Navigating LLM Ethics: Advancements, Challenges, and Future Directions
2406.18841

0
0
🔍
Abstract
This study addresses ethical issues surrounding Large Language Models (LLMs) within the field of artificial intelligence. It explores the common ethical challenges posed by both LLMs and other AI systems, such as privacy and fairness, as well as ethical challenges uniquely arising from LLMs. It highlights challenges such as hallucination, verifiable accountability, and decoding censorship complexity, which are unique to LLMs and distinct from those encountered in traditional AI systems. The study underscores the need to tackle these complexities to ensure accountability, reduce biases, and enhance transparency in the influential role that LLMs play in shaping information dissemination. It proposes mitigation strategies and future directions for LLM ethics, advocating for interdisciplinary collaboration. It recommends ethical frameworks tailored to specific domains and dynamic auditing systems adapted to diverse contexts. This roadmap aims to guide responsible development and integration of LLMs, envisioning a future where ethical considerations govern AI advancements in society.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This study explores the ethical challenges posed by Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of artificial intelligence.
- It examines common ethical issues shared by LLMs and other AI systems, as well as unique challenges specific to LLMs.
- The paper highlights the need to address complexities like hallucination, verifiable accountability, and decoding censorship to ensure LLMs are developed and used responsibly.
- It proposes mitigation strategies and future directions for ethical LLM development, advocating for interdisciplinary collaboration and tailored ethical frameworks.
Plain English Explanation
This paper examines the ethical challenges that come with using Large Language Models (LLMs), a type of artificial intelligence (AI) that can generate human-like text. LLMs have become increasingly influential in shaping how information is shared, but they also raise unique ethical concerns that are different from traditional AI systems.
For example, LLMs can sometimes "hallucinate" or generate completely fabricated information that appears convincing. They also make it difficult to verify the source and accuracy of the information they produce. Additionally, LLMs can be used to evade content moderation or censorship, which raises issues around transparency and accountability.
The researchers argue that addressing these complexities is crucial to ensure LLMs are developed and used in a responsible way that reduces biases, enhances transparency, and maintains accountability. They propose strategies like tailoring ethical frameworks to specific domains and implementing dynamic auditing systems to help guide the ethical integration of LLMs into society.
The ultimate goal is to shape the future of AI advancements, including LLMs, in a way that prioritizes ethical considerations and responsible development. This will help ensure AI, like LLMs, are used in a way that benefits society as a whole.
Technical Explanation
The researchers conducted a comprehensive analysis of the ethical challenges posed by Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of artificial intelligence. They identified common ethical issues shared by LLMs and other AI systems, such as concerns around privacy and fairness.
However, the study also highlighted unique ethical complexities that arise specifically from the use of LLMs. These include the problem of "hallucination," where LLMs can generate completely fabricated information that appears convincing; the difficulty in verifying the source and accuracy of LLM-generated content; and the potential for LLMs to be used to bypass content moderation or censorship, which raises concerns about transparency and accountability.
To address these complexities, the researchers proposed a range of mitigation strategies and future directions for ethical LLM development. These include the need for interdisciplinary collaboration, the development of tailored ethical frameworks for specific domains, and the implementation of dynamic auditing systems that can adapt to diverse contexts.
The researchers emphasized the urgent need to tackle these ethical challenges to ensure the responsible development and integration of LLMs, which have become increasingly influential in shaping information dissemination. By prioritizing ethical considerations, the researchers aim to guide the future of AI advancements in a way that benefits society as a whole.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a thorough and well-researched exploration of the ethical issues surrounding Large Language Models (LLMs). It rightly highlights the unique challenges posed by LLMs, such as the problem of "hallucination" and the difficulty in verifying the accuracy and provenance of LLM-generated content.
One potential limitation of the study is that it does not delve deeply into the specific mechanisms or technical details underlying these ethical challenges. A more in-depth analysis of the inner workings of LLMs and how they contribute to these ethical issues could have provided additional insights.
Additionally, while the paper proposes some mitigation strategies, such as tailored ethical frameworks and dynamic auditing systems, it would have been valuable to see more concrete examples or pilot studies demonstrating the implementation and effectiveness of these approaches.
Furthermore, the paper could have explored the broader societal and political implications of the ethical challenges posed by LLMs. For instance, how might the potential for LLMs to bypass content moderation impact the spread of misinformation or the ability to hold powerful entities accountable?
Overall, the paper provides a solid foundation for understanding the ethical complexities of LLMs and the urgent need to address them. However, further research and practical applications of the proposed solutions could strengthen the impact and real-world applicability of this important work.
Conclusion
This study highlights the critical need to address the ethical challenges posed by Large Language Models (LLMs) in the field of artificial intelligence. By identifying unique complexities such as hallucination, verifiable accountability, and decoding censorship, the researchers underscore the importance of developing responsible strategies for the development and integration of LLMs.
The proposed mitigation strategies, including interdisciplinary collaboration, tailored ethical frameworks, and dynamic auditing systems, offer a promising path forward. Ultimately, this research aims to guide the future of AI advancements, including LLMs, in a way that prioritizes ethical considerations and ensures these powerful technologies are used to benefit society as a whole.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
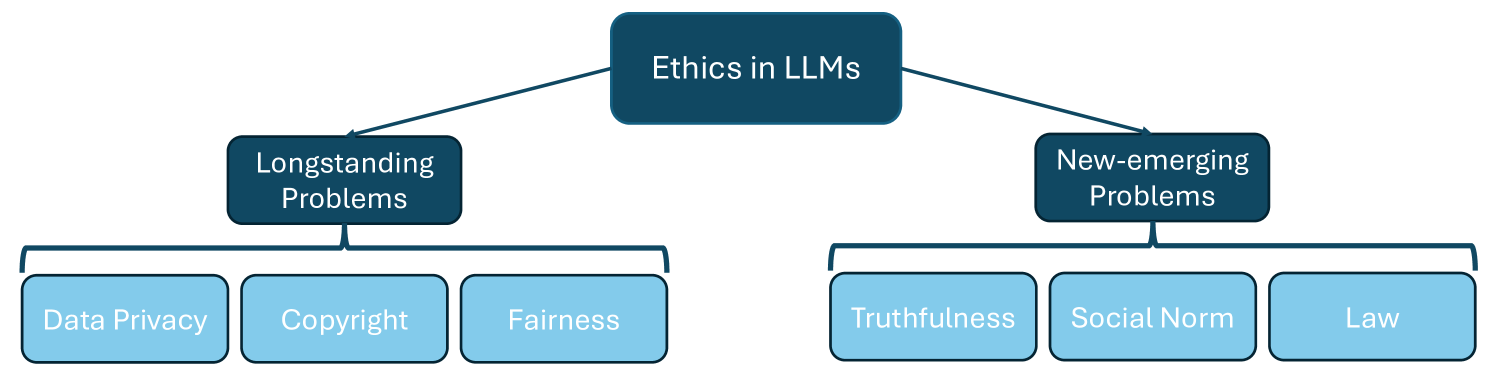
Deconstructing The Ethics of Large Language Models from Long-standing Issues to New-emerging Dilemmas
Chengyuan Deng, Yiqun Duan, Xin Jin, Heng Chang, Yijun Tian, Han Liu, Henry Peng Zou, Yiqiao Jin, Yijia Xiao, Yichen Wang, Shenghao Wu, Zongxing Xie, Kuofeng Gao, Sihong He, Jun Zhuang, Lu Cheng, Haohan Wang

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved unparalleled success across diverse language modeling tasks in recent years. However, this progress has also intensified ethical concerns, impacting the deployment of LLMs in everyday contexts. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of ethical challenges associated with LLMs, from longstanding issues such as copyright infringement, systematic bias, and data privacy, to emerging problems like truthfulness and social norms. We critically analyze existing research aimed at understanding, examining, and mitigating these ethical risks. Our survey underscores integrating ethical standards and societal values into the development of LLMs, thereby guiding the development of responsible and ethically aligned language models.
6/11/2024
🤖
The global landscape of academic guidelines for generative AI and Large Language Models
Junfeng Jiao, Saleh Afroogh, Kevin Chen, David Atkinson, Amit Dhurandhar

0
0
The integration of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) in academia has spurred a global discourse on their potential pedagogical benefits and ethical considerations. Positive reactions highlight some potential, such as collaborative creativity, increased access to education, and empowerment of trainers and trainees. However, negative reactions raise concerns about ethical complexities, balancing innovation and academic integrity, unequal access, and misinformation risks. Through a systematic survey and text-mining-based analysis of global and national directives, insights from independent research, and eighty university-level guidelines, this study provides a nuanced understanding of the opportunities and challenges posed by GAI and LLMs in education. It emphasizes the importance of balanced approaches that harness the benefits of these technologies while addressing ethical considerations and ensuring equitable access and educational outcomes. The paper concludes with recommendations for fostering responsible innovation and ethical practices to guide the integration of GAI and LLMs in academia.
7/1/2024
💬
Modeling Emotions and Ethics with Large Language Models
Edward Y. Chang

0
0
This paper explores the integration of human-like emotions and ethical considerations into Large Language Models (LLMs). We first model eight fundamental human emotions, presented as opposing pairs, and employ collaborative LLMs to reinterpret and express these emotions across a spectrum of intensity. Our focus extends to embedding a latent ethical dimension within LLMs, guided by a novel self-supervised learning algorithm with human feedback (SSHF). This approach enables LLMs to perform self-evaluations and adjustments concerning ethical guidelines, enhancing their capability to generate content that is not only emotionally resonant but also ethically aligned. The methodologies and case studies presented herein illustrate the potential of LLMs to transcend mere text and image generation, venturing into the realms of empathetic interaction and principled decision-making, thereby setting a new precedent in the development of emotionally aware and ethically conscious AI systems.
4/23/2024
💬
Student Perspectives on Using a Large Language Model (LLM) for an Assignment on Professional Ethics
Virginia Grande, Natalie Kiesler, Maria Andreina Francisco R

0
0
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) started a serious discussion among educators on how LLMs would affect, e.g., curricula, assessments, and students' competencies. Generative AI and LLMs also raised ethical questions and concerns for computing educators and professionals. This experience report presents an assignment within a course on professional competencies, including some related to ethics, that computing master's students need in their careers. For the assignment, student groups discussed the ethical process by Lennerfors et al. by analyzing a case: a fictional researcher considers whether to attend the real CHI 2024 conference in Hawaii. The tasks were (1) to participate in in-class discussions on the case, (2) to use an LLM of their choice as a discussion partner for said case, and (3) to document both discussions, reflecting on their use of the LLM. Students reported positive experiences with the LLM as a way to increase their knowledge and understanding, although some identified limitations. The LLM provided a wider set of options for action in the studied case, including unfeasible ones. The LLM would not select a course of action, so students had to choose themselves, which they saw as coherent. From the educators' perspective, there is a need for more instruction for students using LLMs: some students did not perceive the tools as such but rather as an authoritative knowledge base. Therefore, this work has implications for educators considering the use of LLMs as discussion partners or tools to practice critical thinking, especially in computing ethics education.
6/19/2024