Multi-Link Operation and Wireless Digital Twin to Support Enhanced Roaming in Next-Gen Wi-Fi
2404.18313

0
0
🔎
Abstract
The next generation of Wi-Fi is meant to achieve ultra-high reliability for wireless communication. Several approaches are available to this extent, some of which are being considered for inclusion in standards specifications, including coordination of access points to reduce interference. In this paper, we propose a centralized architecture based on digital twins, called WiTwin, with the aim of supporting wireless stations in selecting the optimal association according to a set of parameters. Unlike prior works, we assume that Wi-Fi 7 features like multi-link operation (MLO) are available. Moreover, one of the main goals of this architecture is to preserve communication quality in the presence of mobility, by helping stations to perform reassociation at the right time and in the best way.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- The paper proposes a centralized architecture called WiTwin to help wireless stations select the optimal access point association for improved reliability and quality of service.
- It assumes the availability of Wi-Fi 7 features like multi-link operation (MLO), which allows wireless devices to connect to multiple access points simultaneously.
- A key goal of the architecture is to maintain communication quality as wireless stations move around, by facilitating timely and optimal reassociation.
Plain English Explanation
The next generation of Wi-Fi, known as Wi-Fi 7, aims to provide ultra-reliable wireless communication. One way to achieve this is by coordinating the access points to reduce interference between them. The paper introduces a new system called WiTwin that uses a centralized architecture and digital twins to help wireless devices, like laptops and phones, choose the best access point to connect to.
Unlike previous approaches, WiTwin assumes that Wi-Fi 7 will have advanced features like [object Object], which allows devices to connect to multiple access points at once. This helps maintain high-quality communication even as devices move around, by assisting them in switching between access points at the right time and in the best way.
Technical Explanation
The proposed WiTwin architecture uses a centralized approach, where a control server manages the digital twins of the wireless network and its connected devices. These digital twins are virtual representations that mirror the real-world network, including the access points and client devices.
By monitoring the digital twins, the control server can optimize the association of wireless stations with access points, taking into account factors like signal strength, network load, and mobility patterns. This allows the system to guide stations in selecting the optimal access point to connect to, improving overall network performance and reliability.
The authors assume the availability of Wi-Fi 7 features like [object Object], which enables wireless devices to simultaneously connect to multiple access points. This provides additional opportunities for the WiTwin architecture to maintain communication quality as stations move around the network.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a promising approach to improving the reliability and quality of wireless communications using a centralized digital twin-based architecture. By leveraging upcoming Wi-Fi 7 capabilities like MLO, the WiTwin system aims to optimize access point associations and facilitate seamless mobility for wireless devices.
However, the paper does not address some potential challenges and limitations of this approach. For example, it does not discuss the scalability of the centralized architecture as the number of access points and connected devices grows, or the resilience of the system to failures or security threats in the control server.
Additionally, the paper does not provide experimental results or performance evaluations to validate the claims made about the benefits of the WiTwin system. Further research and real-world deployments would be needed to assess the practicality and effectiveness of this approach in diverse network environments.
Conclusion
The proposed WiTwin architecture represents an innovative approach to enhancing the reliability and quality of wireless communications, leveraging the anticipated capabilities of the next-generation Wi-Fi 7 standard. By centrally managing a digital twin of the network and its connected devices, the system aims to optimize access point associations and maintain high-quality connections even as wireless stations move around.
While the paper outlines the conceptual design of WiTwin, further research and real-world validation are needed to fully assess its potential benefits and limitations. As the industry continues to [object Object], approaches like WiTwin could play a significant role in enabling ultra-reliable wireless communication.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
IEEE 802.11be Network Throughput Optimization with Multi-Link Operation and AP Coordination
Lyutianyang Zhang, Hao Yin, Sumit Roy, Liu Cao, Xiangyu Gao, Vanlin Sathya

0
0
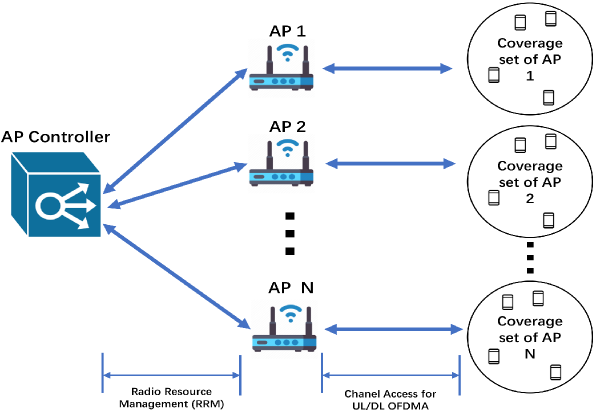
IEEE 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7) introduces a new concept called multi-link operation (MLO), which allows multiple Wi-Fi interfaces in different bands (2.4, 5, and 6 GHz) to work together to increase network throughput, reduce latency, and improve spectrum reuse efficiency in dense overlapping networks. To make the most of MLO, this paper proposes a new data-driven resource allocation algorithm for the 11be network with the aid of an access point (AP) controller. To maximize network throughput, a network topology optimization problem is formulated for 11be network, which is solved by exploiting the totally unimodular property of the bipartite graph formed by the connection between AP and station (STA) in Wi-Fi networks. Subsequently, a proportional fairness algorithm is applied for radio link allocation, network throughput optimization considering the channel condition, and the fairness of the multi-link device (MLD) data rate. The performance of the proposed algorithm on two main MLO implementations - multi-link multi-radio (MLMR) with simultaneous transmission and reception (STR), and the interplay between multiple nodes employing them are evaluated through cross-layer (PHY-MAC) data rate simulation with PHY abstraction.
4/9/2024

Wireless Network Digital Twin for 6G: Generative AI as A Key Enabler
Zhenyu Tao, Wei Xu, Yongming Huang, Xiaoyun Wang, Xiaohu You

0
0
Digital twin, which enables emulation, evaluation, and optimization of physical entities through synchronized digital replicas, has gained increasing attention as a promising technology for intricate wireless networks. For 6G, numerous innovative wireless technologies and network architectures have posed new challenges in establishing wireless network digital twins. To tackle these challenges, artificial intelligence (AI), particularly the flourishing generative AI, emerges as a potential solution. In this article, we discuss emerging prerequisites for wireless network digital twins considering the complicated network architecture, tremendous network scale, extensive coverage, and diversified application scenarios in the 6G era. We further explore the applications of generative AI, such as Transformer and diffusion model, to empower the 6G digital twin from multiple perspectives including physical-digital modeling, synchronization, and slicing capability. Subsequently, we propose a hierarchical generative AI-enabled wireless network digital twin at both the message-level and policy-level, and provide a typical use case with numerical results to validate the effectiveness and efficiency. Finally, open research issues for wireless network digital twins in the 6G era are discussed.
6/21/2024
🧠
Mapping Wireless Networks into Digital Reality through Joint Vertical and Horizontal Learning
Zifan Zhang, Mingzhe Chen, Zhaohui Yang, Yuchen Liu

0
0
In recent years, the complexity of 5G and beyond wireless networks has escalated, prompting a need for innovative frameworks to facilitate flexible management and efficient deployment. The concept of digital twins (DTs) has emerged as a solution to enable real-time monitoring, predictive configurations, and decision-making processes. While existing works primarily focus on leveraging DTs to optimize wireless networks, a detailed mapping methodology for creating virtual representations of network infrastructure and properties is still lacking. In this context, we introduce VH-Twin, a novel time-series data-driven framework that effectively maps wireless networks into digital reality. VH-Twin distinguishes itself through complementary vertical twinning (V-twinning) and horizontal twinning (H-twinning) stages, followed by a periodic clustering mechanism used to virtualize network regions based on their distinct geological and wireless characteristics. Specifically, V-twinning exploits distributed learning techniques to initialize a global twin model collaboratively from virtualized network clusters. H-twinning, on the other hand, is implemented with an asynchronous mapping scheme that dynamically updates twin models in response to network or environmental changes. Leveraging real-world wireless traffic data within a cellular wireless network, comprehensive experiments are conducted to verify that VH-Twin can effectively construct, deploy, and maintain network DTs. Parametric analysis also offers insights into how to strike a balance between twinning efficiency and model accuracy at scale.
4/24/2024
Automatic AI Model Selection for Wireless Systems: Online Learning via Digital Twinning
Qiushuo Hou, Matteo Zecchin, Sangwoo Park, Yunlong Cai, Guanding Yu, Kaushik Chowdhury, Osvaldo Simeone

0
0
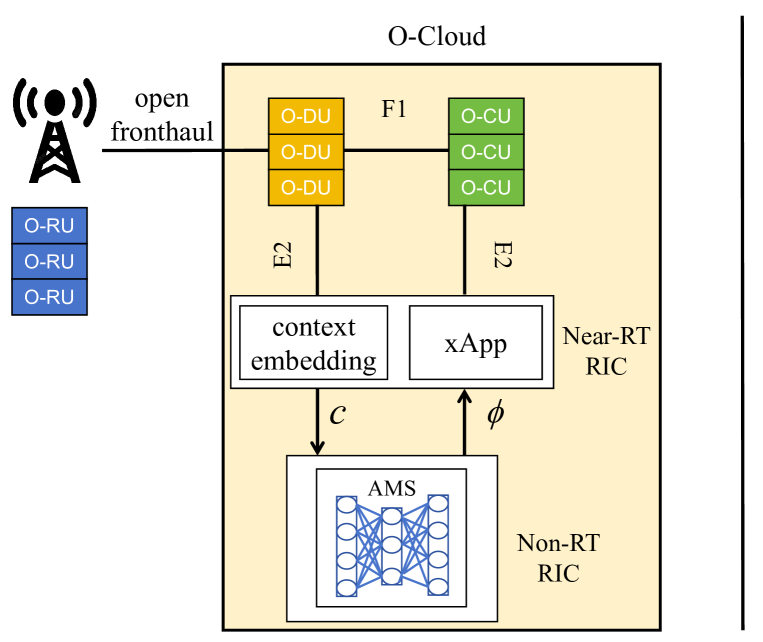
In modern wireless network architectures, such as O-RAN, artificial intelligence (AI)-based applications are deployed at intelligent controllers to carry out functionalities like scheduling or power control. The AI apps are selected on the basis of contextual information such as network conditions, topology, traffic statistics, and design goals. The mapping between context and AI model parameters is ideally done in a zero-shot fashion via an automatic model selection (AMS) mapping that leverages only contextual information without requiring any current data. This paper introduces a general methodology for the online optimization of AMS mappings. Optimizing an AMS mapping is challenging, as it requires exposure to data collected from many different contexts. Therefore, if carried out online, this initial optimization phase would be extremely time consuming. A possible solution is to leverage a digital twin of the physical system to generate synthetic data from multiple simulated contexts. However, given that the simulator at the digital twin is imperfect, a direct use of simulated data for the optimization of the AMS mapping would yield poor performance when tested in the real system. This paper proposes a novel method for the online optimization of AMS mapping that corrects for the bias of the simulator by means of limited real data collected from the physical system. Experimental results for a graph neural network-based power control app demonstrate the significant advantages of the proposed approach.
6/26/2024