Network Sovereignty: A Novel Metric and its Application on Network Design

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
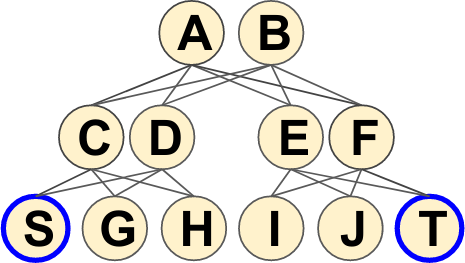
- The paper introduces a new metric called "network sovereignty" to measure the dependability and resilience of communication networks.
- The metric quantifies the diversity of paths available between nodes, capturing the network's ability to maintain connectivity in the face of component failures.
- The authors apply this metric to analyze different network architectures and demonstrate its utility in guiding network design decisions.
Plain English Explanation
The paper introduces a new way to measure how resilient and dependable a communication network is. This "network sovereignty" metric looks at the different paths data can take to travel between points in the network. The more diverse these paths are, the more the network can withstand things like equipment failures or other disruptions and still maintain connections.
By applying this metric to analyze different network designs, the researchers show how it can be a useful tool to help decide how to best set up a network to make it more reliable and less vulnerable to problems. The metric provides a way to quantify the network's ability to keep functioning even when parts of it fail or encounter issues.
Technical Explanation
The paper proposes a new metric called "network sovereignty" to measure the dependability and resilience of communication networks. This metric captures the path set diversity available between nodes, which reflects the network's ability to maintain connectivity even when individual components fail.
The authors demonstrate the utility of this metric by applying it to analyze different network architectures, including those designed for security against [manufacturer failures]. They show how the network sovereignty metric can guide network design decisions to improve overall dependability and resilience.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a novel and well-justified approach to quantifying network resilience through the lens of path set diversity. However, the authors acknowledge that the metric does not capture all aspects of network dependability, such as the reliability of individual components. Additionally, the analysis is primarily theoretical, and further empirical validation may be needed to demonstrate the metric's practical utility in real-world network design scenarios.
Conclusion
The introduction of the network sovereignty metric represents a valuable contribution to the field of network design and analysis. By focusing on the diversity of available communication paths, this metric provides a way to assess a network's ability to maintain crucial connections even in the face of component failures or other disruptions. While not a panacea, this work highlights the importance of considering path-level redundancy when aiming to build more dependable and resilient communication networks.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Network Sovereignty: A Novel Metric and its Application on Network Design
Shakthivelu Janardhanan, Maria Samonaki, Poul Einar Heegaard, Wolfgang Kellerer, Carmen Mas-Machuca
Most network planning problems in literature consider metrics such as cost, availability, and other technology-aware attributes. However, network operators now face new challenges in designing their networks to minimize their dependencies on manufacturers. A low dependency is associated with higher network robustness in case one or more manufacturers fail due to erroneous component design, geopolitical banning of manufacturers, or other reasons discussed in this work. Our work discusses network sovereignty, i.e., the ability to operate a network without dependencies on a particular manufacturer while minimizing the impact of simultaneous manufacturer failure(s). Network sovereignty is considered by solving the manufacturer assignment problem in the network such that robustness is maximized. The three main contributions of this work are (i) the discussion of network sovereignty as a special attribute of dependability, (ii) the introduction of a novel metric -- the Path Set Diversity (PSD) score to measure network sovereignty, and (iii) the introduction of Naga, an ILP formulation to maximize network sovereignty using the PSD score. We compare Naga's performance with centrality metrics-based heuristics and an availability-based optimization. Our work aims to be the foundation to guide network operators in increasing their network sovereignty.
Read more7/8/2024

0
Charting Censorship Resilience and Global Internet Reachability: A Quantitative Approach
Marina Ivanovi'c, Franc{c}ois Wirz, Jordi Subir`a Nieto, Adrian Perrig
Internet censorship and global Internet reachability are prevalent topics of today's Internet. Nonetheless, the impact of network topology and Internet architecture to these aspects of the Internet is under-explored. With the goal of informing policy discussions with an objective basis, we present an approach for evaluating both censorship resilience and global Internet reachability using quantitative network metrics, which are applicable to current BGP/IP networks and also to alternative Internet network architectures. We devise and instantiate the metric on the network topology of multiple countries, comparing the BGP/IP network, an overlay network using a waypoint mechanism for circumventing undesired nodes, and the path-aware Internet architecture SCION. The novelty of the approach resides in providing a metric enabling the analysis of these aspects of the Internet at the routing level, taking into account the innate properties of the routing protocol and architecture. We demonstrate that the Internet topology matters, and strongly influences both censorship resilience and reachability to the global Internet. Finally, we argue that access to multiple paths accompanied with path-awareness could enable a higher level of censorship resilience compared to the current Internet, and reduce the centralization of Internet routing.
Read more7/19/2024


0
Security Evaluation in Software-Defined Networks
Igor Ivki'c, Dominik Thiede, Nicholas Race, Matthew Broadbent, Antonios Gouglidis
Cloud computing has grown in importance in recent years which has led to a significant increase in Data Centre (DC) network requirements. A major driver of this change is virtualisation, which allows computing resources to be deployed on a large scale. However, traditional DCs, with their network topology and proliferation of network endpoints, are struggling to meet the flexible, centrally managed requirements of cloud computing applications. Software-Defined Networks (SDN) promise to offer a solution to these growing networking requirements by separating control functions from data routing. This shift adds more flexibility to networks but also introduces new security issues. This article presents a framework for evaluating security of SDN architectures. In addition, through an experimental study, we demonstrate how this framework can identify the threats and vulnerabilities, calculate their risks and severity, and provide the necessary measures to mitigate them. The proposed framework helps administrators to evaluate SDN security, address identified threats and meet network security requirements.
Read more8/22/2024

0
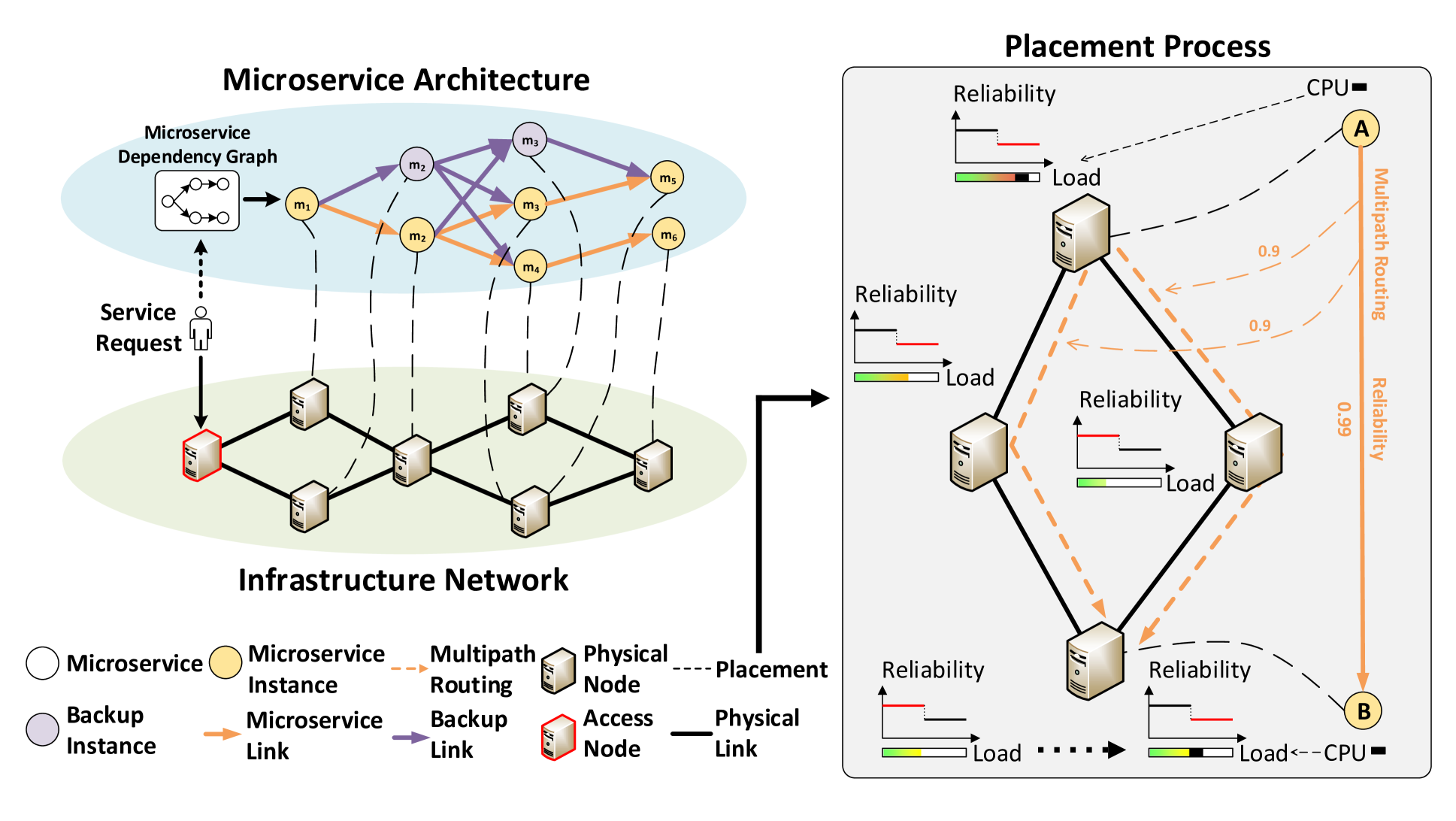
Network-Aware Reliability Modeling and Optimization for Microservice Placement
Fangyu Zhang, Yuang Chen, Hancheng Lu, Yongsheng Huang
Optimizing microservice placement to enhance the reliability of services is crucial for improving the service level of microservice architecture-based mobile networks and Internet of Things (IoT) networks. Despite extensive research on service reliability, the impact of network load and routing on service reliability remains understudied, leading to suboptimal models and unsatisfactory performance. To address this issue, we propose a novel network-aware service reliability model that effectively captures the correlation between network state changes and reliability. Based on this model, we formulate the microservice placement problem as an integer nonlinear programming problem, aiming to maximize service reliability. Subsequently, a service reliability-aware placement (SRP) algorithm is proposed to solve the problem efficiently. To reduce bandwidth consumption, we further discuss the microservice placement problem with the shared backup path mechanism and propose a placement algorithm based on the SRP algorithm using shared path reliability calculation, known as the SRP-S algorithm. Extensive simulations demonstrate that the SRP algorithm reduces service failures by up to 29% compared to the benchmark algorithms. By introducing the shared backup path mechanism, the SRP-S algorithm reduces bandwidth consumption by up to 62% compared to the SRP algorithm with the fully protected path mechanism. It also reduces service failures by up to 21% compared to the SRP algorithm with the shared backup mechanism.
Read more5/29/2024