with carrier aggregation. This accounts for practical constraints like the relationship between transmit power, bandwidth, and achievable rate.
The authors formulate a joint optimization problem to allocate resources like power and bandwidth across the system. They propose a block iterative water-filling algorithm to efficiently solve this complex optimization in a distributed manner.
The algorithm iterates between optimizing the transmit power and bandwidth allocation, converging to a physically-feasible solution. This improves on previous approaches that did not fully capture the underlying physics of the system.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a rigorous analytical framework and efficient optimization algorithm for practical massive MIMO systems. However, it does not consider some real-world implementation challenges, such as the impact of hardware impairments, channel estimation errors, or user mobility.
Additionally, the performance evaluation is limited to simulation-based results. Experimental validation with a prototype or testbed deployment would further strengthen the evidence and insights provided.
Future research could explore extensions to the model, such as incorporating more advanced antenna technologies, non-orthogonal multiple access schemes, or joint optimization with other network resources like caching and computing.
Conclusion
This research presents an important step forward in the design and optimization of next-generation wireless systems based on massive MIMO technology. By developing a physically-consistent model and efficient optimization algorithm, the authors have created a practical framework to improve the performance and reliability of these complex communication networks. The techniques described could have significant implications for the development of 5G, 6G, and beyond.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Physically-consistent Multi-band Massive MIMO Systems: A Radio Resource Management Model
Nuwan Balasuriya, Amine Mezghani, Ekram Hossain
Massive multiple-input multiple-output (mMIMO) antenna systems and inter-band carrier aggregation (CA)-enabled multi-band communication are two key technologies to achieve very high data rates in beyond fifth generation (B5G) wireless systems. We propose a joint optimization framework for such systems where the mMIMO antenna spacing selection, precoder optimization, optimum sub-carrier selection and optimum power allocation are carried out simultaneously. We harness the bandwidth gain existing in a tightly coupled base station mMIMO antenna system to avoid sophisticated, non-practical antenna systems for multi-band operation. In particular, we analyze a multi-band communication system using a circuit-theoretic model to consider physical characteristics of a tightly coupled antenna array, and formulate a joint optimization problem to maximize the sum-rate. As part of the optimization, we also propose a novel block iterative water-filling-based sub-carrier selection and power allocation optimization algorithm for the multi-band mMIMO system. A novel sub-carrier windowing-based sub-carrier selection scheme is also proposed which considers the physical constraints (hardware limitation) at the mobile user devices. We carryout the optimizations in two ways: (i) to optimize the antenna spacing selection in an offline manner, and (ii) to select antenna elements from a dense array dynamically. Via computer simulations, we illustrate superior bandwidth gains present in the tightly-coupled colinear and rectangular planar antenna arrays, compared to the loosely-coupled or tightly-coupled parallel arrays. We further show the optimum sum-rate performance of the proposed optimization-based framework under various power allocation schemes and various user capability scenarios.
Read more7/31/2024
🧪

0
Cell-Free Massive MIMO with Multi-Antenna Users and Phase Misalignments: A Novel Partially Coherent Transmission Framework
Unnikrishnan Kunnath Ganesan, Tung Thanh Vu, Erik G. Larsson
Cell-free massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) is a promising technology for next-generation communication systems. This work proposes a novel partially coherent (PC) transmission framework to cope with the challenge of phase misalignment among the access points (APs), which is important for unlocking the full potential of cell-free massive MIMO technology. With the PC operation, the APs are only required to be phase-aligned within clusters. Each cluster transmits the same data stream towards each user equipment (UE), while different clusters send different data streams. We first propose a novel algorithm to group APs into clusters such that the distance between two APs is always smaller than a reference distance ensuring the phase alignment of these APs. Then, we propose new algorithms that optimize the combining at UEs and precoding at APs to maximize the downlink sum data rates. We also propose a novel algorithm for data stream allocation to further improve the sum data rate of the PC operation. Numerical results show that the PC operation using the proposed framework with a sufficiently small reference distance can offer a sum rate close to the sum rate of the ideal fully coherent (FC) operation that requires network-wide phase alignment. This demonstrates the potential of PC operation in practical deployments of cell-free massive MIMO networks.
Read more4/4/2024
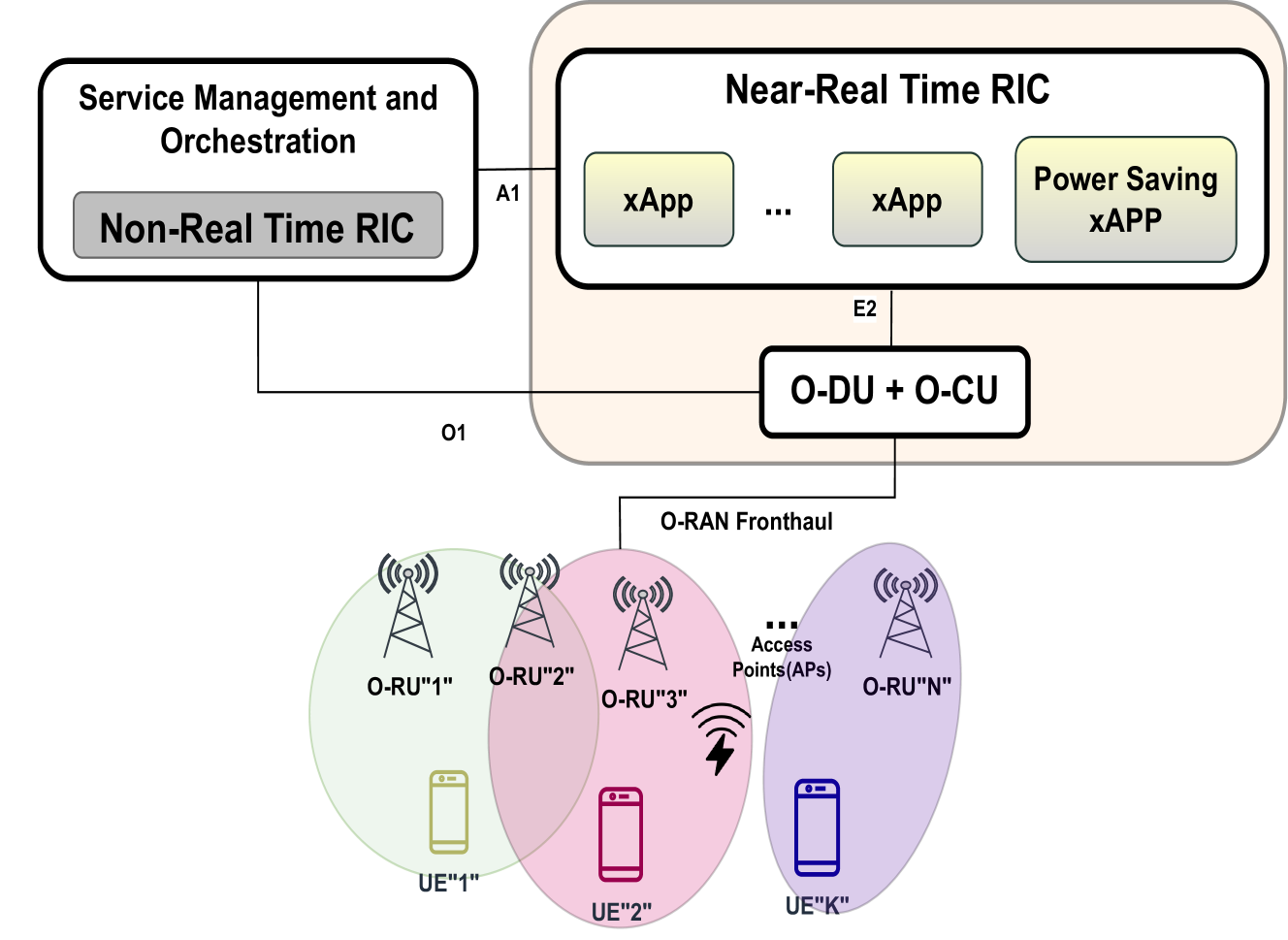

0
Minimizing Power Consumption under SINR Constraints for Cell-Free Massive MIMO in O-RAN
Vaishnavi Kasuluru, Luis Blanco, Miguel Angel Vazquez, Cristian J. Vaca-Rubio, Engin Zeydan
This paper deals with the problem of energy consumption minimization in Open RAN cell-free (CF) massive Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (mMIMO) systems under minimum per-user signal-to-noise-plus-interference ratio (SINR) constraints. Considering that several access points (APs) are deployed with multiple antennas, and they jointly serve multiple users on the same time-frequency resources, we design the precoding vectors that minimize the system power consumption, while preserving a minimum SINR for each user. We use a simple, yet representative, power consumption model, which consists of a fixed term that models the power consumption due to activation of the AP and a variable one that depends on the transmitted power. The mentioned problem boils down to a binary-constrained quadratic optimization problem, which is strongly non-convex. In order to solve this problem, we resort to a novel approach, which is based on the penalized convex-concave procedure. The proposed approach can be implemented in an O-RAN cell-free mMIMO system as an xApp in the near-real time RIC (RAN intelligent Controller). Numerical results show the potential of this approach for dealing with joint precoding optimization and AP selection.
Read more9/9/2024
🗣️

0
Antenna Selection in Polarization Reconfigurable MIMO (PR-MIMO) Communication Systems
Paul S. Oh, Sean S. Kwon, Andreas F. Molisch
Adaptation of a wireless system to the polarization state of the propagation channel can improve reliability and throughput. This paper in particular considers polarization reconfigurable multiple input multiple output (PR-MIMO) systems, where both transmitter and receiver can change the (linear) polarization orientation at each element of their antenna arrays. We first introduce joint polarization pre-post coding to maximize bounds on the capacity and the maximum eigenvalue of the channel matrix. For this we first derive approximate closed form equations of optimal polarization vectors at one link end, and then use iterative joint polarization pre-post coding to pursue joint optimal polarization vectors at both link ends. Next we investigate the combination of PR-MIMO with hybrid antenna selection / maximum ratio transmission (PR-HS/MRT), which can achieve a remarkable improvement of channel capacity and symbol error rate (SER). Further, two novel schemes of element wise and global polarization reconfiguration are presented for PR-HS/MRT. Comprehensive simulation results indicate that the proposed schemes provide 3 to 5 dB SNR gain in PR-MIMO spatial multiplexing and approximately 3 dB SNR gain in PRHS/ MRT, with concomitant improvements of channel capacity and SER.
Read more4/4/2024