IEEE 802.11be Network Throughput Optimization with Multi-Link Operation and AP Coordination
2312.00345

0
0
Abstract
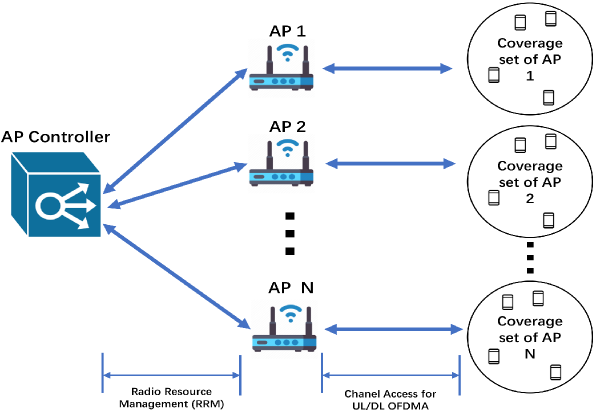
IEEE 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7) introduces a new concept called multi-link operation (MLO), which allows multiple Wi-Fi interfaces in different bands (2.4, 5, and 6 GHz) to work together to increase network throughput, reduce latency, and improve spectrum reuse efficiency in dense overlapping networks. To make the most of MLO, this paper proposes a new data-driven resource allocation algorithm for the 11be network with the aid of an access point (AP) controller. To maximize network throughput, a network topology optimization problem is formulated for 11be network, which is solved by exploiting the totally unimodular property of the bipartite graph formed by the connection between AP and station (STA) in Wi-Fi networks. Subsequently, a proportional fairness algorithm is applied for radio link allocation, network throughput optimization considering the channel condition, and the fairness of the multi-link device (MLD) data rate. The performance of the proposed algorithm on two main MLO implementations - multi-link multi-radio (MLMR) with simultaneous transmission and reception (STR), and the interplay between multiple nodes employing them are evaluated through cross-layer (PHY-MAC) data rate simulation with PHY abstraction.
Create account to get full access
Introduction
Contribution
This paper proposes a new approach to optimizing network throughput in IEEE 802.11be wireless networks. The key ideas are to leverage multi-link operation and multi-access point (AP) coordination to improve performance. Multi-link operation allows a single device to connect to multiple access points simultaneously, while multi-AP coordination enables the APs to work together to allocate radio resources more efficiently.
Plain English Explanation
The paper focuses on improving the speed and efficiency of Wi-Fi 7 (IEEE 802.11be) networks. The main innovations are:
-
Multi-Link Operation: This allows a single device, like a smartphone or laptop, to connect to multiple Wi-Fi access points at the same time. This can boost the device's overall internet speed and reliability.
-
Multi-AP Coordination: The Wi-Fi access points in an area coordinate with each other to strategically assign radio frequencies and other resources. This coordination helps reduce interference and optimize the network's performance.
By combining these two techniques - multi-link operation and multi-AP coordination - the researchers aim to significantly improve the overall throughput and efficiency of 802.11be Wi-Fi networks. This could lead to faster, more reliable internet connections for users, especially in areas with many devices and access points.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a new framework for optimizing network throughput in IEEE 802.11be wireless networks using multi-link operation and multi-AP coordination.
Multi-link operation allows a single station (STA) to connect to multiple access points (APs) simultaneously. This provides the STA with increased bandwidth and reliability, as it can aggregate the capacity of the multiple links. The authors develop an AP-STA pairing algorithm to efficiently match STAs with the best set of APs.
In addition, the paper introduces a multi-AP coordination scheme, where the APs exchange information and collaboratively allocate radio resources. This helps mitigate interference and improve overall network performance. The authors formulate a joint optimization problem to determine the optimal radio link allocation among the APs and STAs.
Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed approach can significantly enhance the sum-rate performance of 802.11be networks compared to traditional single-link and uncoordinated multi-AP scenarios.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a compelling approach to improving Wi-Fi network performance by leveraging multi-link operation and multi-AP coordination. However, the authors do not address potential challenges related to client device compatibility and the complexity of implementing the coordination scheme in real-world deployments.
Furthermore, the simulation-based evaluation may not fully capture the practical considerations and constraints of actual Wi-Fi networks. Additional research and field trials would be necessary to validate the efficacy of the proposed techniques in diverse network environments.
Conclusion
This paper introduces an innovative framework to optimize the throughput of IEEE 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7) networks. By utilizing multi-link operation and multi-AP coordination, the proposed approach can significantly enhance the overall network performance compared to traditional single-link and uncoordinated multi-AP scenarios.
While the simulation results are promising, further research is needed to address potential implementation challenges and validate the effectiveness of the techniques in real-world settings. Nonetheless, the ideas presented in this paper hold significant potential to improve the user experience and enable more efficient utilization of wireless network resources.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
🔎
Multi-Link Operation and Wireless Digital Twin to Support Enhanced Roaming in Next-Gen Wi-Fi
Stefano Scanzio, Matteo Rosani, Gabriele Formis, Dave Cavalcanti, Valerio Frascolla, Guido Marchetto, Gianluca Cena

0
0
The next generation of Wi-Fi is meant to achieve ultra-high reliability for wireless communication. Several approaches are available to this extent, some of which are being considered for inclusion in standards specifications, including coordination of access points to reduce interference. In this paper, we propose a centralized architecture based on digital twins, called WiTwin, with the aim of supporting wireless stations in selecting the optimal association according to a set of parameters. Unlike prior works, we assume that Wi-Fi 7 features like multi-link operation (MLO) are available. Moreover, one of the main goals of this architecture is to preserve communication quality in the presence of mobility, by helping stations to perform reassociation at the right time and in the best way.
4/30/2024
Joint AP-UE Association and Power Factor Optimization for Distributed Massive MIMO
Mohd Saif Ali Khan, Samar Agnihotri, Karthik R. M

0
0
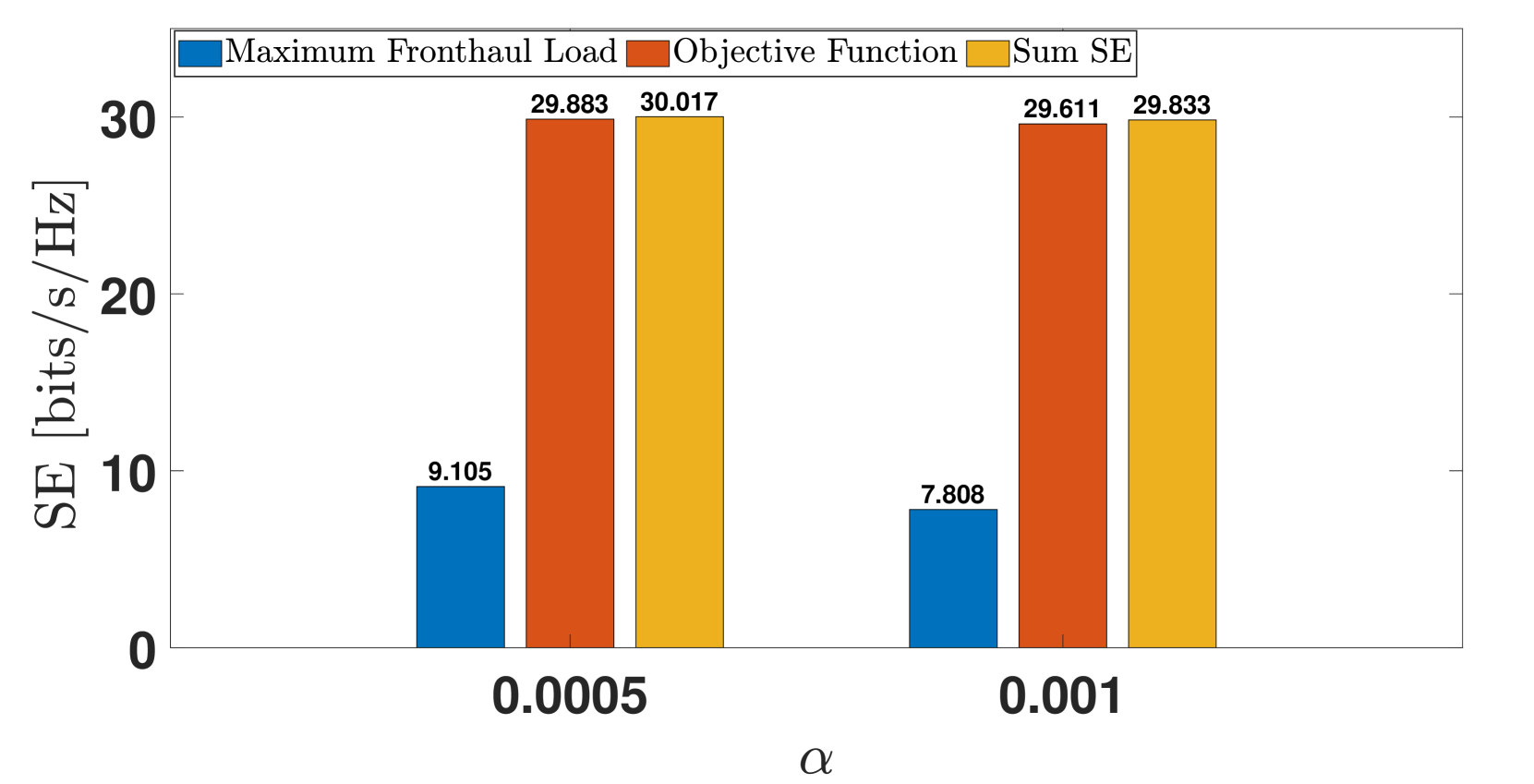
The uplink sum-throughput of distributed massive multiple-input-multiple-output (mMIMO) networks depends majorly on Access point (AP)-User Equipment (UE) association and power control. The AP-UE association and power control both are important problems in their own right in distributed mMIMO networks to improve scalability and reduce front-haul load of the network, and to enhance the system performance by mitigating the interference and boosting the desired signals, respectively. Unlike previous studies, which focused primarily on addressing these two problems separately, this work addresses the uplink sum-throughput maximization problem in distributed mMIMO networks by solving the joint AP-UE association and power control problem, while maintaining Quality-of-Service (QoS) requirements for each UE. To improve scalability, we present an l1-penalty function that delicately balances the trade-off between spectral efficiency (SE) and front-haul signaling load. Our proposed methodology leverages fractional programming, Lagrangian dual formation, and penalty functions to provide an elegant and effective iterative solution with guaranteed convergence. Extensive numerical simulations validate the efficacy of the proposed technique for maximizing sum-throughput while considering the joint AP-UE association and power control problem, demonstrating its superiority over approaches that address these problems individually. Furthermore, the results show that the introduced penalty function can help us effectively control the maximum front-haul load.
5/14/2024
User Association and Channel Allocation in 5G Mobile Asymmetric Multi-band Heterogeneous Networks
Miao Dai, Gang Sun, Hongfang Yu, Sheng Wang, Dusit Niyato

0
0
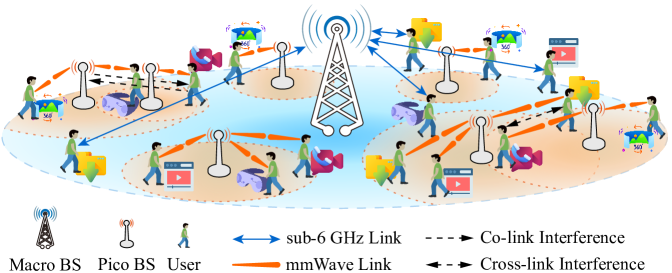
With the proliferation of mobile terminals and the continuous upgrading of services, 4G LTE networks are showing signs of weakness. To enhance the capacity of wireless networks, millimeter waves are introduced to drive the evolution of networks towards multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks. The distinct propagation characteristics of mmWaves and microwaves, as well as the vastly different hardware configurations of heterogeneous base stations, make traditional access strategies no longer effective. Therefore, to narrowing the gap between theory and practice, we investigate the access strategy in multi-band 5G heterogeneous networks, taking into account the characteristics of mobile users, asynchronous switching between uplink and downlink of pico base stations, asymmetric service requirements, and user communication continuity. We formulate the problem as integer nonlinear programming and prove its intractability. Thereby, we decouple it into three subproblems: user association, switch point selection, and subchannel allocation, and design an algorithm based on optimal matching and spectral clustering to solve it efficiently. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms the comparison methods in terms of overall data rate, effective data rate, and number of satisfied users.
5/30/2024

Uplink resource allocation optimization for user-centric cell-free MIMO networks
Zehua Li, Raviraj Adve

0
0
We examine the problem of optimizing resource allocation in the uplink for a user-centric, cell-free, multi-input multi-output network. We start by modeling and developing resource allocation algorithms for two standard network operation modes. The centralized mode provides high data rates but suffers multiple issues, including scalability. On the other hand, the distributed mode has the opposite problem: relatively low rates, but is scalable. To address these challenges, we combine the strength of the two standard modes, creating a new semi-distributed operation mode. To avoid the need for information exchange between access points, we introduce a new quality of service metric to decentralize the resource allocation algorithms. Our results show that we can eliminate the need for information exchange with a relatively small penalty on data rates.
6/11/2024