Operating System And Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Provides a systematic review of the relationship between operating systems and artificial intelligence (AI)
- Examines how operating systems and AI can work together to enhance computing capabilities
- Explores the challenges and opportunities in integrating AI into operating systems
Plain English Explanation
The paper explores the intersection of operating systems and artificial intelligence. Operating systems are the software that manage a computer's hardware and provide a platform for running applications. AI refers to the development of computer systems that can perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence, such as learning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
The researchers examine how operating systems and AI can be integrated to create more advanced and capable computing systems. For example, AI techniques could be used to optimize resource allocation, improve system performance, and enhance security within an operating system. Conversely, operating systems could provide the necessary infrastructure and support to deploy and manage AI applications effectively.
The paper also discusses the challenges involved in seamlessly integrating AI into operating systems. These include issues related to system complexity, security, resource management, and the need for new programming models and development tools. Overcoming these challenges could unlock significant potential in areas such as cloud computing, edge devices, and high-performance computing.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents a systematic review of the existing research on the relationship between operating systems and AI. The authors conducted a comprehensive literature search to identify relevant studies, which they then analyzed and synthesized to provide an overview of the current state of the field.
The review covers various ways in which operating systems and AI can be integrated, including:
- Resource Management: AI techniques can be used to optimize resource allocation, such as CPU, memory, and energy, to improve overall system performance and efficiency.
- System Optimization: AI models can be trained to monitor system behavior and make dynamic adjustments to enhance performance, reliability, and security.
- AI-Powered Applications: Operating systems can provide the necessary infrastructure and support for deploying and managing AI-powered applications, such as virtual assistants and computer vision systems.
- Programming Models and Tools: New programming models and development tools may be required to enable seamless integration of AI into operating systems, addressing challenges related to system complexity and maintainability.
The paper also discusses the key challenges and opportunities in this area, such as the need for robust security mechanisms, the management of system complexity, and the potential impact on cloud computing, edge devices, and high-performance computing.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive and well-structured review of the existing research on the integration of operating systems and AI. The authors have done a thorough job of identifying and synthesizing the relevant literature, highlighting the various ways in which these two domains can be combined to enhance computing capabilities.
One potential limitation of the review is that it may not capture the latest developments in this rapidly evolving field, as the paper was likely written some time before its publication. Additionally, the review focuses primarily on the technical aspects of the integration, and does not delve deeply into the broader societal and ethical implications of AI-powered operating systems, such as issues related to privacy, bias, and accountability.
Further research could explore these broader implications, as well as investigate more specific use cases and real-world deployments of AI-infused operating systems. Empirical studies evaluating the performance and effectiveness of such systems would also be valuable in providing a more nuanced understanding of the benefits and challenges involved.
Conclusion
This systematic review underscores the significant potential of integrating operating systems and AI to create more advanced and capable computing systems. By harnessing the strengths of both domains, researchers and developers can address challenges related to resource management, system optimization, and the deployment of AI-powered applications.
However, the successful integration of operating systems and AI also requires addressing complex technical and societal challenges, such as ensuring robust security, managing system complexity, and addressing the ethical implications of AI-powered systems. Ongoing research and innovation in this area can help unlock the full potential of this convergence, with far-reaching implications for various industries and applications.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Operating System And Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review
Yifan Zhang, Xinkui Zhao, Jianwei Yin, Lufei Zhang, Zuoning Chen
In the dynamic landscape of technology, the convergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Operating Systems (OS) has emerged as a pivotal arena for innovation. Our exploration focuses on the symbiotic relationship between AI and OS, emphasizing how AI-driven tools enhance OS performance, security, and efficiency, while OS advancements facilitate more sophisticated AI applications. We delve into various AI techniques employed to optimize OS functionalities, including memory management, process scheduling, and intrusion detection. Simultaneously, we analyze the role of OS in providing essential services and infrastructure that enable effective AI application execution, from resource allocation to data processing. The article also addresses challenges and future directions in this domain, emphasizing the imperative of secure and efficient AI integration within OS frameworks. By examining case studies and recent developments, our review provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of AI-OS integration, underscoring its significance in shaping the next generation of computing technologies. Finally, we explore the promising prospects of Intelligent OSes, considering not only how innovative OS architectures will pave the way for groundbreaking opportunities but also how AI will significantly contribute to advancing these next-generation OSs.
Read more7/23/2024
🤖

0
Integrative Approaches in Cybersecurity and AI
Marwan Omar
In recent years, the convergence of cybersecurity, artificial intelligence (AI), and data management has emerged as a critical area of research, driven by the increasing complexity and interdependence of modern technological ecosystems. This paper provides a comprehensive review and analysis of integrative approaches that harness AI techniques to enhance cybersecurity frameworks and optimize data management practices. By exploring the synergies between these domains, we identify key trends, challenges, and future directions that hold the potential to revolutionize the way organizations protect, analyze, and leverage their data. Our findings highlight the necessity of cross-disciplinary strategies that incorporate AI-driven automation, real-time threat detection, and advanced data analytics to build more resilient and adaptive security architectures.
Read more8/13/2024


0
Artificial Intelligence in Industry 4.0: A Review of Integration Challenges for Industrial Systems
Alexander Windmann, Philipp Wittenberg, Marvin Schieseck, Oliver Niggemann
In Industry 4.0, Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) generate vast data sets that can be leveraged by Artificial Intelligence (AI) for applications including predictive maintenance and production planning. However, despite the demonstrated potential of AI, its widespread adoption in sectors like manufacturing remains limited. Our comprehensive review of recent literature, including standards and reports, pinpoints key challenges: system integration, data-related issues, managing workforce-related concerns and ensuring trustworthy AI. A quantitative analysis highlights particular challenges and topics that are important for practitioners but still need to be sufficiently investigated by academics. The paper briefly discusses existing solutions to these challenges and proposes avenues for future research. We hope that this survey serves as a resource for practitioners evaluating the cost-benefit implications of AI in CPS and for researchers aiming to address these urgent challenges.
Read more7/8/2024
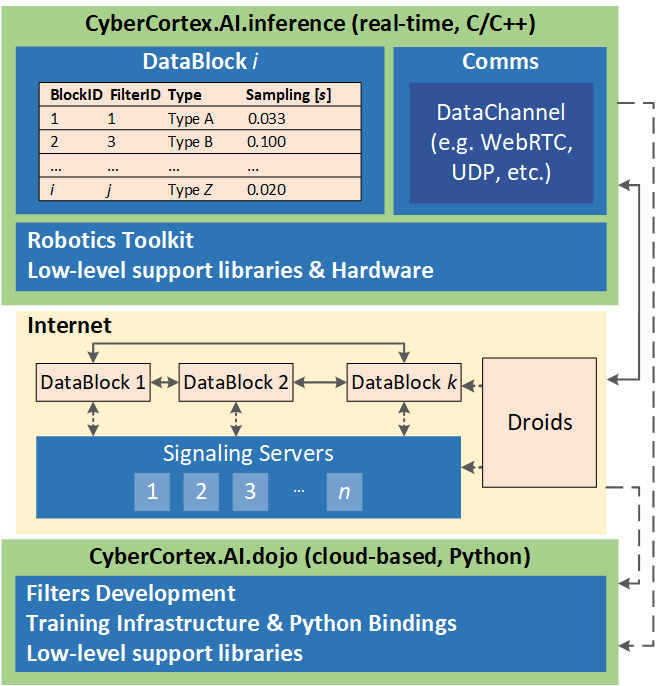

0
CyberCortex.AI: An AI-based Operating System for Autonomous Robotics and Complex Automation
Sorin Grigorescu, Mihai Zaha
The underlying framework for controlling autonomous robots and complex automation applications are Operating Systems (OS) capable of scheduling perception-and-control tasks, as well as providing real-time data communication to other robotic peers and remote cloud computers. In this paper, we introduce CyberCortex.AI, a robotics OS designed to enable heterogeneous AI-based robotics and complex automation applications. CyberCortex.AI is a decentralized distributed OS which enables robots to talk to each other, as well as to High Performance Computers (HPC) in the cloud. Sensory and control data from the robots is streamed towards HPC systems with the purpose of training AI algorithms, which are afterwards deployed on the robots. Each functionality of a robot (e.g. sensory data acquisition, path planning, motion control, etc.) is executed within a so-called DataBlock of Filters shared through the internet, where each filter is computed either locally on the robot itself, or remotely on a different robotic system. The data is stored and accessed via a so-called textit{Temporal Addressable Memory} (TAM), which acts as a gateway between each filter's input and output. CyberCortex.AI has two main components: i) the CyberCortex.AI.inference system, which is a real-time implementation of the DataBlock running on the robots' embedded hardware, and ii) the CyberCortex.AI.dojo, which runs on an HPC computer in the cloud, and it is used to design, train and deploy AI algorithms. We present a quantitative and qualitative performance analysis of the proposed approach using two collaborative robotics applications: textit{i}) a forest fires prevention system based on an Unitree A1 legged robot and an Anafi Parrot 4K drone, as well as textit{ii}) an autonomous driving system which uses CyberCortex.AI for collaborative perception and motion control.
Read more9/4/2024