Optimal Operation of Active RIS-Aided Wireless Powered Communications in IoT Networks

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper discusses the optimal operation of active reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided wireless powered communications in IoT networks.
- It presents an optimization framework to maximize the sum throughput of IoT devices while considering the energy harvesting and transmission phases.
- The proposed approach dynamically adjusts the RIS reflection coefficients and the IoT device transmit power to optimize the system performance.
Plain English Explanation
The research paper focuses on improving the efficiency of wireless communications in the Internet of Things (IoT) networks. IoT networks are systems where many different devices, like sensors and appliances, are connected to the internet and can communicate with each other.
One way to enhance these IoT networks is by using a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS). An RIS is a special type of surface that can actively control the reflection of wireless signals. This allows the RIS to focus the signals and improve the communication between IoT devices.
The researchers developed an optimization framework to determine the best way to operate the RIS and control the power used by the IoT devices. The goal is to maximize the overall data throughput of the IoT network, while also considering the energy harvesting and transmission needs of the individual devices.
By dynamically adjusting the RIS reflection coefficients and the IoT device transmit power, the proposed approach can help optimize the performance of the entire system. This could lead to more efficient and reliable wireless communications in IoT networks, which is important as these networks become more widespread.
Technical Explanation
The paper presents an optimization framework for the optimal operation of active RIS-aided wireless powered communications in IoT networks. The goal is to maximize the sum throughput of the IoT devices, considering both the energy harvesting and data transmission phases.
The system model includes an access point that wirelessly powers the IoT devices using a dedicated energy signal. The IoT devices then use the harvested energy to transmit their data to the access point, with the assistance of an active RIS. The RIS can dynamically adjust its reflection coefficients to optimize the wireless links.
The researchers formulate an optimization problem to jointly optimize the RIS reflection coefficients and the IoT device transmit power. This involves considering the trade-off between energy harvesting and data transmission, as well as the coupling between the RIS and the IoT device power allocation.
To solve this problem, the authors propose an efficient algorithm that iteratively updates the RIS coefficients and the IoT device transmit power. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed approach can significantly improve the sum throughput compared to benchmark schemes, especially in scenarios with limited energy harvesting resources.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a valuable optimization framework for active RIS-aided wireless powered communications in IoT networks. The key strengths of the research include:
- Addressing an important problem in the context of IoT networks, which are becoming increasingly widespread and rely on efficient wireless communications.
- Incorporating the trade-off between energy harvesting and data transmission, which is crucial for battery-powered IoT devices.
- Proposing an efficient algorithm to jointly optimize the RIS reflection coefficients and IoT device transmit power.
However, the paper also has some limitations:
- The system model assumes perfect channel state information, which may not always be realistic in practical scenarios.
- The analysis is limited to a single-cell setup, while real-world IoT networks may involve interference from neighboring cells.
- The proposed solution may require significant computational resources, which could be a challenge for resource-constrained IoT devices.
Future research could explore ways to address these limitations, such as incorporating imperfect CSI, multi-cell interference, and distributed optimization algorithms. Additionally, experimental validation of the proposed approach would provide valuable insights into its real-world performance.
Conclusion
The research paper presents an optimization framework for the optimal operation of active RIS-aided wireless powered communications in IoT networks. By jointly optimizing the RIS reflection coefficients and IoT device transmit power, the proposed approach can significantly improve the overall system throughput.
This work highlights the potential of active RIS technology to enhance the efficiency and reliability of wireless communications in IoT networks, which is crucial as these networks continue to grow in scale and importance. The findings of this research could contribute to the development of more advanced and energy-efficient IoT systems, with the potential to benefit a wide range of applications and industries.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Optimal Operation of Active RIS-Aided Wireless Powered Communications in IoT Networks
Waqas Khalid, A. -A. A. Boulogeorgos, Trinh Van Chien, Junse Lee, Howon Lee, Heejung Yu
Wireless-powered communications (WPCs) are increasingly crucial for extending the lifespan of low-power Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Furthermore, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) can create favorable electromagnetic environments by providing alternative signal paths to counteract blockages. The strategic integration of WPC and RIS technologies can significantly enhance energy transfer and data transmission efficiency. However, passive RISs suffer from double-fading attenuation over RIS-aided cascaded links. In this article, we propose the application of an active RIS within WPC-enabled IoT networks. The enhanced flexibility of the active RIS in terms of energy transfer and information transmission is investigated using adjustable parameters. We derive novel closed-form expressions for the ergodic rate and outage probability by incorporating key parameters, including signal amplification, active noise, power consumption, and phase quantization errors. Additionally, we explore the optimization of WPC scenarios, focusing on the time-switching factor and power consumption of the active RIS. The results validate our analysis, demonstrating that an active RIS significantly enhances WPC performance compared to a passive RIS.
Read more9/17/2024


0
Active Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-Aided Terahertz Wireless Communications
Waqas Khalid, Heejung Yu, Yazdan Ahmad Qadri
Terahertz (THz) communication is expected to be a key technology for future sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks. Furthermore, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS) have been proposed to modify the wireless propagation environment and enhance system performance. Given the sensitivity to blockages and limited coverage range, RIS is particularly promising for THz communications. Active RIS can overcome the multiplicative fading effect in RIS-aided communications. In this paper, we explore active RIS-assisted THz communications. We formulate the ergodic rate, considering factors associated with active RIS, including active noise and signal amplification, and THz signals, including molecular absorption and beam misalignment
Read more7/29/2024
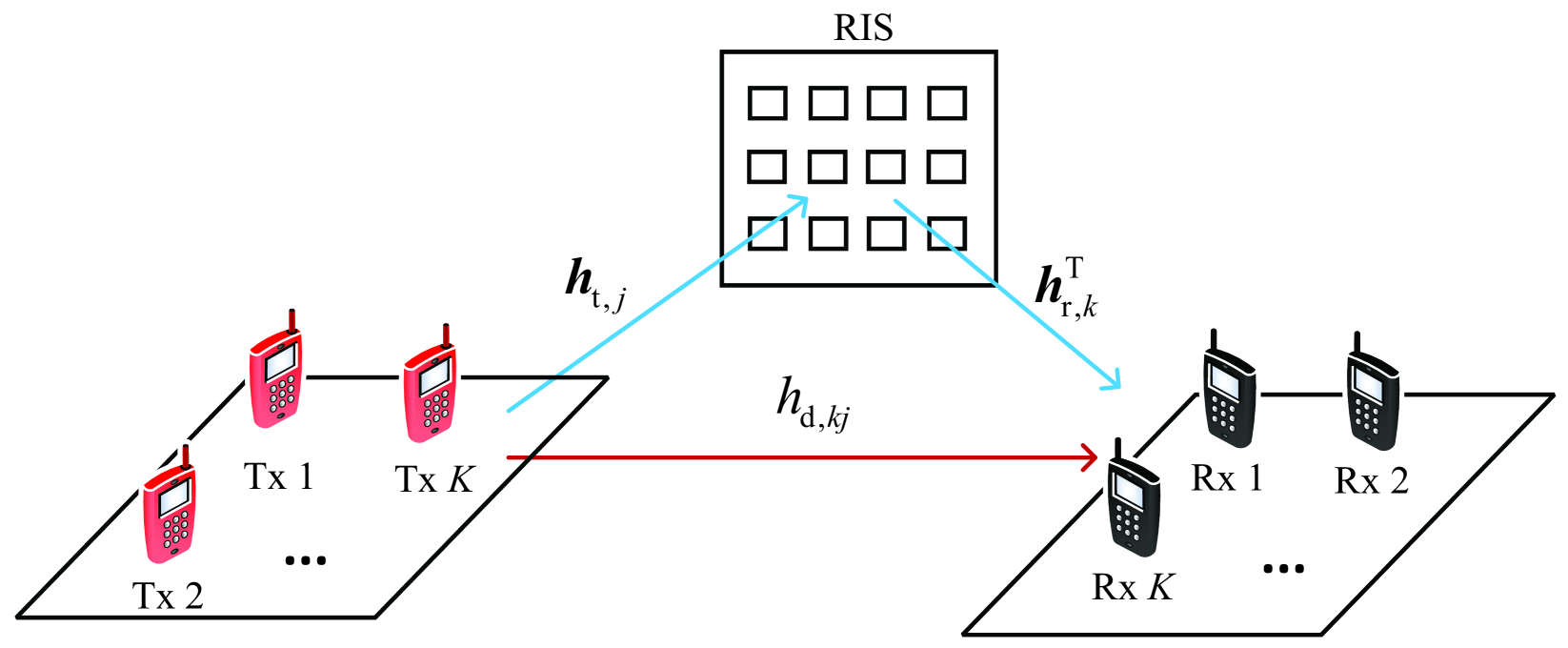

0
Power-Aware Sparse Reflect Beamforming in Active RIS-aided Interference Channels
Ruizhe Long, Hu Zhou, Ying-Chang Liang
Active reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) has attracted significant attention in wireless communications, due to its reflecting elements (REs) capable of reflecting incident signals with not only phase shifts but also amplitude amplifications. In this paper, we are interested in active RIS-aided interference channels in which $K$ user pairs share the same time and frequency resources with the aid of active RIS. Thanks to the promising amplitude amplification capability, activating a moderate number of REs, rather than all of them, is sufficient for the active RIS to mitigate cross-channel interferences. Motivated by this, we propose a power-aware sparse reflect beamforming design for the active RIS-aided interference channels, which allows the active RIS to flexibly adjust the number of activated REs for the sake of reducing hardware and power costs. Specifically, we establish the power consumption model in which only those activated REs consume the biasing and operation power that supports the amplitude amplification, yielding an $ell_0$-norm power consumption function. Based on the proposed model, we investigate a sum-rate maximization problem and an active RIS power minimization problem by carefully designing the sparse reflect beamforming vector. To solve these problems, we first replace the nonconvex $ell_0$-norm function with an iterative reweighted $ell_1$-norm function. Then, fractional programming is used to solve the sum-rate maximization, while semidefinite programming together with the difference-of-convex algorithm (DCA) is used to solve the active RIS power minimization. Numerical results show that the proposed sparse designs can notably increase the sum rate of user pairs and decrease the power consumption of active RIS in interference channels.
Read more4/1/2024


0
Active RIS-Aided Terahertz Communications with Phase Error and Beam Misalignment
Waqas Khalid, Heejung Yu, Farman Ali, Huiping Huang
Terahertz (THz) communications will be pivotal in sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks, offering significantly wider bandwidths and higher data rates. However, the unique propagation characteristics of the THz frequency band, such as high path loss and sensitivity to blockages, pose substantial challenges. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) present a promising solution for enhancing THz communications by dynamically shaping the propagation environment to address these issues. Active RISs, in particular, can amplify reflected signals, effectively mitigating the multiplicative fading effects in RIS-aided links. Given the highly directional nature of THz signals, beam misalignment is a significant concern, while discrete phase shifting is more practical for real-world RIS deployment compared to continuous adjustments. This paper investigates the performance of active-RIS-aided THz communication systems, focusing on discrete phase shifts and beam misalignment. An expression for the ergodic capacity is derived, incorporating critical system parameters to assess performance. Numerical results offer insights into optimizing active-RIS-aided THz communication systems.
Read more9/17/2024