Training a Vision Language Model as Smartphone Assistant
2404.08755

0
0
Abstract
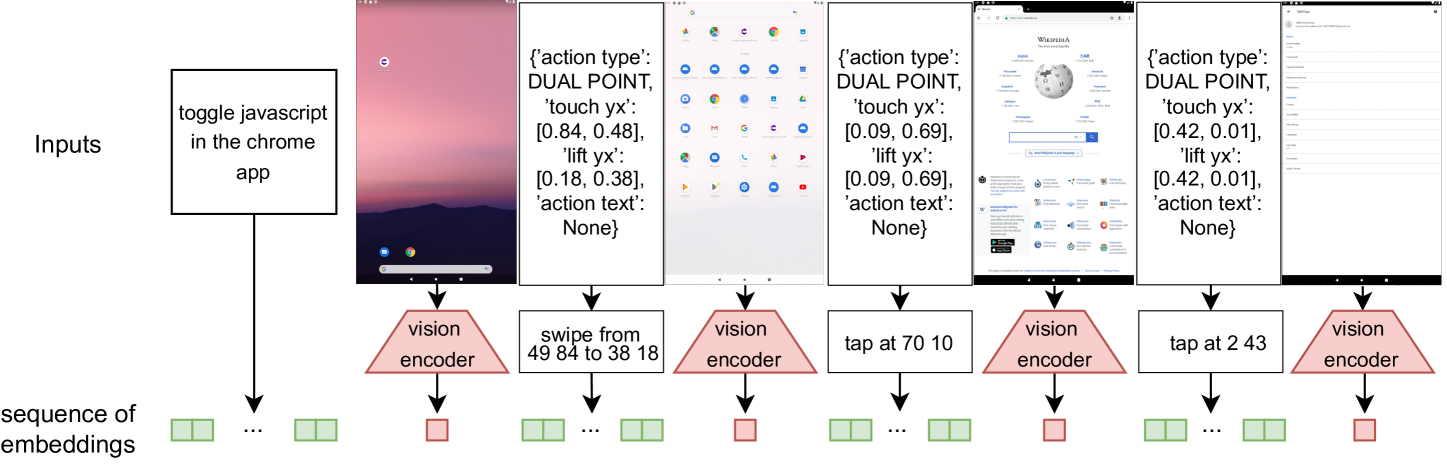
Addressing the challenge of a digital assistant capable of executing a wide array of user tasks, our research focuses on the realm of instruction-based mobile device control. We leverage recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) and present a visual language model (VLM) that can fulfill diverse tasks on mobile devices. Our model functions by interacting solely with the user interface (UI). It uses the visual input from the device screen and mimics human-like interactions, encompassing gestures such as tapping and swiping. This generality in the input and output space allows our agent to interact with any application on the device. Unlike previous methods, our model operates not only on a single screen image but on vision-language sentences created from sequences of past screenshots along with corresponding actions. Evaluating our method on the challenging Android in the Wild benchmark demonstrates its promising efficacy and potential.
Get summaries of the top AI research delivered straight to your inbox:
Overview
- This paper explores the use of a vision-language model as an assistant for smartphone users, aiming to enhance the capabilities of existing personal assistants.
- The researchers investigate how a large language model trained on multimodal data can be adapted to assist with various tasks on a smartphone platform.
- The paper covers the development and evaluation of the vision-language model, as well as its integration with smartphone functionalities to create a more capable and versatile personal assistant.
Plain English Explanation
The paper focuses on using a special type of AI model called a "vision-language model" as a virtual assistant for smartphones. Vision-language models are a new kind of AI that can understand and process both images and text. The researchers wanted to see if they could take one of these models and adapt it to be a more helpful personal assistant on smartphones, going beyond what current voice assistants can do.
The key idea is to leverage the unique abilities of vision-language models, which can understand the context and meaning of both visual and textual information, to assist users with a wider range of tasks on their smartphones. This could include things like interpreting images, answering questions about the contents of an image, or even helping with tasks that involve both visual and textual information, like reading and understanding documents.
By integrating this advanced AI technology into a smartphone assistant, the researchers hope to create a more capable and versatile tool that can better assist users in their daily lives. This could lead to improvements in areas like link to "Enhancing Robot Explanation Capabilities Through Vision-Language" or link to "VoicePilot: Harnessing LLMs as Speech Interfaces for Physically Embodied AI", where AI systems can provide more natural and effective assistance by understanding both visual and textual information.
Technical Explanation
The paper describes the development and evaluation of a vision-language model that is adapted to function as a smartphone assistant. The researchers start by training a large language model on a diverse dataset of text and images, giving the model the ability to understand and process both types of information.
They then fine-tune this vision-language model to perform specific tasks that would be useful for a smartphone assistant, such as answering questions about images, summarizing documents, or providing recommendations based on the user's context. This fine-tuning process involves further training the model on smartphone-specific data and tasks, enabling it to better understand and assist with the types of activities users might perform on their devices.
To integrate the vision-language model into a smartphone platform, the researchers develop a system that can seamlessly connect the model's capabilities with the various functionalities of the smartphone, such as the camera, messaging apps, and virtual assistant interface. This allows users to naturally interact with the vision-language model using a combination of voice, text, and visual input, just as they would with a traditional virtual assistant.
The paper also presents an evaluation of the vision-language model's performance on a range of smartphone-related tasks, link to "Vision-Language Models for Medical Report Generation from Visual Information" and link to "VIAssist: Adapting Multi-Modal Large Language Models for Personalized Assistance", demonstrating its potential to enhance the capabilities of existing personal assistants and provide a more versatile and intelligent user experience.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to leveraging vision-language models for smartphone assistance, but it also acknowledges several limitations and areas for further research. One key concern is the potential for privacy and security issues, as the vision-language model would be processing a significant amount of user data and interactions. The researchers mention the need for robust privacy safeguards and user control mechanisms to address these concerns.
Additionally, the paper notes that the performance of the vision-language model may be dependent on the quality and diversity of the training data, as well as the specific tasks and contexts it is designed to handle. Further research may be needed to ensure the model's generalization and adaptability to a wide range of user needs and environments.
While the paper demonstrates the potential of vision-language models for smartphone assistance, it also highlights the importance of carefully considering the ethical implications and potential societal impacts of such technology, particularly in terms of link to "Exploring the Frontier of Vision-Language Models: A Survey of Current Capabilities and Limitations". Ongoing research and development in this area should prioritize user privacy, fairness, and responsible deployment to ensure the technology benefits users without causing unintended harm.
Conclusion
This paper explores the use of a vision-language model as a smartphone assistant, aiming to enhance the capabilities of existing personal assistants. By leveraging the unique abilities of vision-language models to understand both visual and textual information, the researchers develop a system that can assist users with a wider range of tasks on their smartphones.
The technical details of the vision-language model's development and integration with smartphone functionalities are covered, along with an evaluation of its performance on various tasks. While the paper highlights the potential benefits of this approach, it also acknowledges the need to address privacy, security, and ethical considerations as this technology continues to evolve.
Overall, the research presented in this paper represents an important step towards creating more intelligent and versatile personal assistants that can better support users in their daily lives.
Related Papers

Large Language User Interfaces: Voice Interactive User Interfaces powered by LLMs
Syed Mekael Wasti, Ken Q. Pu, Ali Neshati

0
0
The evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) has showcased remarkable capacities for logical reasoning and natural language comprehension. These capabilities can be leveraged in solutions that semantically and textually model complex problems. In this paper, we present our efforts toward constructing a framework that can serve as an intermediary between a user and their user interface (UI), enabling dynamic and real-time interactions. We employ a system that stands upon textual semantic mappings of UI components, in the form of annotations. These mappings are stored, parsed, and scaled in a custom data structure, supplementary to an agent-based prompting backend engine. Employing textual semantic mappings allows each component to not only explain its role to the engine but also provide expectations. By comprehending the needs of both the user and the components, our LLM engine can classify the most appropriate application, extract relevant parameters, and subsequently execute precise predictions of the user's expected actions. Such an integration evolves static user interfaces into highly dynamic and adaptable solutions, introducing a new frontier of intelligent and responsive user experiences.
4/17/2024
Exploring the Frontier of Vision-Language Models: A Survey of Current Methodologies and Future Directions
Akash Ghosh, Arkadeep Acharya, Sriparna Saha, Vinija Jain, Aman Chadha

0
0
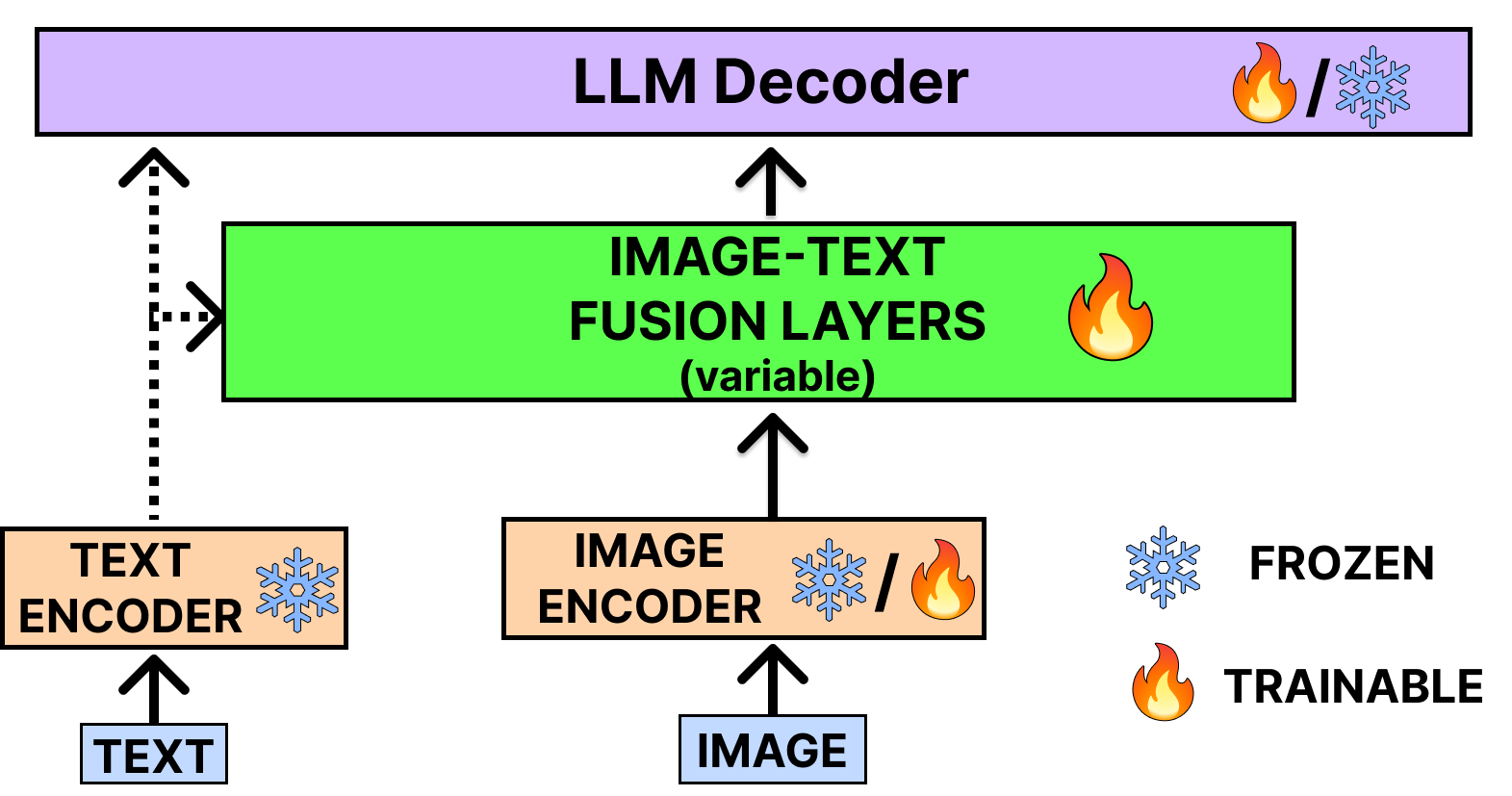
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has significantly reshaped the trajectory of the AI revolution. Nevertheless, these LLMs exhibit a notable limitation, as they are primarily adept at processing textual information. To address this constraint, researchers have endeavored to integrate visual capabilities with LLMs, resulting in the emergence of Vision-Language Models (VLMs). These advanced models are instrumental in tackling more intricate tasks such as image captioning and visual question answering. In our comprehensive survey paper, we delve into the key advancements within the realm of VLMs. Our classification organizes VLMs into three distinct categories: models dedicated to vision-language understanding, models that process multimodal inputs to generate unimodal (textual) outputs and models that both accept and produce multimodal inputs and outputs.This classification is based on their respective capabilities and functionalities in processing and generating various modalities of data.We meticulously dissect each model, offering an extensive analysis of its foundational architecture, training data sources, as well as its strengths and limitations wherever possible, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of its essential components. We also analyzed the performance of VLMs in various benchmark datasets. By doing so, we aim to offer a nuanced understanding of the diverse landscape of VLMs. Additionally, we underscore potential avenues for future research in this dynamic domain, anticipating further breakthroughs and advancements.
4/16/2024
Enhancing Robot Explanation Capabilities through Vision-Language Models: a Preliminary Study by Interpreting Visual Inputs for Improved Human-Robot Interaction
David Sobr'in-Hidalgo, Miguel 'Angel Gonz'alez-Santamarta, 'Angel Manuel Guerrero-Higueras, Francisco Javier Rodr'iguez-Lera, Vicente Matell'an-Olivera

0
0
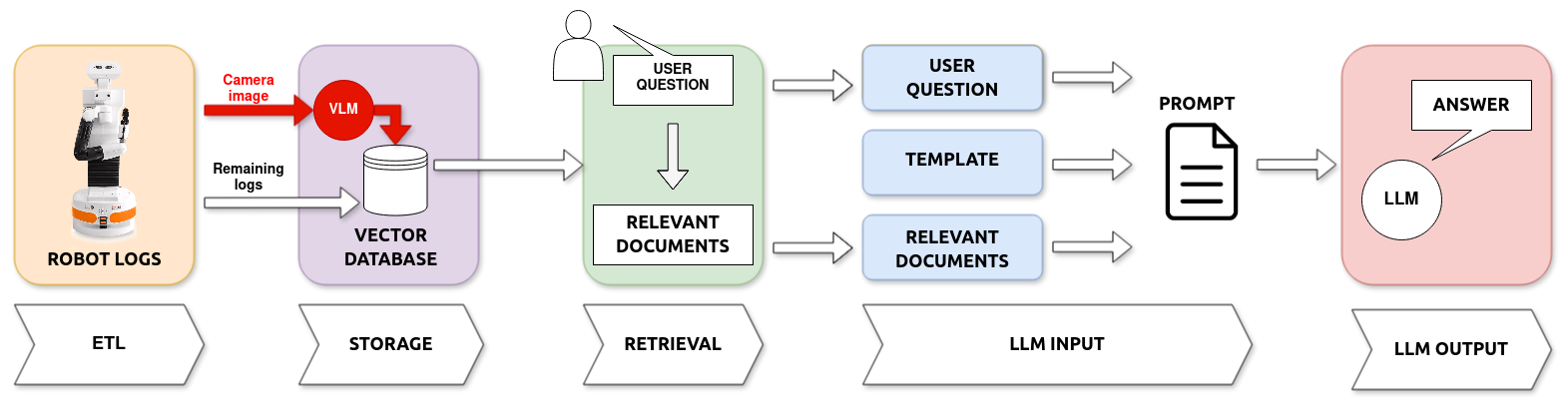
This paper presents an improved system based on our prior work, designed to create explanations for autonomous robot actions during Human-Robot Interaction (HRI). Previously, we developed a system that used Large Language Models (LLMs) to interpret logs and produce natural language explanations. In this study, we expand our approach by incorporating Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling the system to analyze textual logs with the added context of visual input. This method allows for generating explanations that combine data from the robot's logs and the images it captures. We tested this enhanced system on a basic navigation task where the robot needs to avoid a human obstacle. The findings from this preliminary study indicate that adding visual interpretation improves our system's explanations by precisely identifying obstacles and increasing the accuracy of the explanations provided.
4/16/2024
Effectiveness Assessment of Recent Large Vision-Language Models
Yao Jiang, Xinyu Yan, Ge-Peng Ji, Keren Fu, Meijun Sun, Huan Xiong, Deng-Ping Fan, Fahad Shahbaz Khan

0
0
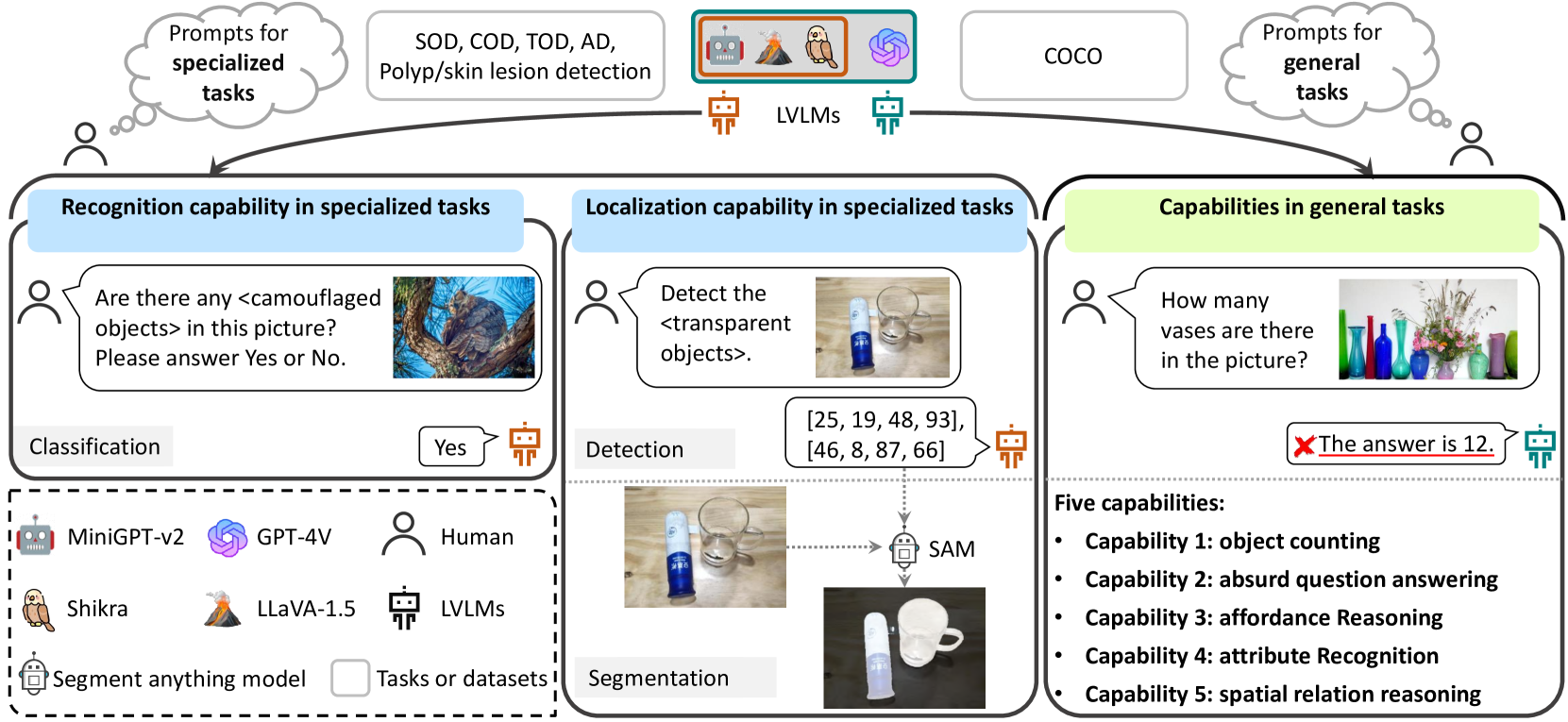
The advent of large vision-language models (LVLMs) represents a noteworthy advancement towards the pursuit of artificial general intelligence. However, the model efficacy across both specialized and general tasks warrants further investigation. This paper endeavors to evaluate the competency of popular LVLMs in specialized and general tasks, respectively, aiming to offer a comprehensive understanding of these novel models. To gauge their efficacy in specialized tasks, we employ six challenging tasks across three distinct application scenarios, namely natural, healthcare, and industrial ones. Such six tasks include salient/camouflaged/transparent object detection, as well as polyp detection, skin lesion detection, and industrial anomaly detection. We examine the performance of three recent open-source LVLMs, including MiniGPT-v2, LLaVA-1.5, and Shikra, on both visual recognition and localization under these tasks. Moreover, we conduct empirical investigations utilizing the aforementioned LVLMs together with GPT-4V, assessing their multi-modal understanding capabilities in general tasks including object counting, absurd question answering, affordance reasoning, attribute recognition, and spatial relation reasoning. Our investigations reveal that these LVLMs demonstrate limited proficiency not only in specialized tasks but also in general tasks. We delve deep into this inadequacy and uncover several potential factors, including limited cognition in specialized tasks, object hallucination, text-to-image interference, and decreased robustness in complex problems. We hope this study could provide useful insights for the future development of LVLMs, helping researchers improve LVLMs to cope with both general and specialized applications.
5/7/2024