Mobile-Agent: Autonomous Multi-Modal Mobile Device Agent with Visual Perception
2401.16158

0
0
Abstract
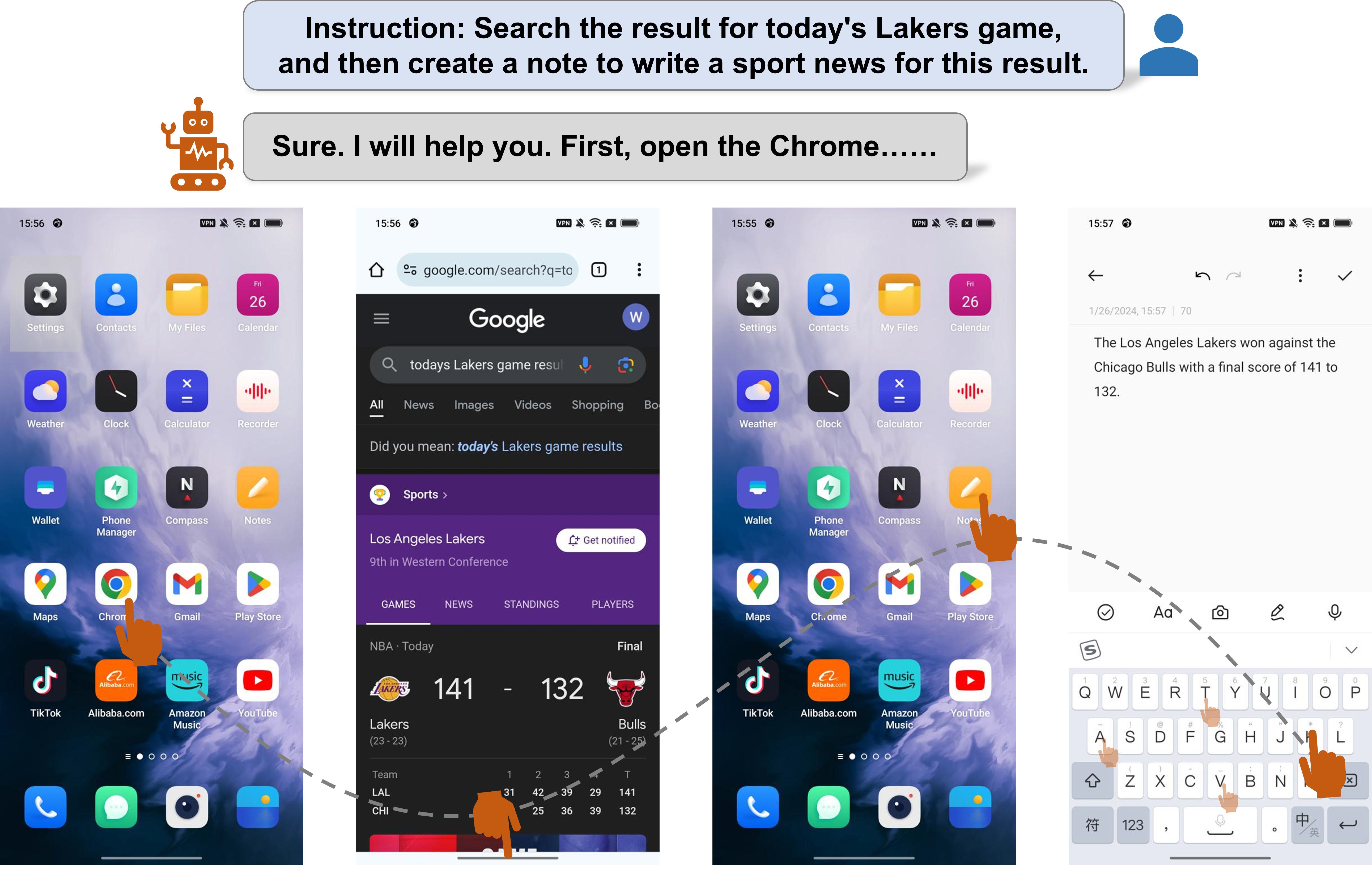
Mobile device agent based on Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLM) is becoming a popular application. In this paper, we introduce Mobile-Agent, an autonomous multi-modal mobile device agent. Mobile-Agent first leverages visual perception tools to accurately identify and locate both the visual and textual elements within the app's front-end interface. Based on the perceived vision context, it then autonomously plans and decomposes the complex operation task, and navigates the mobile Apps through operations step by step. Different from previous solutions that rely on XML files of Apps or mobile system metadata, Mobile-Agent allows for greater adaptability across diverse mobile operating environments in a vision-centric way, thereby eliminating the necessity for system-specific customizations. To assess the performance of Mobile-Agent, we introduced Mobile-Eval, a benchmark for evaluating mobile device operations. Based on Mobile-Eval, we conducted a comprehensive evaluation of Mobile-Agent. The experimental results indicate that Mobile-Agent achieved remarkable accuracy and completion rates. Even with challenging instructions, such as multi-app operations, Mobile-Agent can still complete the requirements. Code and model will be open-sourced at https://github.com/X-PLUG/MobileAgent.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- The research paper discusses the development of a novel mobile agent called "Mobile-Agent" that can operate autonomously on mobile devices and leverage visual perception capabilities.
- The Mobile-Agent is designed to be a multi-modal agent that can interact with users through various modalities, including visual, audio, and touch.
- The key focus of the paper is on the visual perception capabilities of the Mobile-Agent, which enable it to understand and interact with its surrounding environment.
Plain English Explanation
The research paper describes the development of a new type of virtual assistant or agent that can run on mobile devices like smartphones or tablets. This agent, called "Mobile-Agent," is designed to be able to act and make decisions on its own, without needing constant supervision or control by the human user.
One of the key features of the Mobile-Agent is its ability to perceive and understand the visual world around it. This is similar to how virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa can see and recognize objects, but the Mobile-Agent takes this a step further. The agent can use its visual perception capabilities to navigate its environment, identify objects and people, and even respond to visual cues from the user.
For example, the Mobile-Agent could potentially see that the user is looking at a specific item on their screen and offer relevant information or suggestions. Or it could notice that the user is in a particular location and automatically provide useful local information or services. This multi-modal interaction, combining visual, audio, and touch inputs, is a key part of what makes the Mobile-Agent a novel and potentially powerful virtual assistant.
Technical Explanation
The core innovation of the Mobile-Agent is its ability to leverage visual perception to interact with and understand its environment. This builds on the advances in computer vision and large language models that have enabled virtual assistants to become more visually aware.
The researchers have developed a specialized neural network architecture that allows the Mobile-Agent to process visual inputs from the device's camera, identify objects and scenes, and then use that information to make decisions and take actions. [This is similar to the Octopus V3 system, which also aims to bring advanced perceptual capabilities to mobile devices.]
The paper describes the training process for the visual perception model, as well as how the agent integrates this visual understanding with other modalities like speech and touch to provide a seamless multi-modal interaction experience for the user. Experiments demonstrate the agent's ability to navigate virtual environments, identify objects, and respond to visual prompts from the user.
Critical Analysis
The research represents an interesting advance in the field of autonomous mobile agents and virtual assistants. The inclusion of visual perception capabilities is a significant step forward that could enable these agents to become more aware of and responsive to their surroundings.
However, the paper does not address some potential limitations or concerns with this technology. For example, there may be privacy implications of a mobile agent that can constantly perceive and analyze the user's visual environment. Additionally, the robustness and reliability of the visual perception model in real-world, noisy conditions is not fully explored.
Further research would be needed to understand the broader implications and potential risks of deploying such autonomous agents with advanced perceptual capabilities on personal mobile devices. Careful consideration of ethical and security concerns will be crucial as this technology continues to evolve.
Conclusion
The Mobile-Agent research represents an important step forward in the development of autonomous, multi-modal virtual assistants for mobile devices. By endowing these agents with visual perception capabilities, the researchers have opened up new possibilities for how users can interact with and rely on these intelligent systems in their daily lives.
While there are certainly some open questions and potential concerns that need to be addressed, the core ideas and technical innovations presented in this paper are quite compelling. As the field of mobile autonomy and perceptual intelligence continues to advance, the Mobile-Agent could serve as a valuable model for how these capabilities can be brought to the ubiquitous personal devices we all rely on.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Benchmarking Mobile Device Control Agents across Diverse Configurations
Juyong Lee, Taywon Min, Minyong An, Changyeon Kim, Kimin Lee

0
0
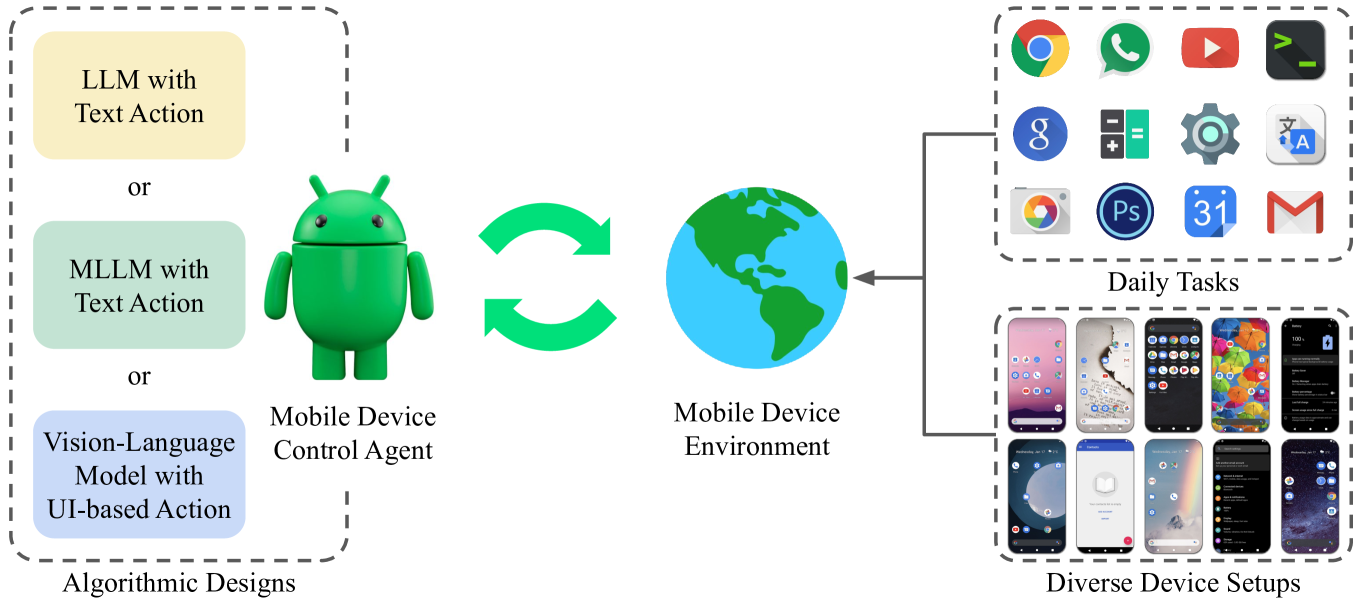
Developing autonomous agents for mobile devices can significantly enhance user interactions by offering increased efficiency and accessibility. However, despite the growing interest in mobile device control agents, the absence of a commonly adopted benchmark makes it challenging to quantify scientific progress in this area. In this work, we introduce B-MoCA: a novel benchmark designed specifically for evaluating mobile device control agents. To create a realistic benchmark, we develop B-MoCA based on the Android operating system and define 60 common daily tasks. Importantly, we incorporate a randomization feature that changes various aspects of mobile devices, including user interface layouts and language settings, to assess generalization performance. We benchmark diverse agents, including agents employing large language models (LLMs) or multi-modal LLMs as well as agents trained from scratch using human expert demonstrations. While these agents demonstrate proficiency in executing straightforward tasks, their poor performance on complex tasks highlights significant opportunities for future research to enhance their effectiveness. Our source code is publicly available at https://b-moca.github.io.
4/26/2024
Octopus v3: Technical Report for On-device Sub-billion Multimodal AI Agent
Wei Chen, Zhiyuan Li

0
0
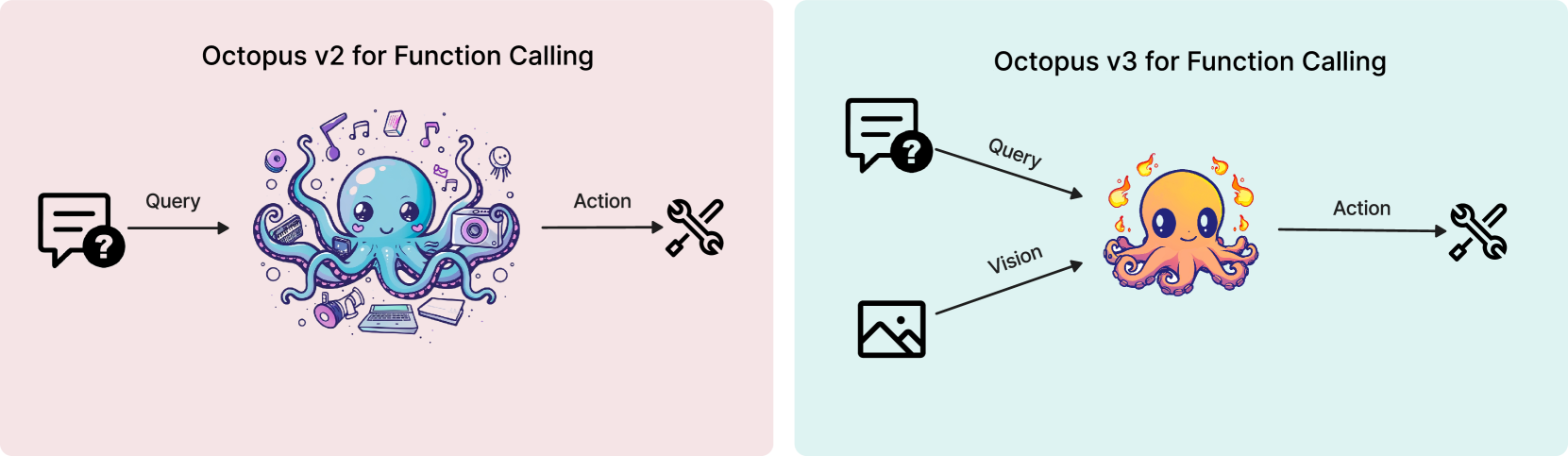
A multimodal AI agent is characterized by its ability to process and learn from various types of data, including natural language, visual, and audio inputs, to inform its actions. Despite advancements in large language models that incorporate visual data, such as GPT-4V, effectively translating image-based data into actionable outcomes for AI agents continues to be challenging. In this paper, we introduce a multimodal model that incorporates the concept of functional token specifically designed for AI agent applications. To ensure compatibility with edge devices, our model is optimized to a compact size of less than 1B parameters. Like GPT-4, our model can process both English and Chinese. We demonstrate that this model is capable of operating efficiently on a wide range of edge devices, including as constrained as a Raspberry Pi.
4/19/2024
Training a Vision Language Model as Smartphone Assistant
Nicolai Dorka, Janusz Marecki, Ammar Anwar

0
0
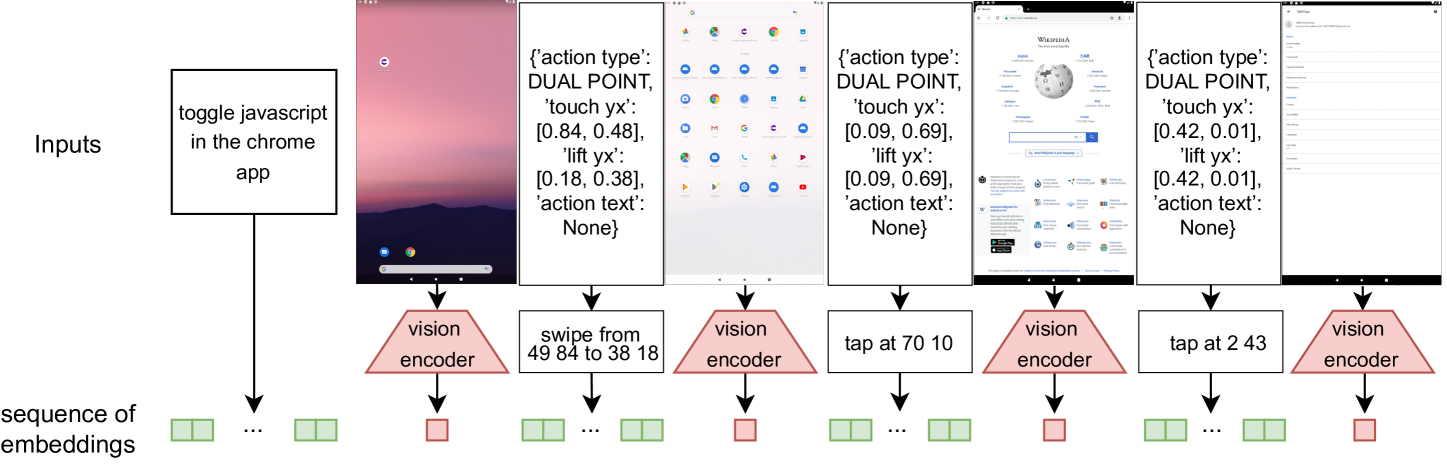
Addressing the challenge of a digital assistant capable of executing a wide array of user tasks, our research focuses on the realm of instruction-based mobile device control. We leverage recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) and present a visual language model (VLM) that can fulfill diverse tasks on mobile devices. Our model functions by interacting solely with the user interface (UI). It uses the visual input from the device screen and mimics human-like interactions, encompassing gestures such as tapping and swiping. This generality in the input and output space allows our agent to interact with any application on the device. Unlike previous methods, our model operates not only on a single screen image but on vision-language sentences created from sequences of past screenshots along with corresponding actions. Evaluating our method on the challenging Android in the Wild benchmark demonstrates its promising efficacy and potential.
4/16/2024
🔍
MMAC-Copilot: Multi-modal Agent Collaboration Operating System Copilot
Zirui Song, Yaohang Li, Meng Fang, Zhenhao Chen, Zecheng Shi, Yuan Huang, Ling Chen

0
0
Autonomous virtual agents are often limited by their singular mode of interaction with real-world environments, restricting their versatility. To address this, we propose the Multi-Modal Agent Collaboration framework (MMAC-Copilot), a framework utilizes the collective expertise of diverse agents to enhance interaction ability with operating systems. The framework introduces a team collaboration chain, enabling each participating agent to contribute insights based on their specific domain knowledge, effectively reducing the hallucination associated with knowledge domain gaps. To evaluate the performance of MMAC-Copilot, we conducted experiments using both the GAIA benchmark and our newly introduced Visual Interaction Benchmark (VIBench). VIBench focuses on non-API-interactable applications across various domains, including 3D gaming, recreation, and office scenarios. MMAC-Copilot achieved exceptional performance on GAIA, with an average improvement of 6.8% over existing leading systems. Furthermore, it demonstrated remarkable capability on VIBench, particularly in managing various methods of interaction within systems and applications. These results underscore MMAC-Copilot's potential in advancing the field of autonomous virtual agents through its innovative approach to agent collaboration.
5/7/2024