Student Perspectives on Using a Large Language Model (LLM) for an Assignment on Professional Ethics
2406.11858

0
0
💬
Abstract
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) started a serious discussion among educators on how LLMs would affect, e.g., curricula, assessments, and students' competencies. Generative AI and LLMs also raised ethical questions and concerns for computing educators and professionals. This experience report presents an assignment within a course on professional competencies, including some related to ethics, that computing master's students need in their careers. For the assignment, student groups discussed the ethical process by Lennerfors et al. by analyzing a case: a fictional researcher considers whether to attend the real CHI 2024 conference in Hawaii. The tasks were (1) to participate in in-class discussions on the case, (2) to use an LLM of their choice as a discussion partner for said case, and (3) to document both discussions, reflecting on their use of the LLM. Students reported positive experiences with the LLM as a way to increase their knowledge and understanding, although some identified limitations. The LLM provided a wider set of options for action in the studied case, including unfeasible ones. The LLM would not select a course of action, so students had to choose themselves, which they saw as coherent. From the educators' perspective, there is a need for more instruction for students using LLMs: some students did not perceive the tools as such but rather as an authoritative knowledge base. Therefore, this work has implications for educators considering the use of LLMs as discussion partners or tools to practice critical thinking, especially in computing ethics education.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- The paper discusses how the rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) has sparked discussions among educators on how they will impact curricula, assessments, and student competencies.
- It also explores the ethical questions and concerns that generative AI and LLMs have raised for computing educators and professionals.
- The paper presents an assignment within a course on professional competencies, including ethics, for computing master's students.
- The assignment involved students discussing an ethical case study, using an LLM as a discussion partner, and reflecting on the experience.
Plain English Explanation
As large language models (LLMs) have become more advanced, educators have started to think about how they might affect the way students learn and are evaluated. These powerful AI systems have also raised ethical questions for people working in the computing field.
In this study, the researchers gave students in a master's-level course an assignment related to professional ethics. The students were asked to discuss a fictional scenario where a researcher is deciding whether to attend a conference in Hawaii. They used an LLM as a partner to help them explore the ethical considerations involved.
The students found the LLM to be a useful tool for expanding their knowledge and understanding of the case. However, they also recognized that the LLM suggested some unrealistic options. Ultimately, the students had to choose the course of action themselves, which the researchers saw as a positive outcome.
The researchers noted that some students didn't fully perceive the LLM as a tool, but rather as an authoritative source of information. This suggests that educators may need to provide more guidance to students on how to effectively use LLMs, especially when it comes to practicing critical thinking around ethical dilemmas.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents an assignment within a course on professional competencies, including ethics, for computing master's students. The assignment involved three main tasks:
- Participating in in-class discussions on a case study about a fictional researcher considering whether to attend the real CHI 2024 conference in Hawaii.
- Using an LLM of their choice as a discussion partner for the case study.
- Documenting both the in-class discussions and the discussions with the LLM, and reflecting on their experience using the LLM.
The students reported positive experiences with the LLM, noting that it helped increase their knowledge and understanding of the case. However, they also identified limitations, as the LLM suggested some unfeasible options. Importantly, the LLM did not select a course of action, so the students had to choose for themselves, which the researchers saw as a coherent outcome.
The researchers observed that some students did not perceive the LLM as a tool, but rather as an authoritative source of knowledge. This suggests a need for more instruction for students on using LLMs, particularly when it comes to practicing critical thinking around ethical concerns related to LLMs and navigating their moral implications.
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge that their study is limited in scope, as it only involved a single assignment within a single course. They also note that the students' experiences may have been influenced by their prior knowledge and familiarity with LLMs.
One potential concern is that students may become overly reliant on LLMs as a source of information, rather than developing their own critical thinking skills. The researchers emphasize the need for careful guidance and instruction to help students use LLMs effectively as tools, rather than treating them as authoritative sources.
Additionally, the paper does not delve deeply into the specific ethical considerations or dilemmas that were explored in the case study. It would be interesting to see a more detailed analysis of the ethical issues raised and how the LLM and students grappled with them.
Overall, the study provides a useful starting point for understanding how LLMs can be integrated into computing ethics education. However, more research is needed to fully explore the long-term implications and best practices for using LLMs in this context.
Conclusion
This paper presents an interesting approach to integrating large language models (LLMs) into a computing ethics course. The researchers found that students generally had positive experiences using an LLM as a discussion partner, but they also identified the need for more guidance and instruction on effectively using these tools.
The findings suggest that LLMs can be a valuable resource for expanding students' knowledge and understanding of ethical dilemmas, but educators must be careful to ensure that students develop their own critical thinking skills and do not simply rely on the LLM as an authoritative source.
As the use of LLMs in education continues to evolve, this study offers important insights for computing educators and highlights the need for further research on the ethical implications and best practices for integrating these powerful AI systems into the classroom.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
👁️
I'm categorizing LLM as a productivity tool: Examining ethics of LLM use in HCI research practices
Shivani Kapania, Ruiyi Wang, Toby Jia-Jun Li, Tianshi Li, Hong Shen

0
0
Large language models are increasingly applied in real-world scenarios, including research and education. These models, however, come with well-known ethical issues, which may manifest in unexpected ways in human-computer interaction research due to the extensive engagement with human subjects. This paper reports on research practices related to LLM use, drawing on 16 semi-structured interviews and a survey conducted with 50 HCI researchers. We discuss the ways in which LLMs are already being utilized throughout the entire HCI research pipeline, from ideation to system development and paper writing. While researchers described nuanced understandings of ethical issues, they were rarely or only partially able to identify and address those ethical concerns in their own projects. This lack of action and reliance on workarounds was explained through the perceived lack of control and distributed responsibility in the LLM supply chain, the conditional nature of engaging with ethics, and competing priorities. Finally, we reflect on the implications of our findings and present opportunities to shape emerging norms of engaging with large language models in HCI research.
4/1/2024
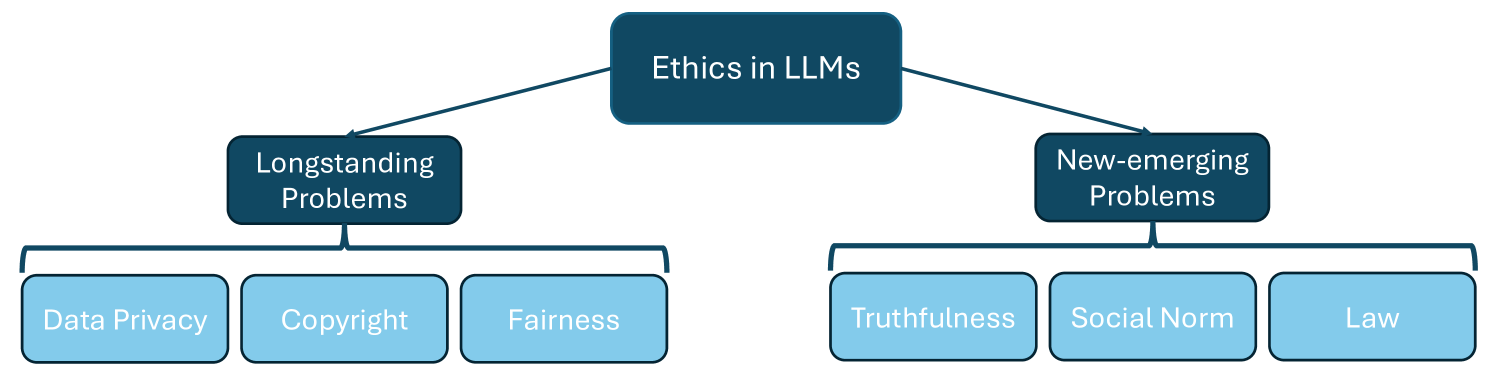
Deconstructing The Ethics of Large Language Models from Long-standing Issues to New-emerging Dilemmas
Chengyuan Deng, Yiqun Duan, Xin Jin, Heng Chang, Yijun Tian, Han Liu, Henry Peng Zou, Yiqiao Jin, Yijia Xiao, Yichen Wang, Shenghao Wu, Zongxing Xie, Kuofeng Gao, Sihong He, Jun Zhuang, Lu Cheng, Haohan Wang

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved unparalleled success across diverse language modeling tasks in recent years. However, this progress has also intensified ethical concerns, impacting the deployment of LLMs in everyday contexts. This paper provides a comprehensive survey of ethical challenges associated with LLMs, from longstanding issues such as copyright infringement, systematic bias, and data privacy, to emerging problems like truthfulness and social norms. We critically analyze existing research aimed at understanding, examining, and mitigating these ethical risks. Our survey underscores integrating ethical standards and societal values into the development of LLMs, thereby guiding the development of responsible and ethically aligned language models.
6/11/2024
🔍
Navigating LLM Ethics: Advancements, Challenges, and Future Directions
Junfeng Jiao, Saleh Afroogh, Yiming Xu, Connor Phillips

0
0
This study addresses ethical issues surrounding Large Language Models (LLMs) within the field of artificial intelligence. It explores the common ethical challenges posed by both LLMs and other AI systems, such as privacy and fairness, as well as ethical challenges uniquely arising from LLMs. It highlights challenges such as hallucination, verifiable accountability, and decoding censorship complexity, which are unique to LLMs and distinct from those encountered in traditional AI systems. The study underscores the need to tackle these complexities to ensure accountability, reduce biases, and enhance transparency in the influential role that LLMs play in shaping information dissemination. It proposes mitigation strategies and future directions for LLM ethics, advocating for interdisciplinary collaboration. It recommends ethical frameworks tailored to specific domains and dynamic auditing systems adapted to diverse contexts. This roadmap aims to guide responsible development and integration of LLMs, envisioning a future where ethical considerations govern AI advancements in society.
7/1/2024

Exploring and steering the moral compass of Large Language Models
Alejandro Tlaie

0
0
Large Language Models (LLMs) have become central to advancing automation and decision-making across various sectors, raising significant ethical questions. This study proposes a comprehensive comparative analysis of the most advanced LLMs to assess their moral profiles. We subjected several state-of-the-art models to a selection of ethical dilemmas and found that all the proprietary ones are mostly utilitarian and all of the open-weights ones align mostly with values-based ethics. Furthermore, when using the Moral Foundations Questionnaire, all models we probed - except for Llama 2-7B - displayed a strong liberal bias. Lastly, in order to causally intervene in one of the studied models, we propose a novel similarity-specific activation steering technique. Using this method, we were able to reliably steer the model's moral compass to different ethical schools. All of these results showcase that there is an ethical dimension in already deployed LLMs, an aspect that is generally overlooked.
6/7/2024