Optimizing Layerwise Microservice Management in Heterogeneous Wireless Networks
2405.11359

0
0
Abstract
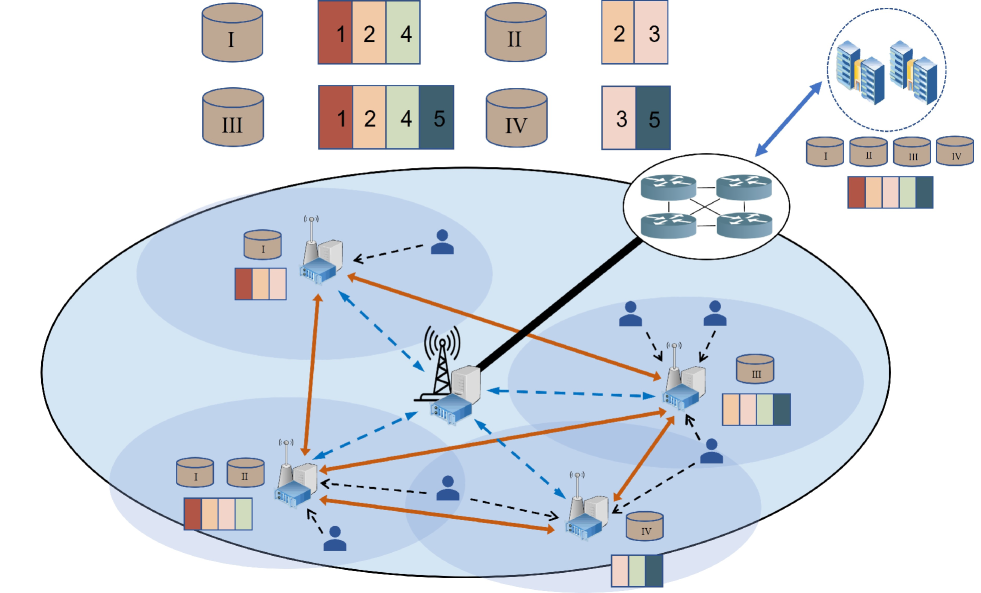
Small cells with edge computing are densely deployed in 5G mobile networks to provide high throughput communication and low-latency computation. The flexibility of edge computation is empowered by the deployment of lightweight container-based microservices. In this paper, we take the first step toward optimizing the microservice management in small-cell networks. The prominent feature is that each microservice consists of multiple image layers and different microservices may share some basic layers, thus bringing deep coupling in their placement and service provision. Our objective is to minimize the expected total latency of microservice requests under the storage, communication and computing constraints of the sparsely interconnected small cell nodes. We formulate a binary quadratic program (BQP) with the multi-dimensional strategy of the image layer placement, the access selection and the task assignment. The BQP problem is then transformed into an ILP problem, and is solved by use of a novel sphere-box alternating direction multipliers method (ADMM) with reasonable complexity $O(q^{4})$, where $q$ is the number of variables in the transformed problem. Trace-driven experiments show that the gap between our proposed algorithm and the optimal is reduced by 35$%$ compared with benchmark algorithms.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper presents an optimization framework for managing microservices in heterogeneous wireless networks, such as small cell networks and mobile edge computing environments.
- The proposed approach aims to optimize the placement and resource allocation of microservices across a multi-layer network infrastructure to improve performance and reduce costs.
- The authors formulate the problem as a binary quadratic program and solve it using a sphere-box Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) algorithm.
Plain English Explanation
In modern computing, applications are often broken down into smaller, modular components called microservices. These microservices can be deployed and scaled independently, allowing for more flexible and efficient system management. However, in a heterogeneous wireless network, such as one that combines small cell networks and mobile edge computing, the placement and resource allocation of these microservices can be a complex optimization problem.
This paper presents a framework to help solve this problem. The researchers formulate the microservice management task as a binary quadratic program, which is a type of optimization problem. They then use a technique called the sphere-box Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) to solve this optimization problem and determine the best way to distribute the microservices across the network infrastructure.
The key idea is to find the optimal placement of microservices and the corresponding resource allocation (such as CPU, memory, and bandwidth) to improve overall performance and reduce costs. This could be important in scenarios where computing resources are limited, or where the network infrastructure is diverse and needs to be managed efficiently.
By breaking down the problem in this way and using advanced optimization techniques, the researchers aim to provide a systematic approach to managing microservices in complex, heterogeneous wireless environments. This could have applications in link to "optimal-service-placement-request-routing-cpu-sizing", link to "cost-minimization-multi-cloud-systems-runtime-microservice", link to "slice-aware-resource-allocation-admission-control-smart", and other areas where efficient microservice management is crucial.
Technical Explanation
The researchers formulate the microservice management problem as a binary quadratic program, where the decision variables represent the placement of microservices across the network infrastructure. The objective function aims to minimize the overall cost, which includes factors such as service latency, resource utilization, and network congestion.
To solve this optimization problem, the authors propose a sphere-box Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) algorithm. This algorithm iteratively updates the placement decisions and the resource allocation, converging to the optimal solution. The sphere-box ADMM approach is designed to handle the binary nature of the placement decisions, which makes the problem challenging to solve using traditional optimization methods.
The proposed framework is evaluated through simulations, considering a heterogeneous network with small cells and mobile edge computing nodes. The results demonstrate that the sphere-box ADMM algorithm can effectively optimize the microservice placement and resource allocation, leading to improvements in performance metrics such as link to "multi-scale-topology-optimization-using-neural-networks" and link to "enhancing-sum-rate-performance-constrained-multicell-networks".
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a well-designed optimization framework for microservice management in heterogeneous wireless networks. The binary quadratic programming formulation and the sphere-box ADMM algorithm appear to be suitable approaches for this problem, as they can handle the complex constraints and decision variables involved.
However, the authors do not provide a detailed analysis of the computational complexity of the proposed algorithm, which could be an important consideration for real-world deployments. Additionally, the simulation-based evaluation, while informative, may not fully capture the challenges of implementing this framework in a live network environment.
Further research could explore the performance of the proposed approach under different network topologies, traffic patterns, and microservice characteristics. Investigating the scalability of the algorithm as the number of microservices and network nodes increases would also be valuable.
Conclusion
This paper introduces an optimization-based framework for managing microservices in heterogeneous wireless networks, such as small cell networks and mobile edge computing environments. By formulating the problem as a binary quadratic program and solving it using a sphere-box ADMM algorithm, the researchers demonstrate a systematic approach to optimizing microservice placement and resource allocation.
The proposed framework could have significant implications for improving the performance and cost-efficiency of microservice-based applications in diverse network settings. The techniques presented in this paper could be further developed and applied to link to "optimal-service-placement-request-routing-cpu-sizing", link to "cost-minimization-multi-cloud-systems-runtime-microservice", link to "slice-aware-resource-allocation-admission-control-smart", and other areas where efficient microservice management is crucial.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
Optimal Service Placement, Request Routing and CPU Sizing in Cooperative Mobile Edge Computing Networks for Delay-Sensitive Applications
Naeimeh Omidvar, Mahdieh Ahmadi, Seyed Mohammad Hosseini

0
0
We study joint optimization of service placement, request routing, and CPU sizing in a cooperative MEC system. The problem is considered from the perspective of the service provider (SP), which delivers heterogeneous MEC-enabled delay-sensitive services, and needs to pay for the used resources to the mobile network operators and the cloud provider, while earning revenue from the served requests. We formulate the problem of maximizing the SP's total profit subject to the computation, storage, and communication constraints of each edge node and end-to-end delay requirements of the services as a mixed-integer non-convex optimization problem, and prove it to be NP-hard. To tackle the challenges in solving the problem, we first introduce a design trade-off parameter for different delay requirements of each service, which maintains flexibility in prioritizing them, and transform the original optimization problem by the new delay constraints. Then, by exploiting a hidden convexity, we reformulate the delay constraints into an equivalent form. Next, to handle the challenge of the complicating (integer) variables, using primal decomposition, we decompose the problem into an equivalent form of master and inner sub-problems over the mixed and real variables, respectively. We then employ a cutting-plane approach for building up adequate representations of the extremal value of the inner problem as a function of the complicating variables and the set of values of the complicating variables for which the inner problem is feasible. Finally, we propose a solution strategy based on generalized Benders decomposition and prove its convergence to the optimal solution within a limited number of iterations. Extensive simulation results demonstrate that the proposed scheme significantly outperforms the existing mechanisms in terms of the SP's profit, cache hit ratio, running time, and end-to-end delay.
5/20/2024
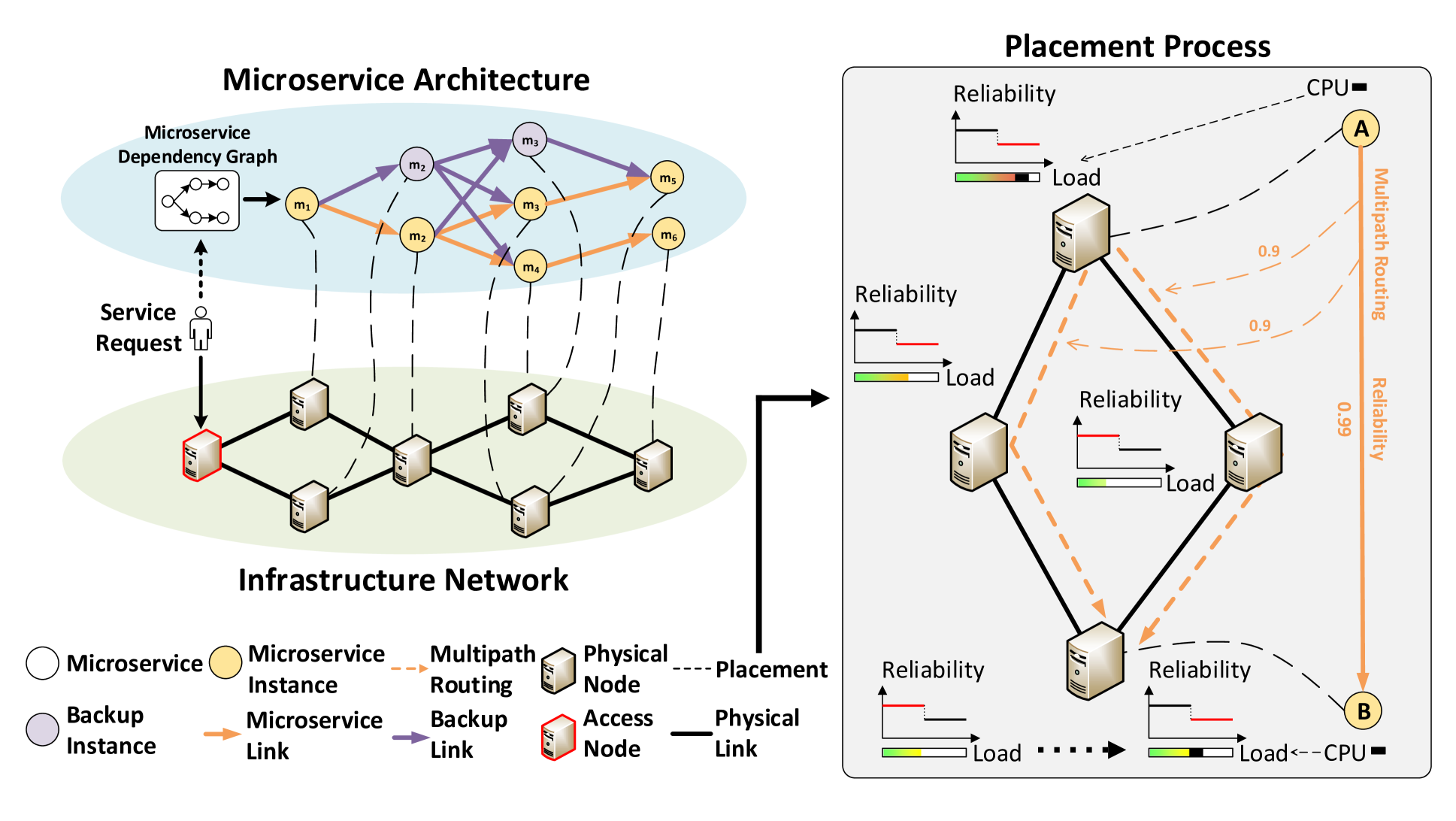
Network-Aware Reliability Modeling and Optimization for Microservice Placement
Fangyu Zhang, Yuang Chen, Hancheng Lu, Yongsheng Huang

0
0
Optimizing microservice placement to enhance the reliability of services is crucial for improving the service level of microservice architecture-based mobile networks and Internet of Things (IoT) networks. Despite extensive research on service reliability, the impact of network load and routing on service reliability remains understudied, leading to suboptimal models and unsatisfactory performance. To address this issue, we propose a novel network-aware service reliability model that effectively captures the correlation between network state changes and reliability. Based on this model, we formulate the microservice placement problem as an integer nonlinear programming problem, aiming to maximize service reliability. Subsequently, a service reliability-aware placement (SRP) algorithm is proposed to solve the problem efficiently. To reduce bandwidth consumption, we further discuss the microservice placement problem with the shared backup path mechanism and propose a placement algorithm based on the SRP algorithm using shared path reliability calculation, known as the SRP-S algorithm. Extensive simulations demonstrate that the SRP algorithm reduces service failures by up to 29% compared to the benchmark algorithms. By introducing the shared backup path mechanism, the SRP-S algorithm reduces bandwidth consumption by up to 62% compared to the SRP algorithm with the fully protected path mechanism. It also reduces service failures by up to 21% compared to the SRP algorithm with the shared backup mechanism.
5/29/2024
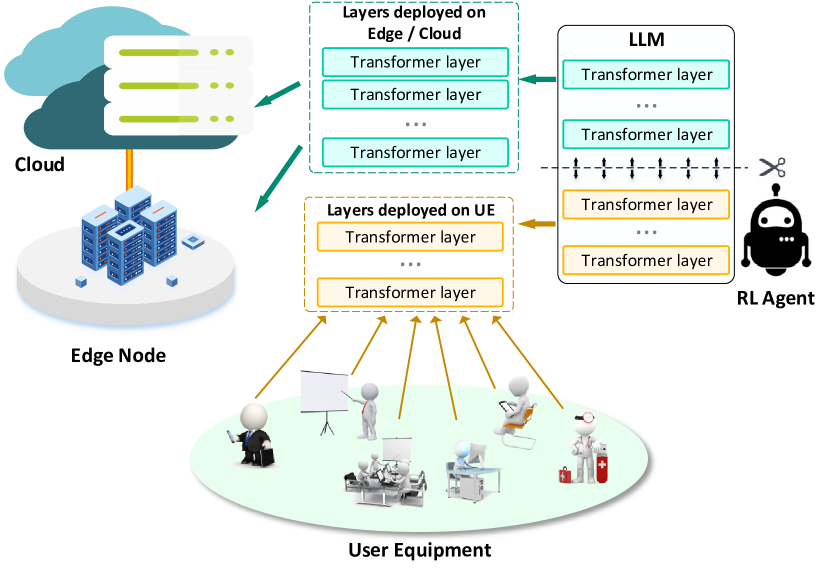
Adaptive Layer Splitting for Wireless LLM Inference in Edge Computing: A Model-Based Reinforcement Learning Approach
Yuxuan Chen, Rongpeng Li, Xiaoxue Yu, Zhifeng Zhao, Honggang Zhang

0
0
Optimizing the deployment of large language models (LLMs) in edge computing environments is critical for enhancing privacy and computational efficiency. Toward efficient wireless LLM inference in edge computing, this study comprehensively analyzes the impact of different splitting points in mainstream open-source LLMs. On this basis, this study introduces a framework taking inspiration from model-based reinforcement learning (MBRL) to determine the optimal splitting point across the edge and user equipment (UE). By incorporating a reward surrogate model, our approach significantly reduces the computational cost of frequent performance evaluations. Extensive simulations demonstrate that this method effectively balances inference performance and computational load under varying network conditions, providing a robust solution for LLM deployment in decentralized settings.
6/11/2024

Placing Timely Refreshing Services at the Network Edge
Xishuo Li, Shan Zhang, Hongbin Luo, Xiao Ma, Junyi He

0
0
Accommodating services at the network edge is favorable for time-sensitive applications. However, maintaining service usability is resource-consuming in terms of pulling service images to the edge, synchronizing databases of service containers, and hot updates of service modules. Accordingly, it is critical to determine which service to place based on the received user requests and service refreshing (maintaining) cost, which is usually neglected in existing studies. In this work, we study how to cooperatively place timely refreshing services and offload user requests among edge servers to minimize the backhaul transmission costs. We formulate an integer non-linear programming problem and prove its NP-hardness. This problem is highly non-tractable due to the complex spatial-and-temporal coupling effect among service placement, offloading, and refreshing costs. We first decouple the problem in the temporal domain by transforming it into a Markov shortest-path problem. We then propose a light-weighted Discounted Value Approximation (DVA) method, which further decouples the problem in the spatial domain by estimating the offloading costs among edge servers. The worst performance of DVA is proved to be bounded. 5G service placement testbed experiments and real-trace simulations show that DVA reduces the total transmission cost by up to 59.1% compared with the state-of-the-art baselines.
6/26/2024