Optimizing Structured Data Processing through Robotic Process Automation

0
📊
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a game-changing technology for data extraction and analysis.
- It has revolutionized how organizations process and analyze large volumes of documents like invoices, purchase orders, and payment advices.
- This study investigates the use of RPA for structured data extraction and evaluates its advantages over manual processes.
Plain English Explanation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that allows computers to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks that would typically be done by humans. In this study, the researchers looked at how effective RPA is at extracting important information from invoices, purchase orders, and other business documents.
Traditionally, companies would have employees manually read through these documents and pull out the key data. This can be time-consuming and prone to human error. With RPA, specialized software "bots" can quickly scan the documents and extract the relevant information with high accuracy.
The researchers compared the efficiency and accuracy of RPA bots to human workers performing the same data extraction tasks. They tested this across four different scenarios, involving varying numbers of invoices. The results showed that the RPA bots were significantly faster at completing the tasks and made zero errors, while the human workers took longer and had some mistakes.
These findings demonstrate the transformative potential of RPA technology. By automating these types of data extraction processes, businesses can improve their operational efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance the reliability of their operations. This allows them to focus their human resources on more strategic, high-value activities.
Technical Explanation
This study evaluates the use of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for structured data extraction from business documents like invoices, purchase orders, and payment advices. The researchers compared the efficiency and accuracy of RPA software bots against manual, human-performed data extraction tasks.
Across four distinct scenarios involving varying numbers of invoices, the researchers measured the time and effort required for task completion, as well as the error rates between the manual and RPA processes. The RPA system consistently demonstrated significant efficiency gains, with the bots completing the tasks in much less time compared to the human workers.
Moreover, the RPA system achieved perfect accuracy, with no errors in the data extraction, whereas the manual process had some mistakes. These results highlight the transformative potential of RPA in optimizing operational efficiency, reducing human labor costs, and improving overall business performance by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks.
Critical Analysis
The research provides compelling evidence for the advantages of using RPA technology over manual data extraction processes. However, it's important to consider some potential limitations and areas for further exploration.
The study focuses solely on structured data extraction from invoices, which may not represent the full range of document types and unstructured data that organizations need to process. Further research could investigate the effectiveness of RPA in handling more complex, less standardized documents.
Additionally, the study does not address the technical details of the RPA system's architecture or the specific algorithms and techniques used. Examining these aspects could provide valuable insights into the underlying capabilities and potential areas for improvement.
While the RPA system achieved perfect accuracy in this study, real-world deployment may introduce new challenges and edge cases that could affect its reliability. Ongoing monitoring and refinement of the RPA processes would be essential to maintain the desired level of performance.
Overall, this research highlights the significant benefits of RPA technology, but there is still room for further exploration and refinement to fully unlock its transformative potential in business operations.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates the powerful capabilities of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in structured data extraction, offering substantial improvements in efficiency and accuracy over manual, human-driven processes. The results underscore the transformative potential of RPA in optimizing business operations, reducing labor costs, and enhancing overall process reliability.
As organizations continue to grapple with the growing volume and complexity of their data, the adoption of RPA technology can be a game-changer, freeing up human resources to focus on more strategic, value-added activities. By automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, RPA can drive significant operational efficiencies and create new opportunities for organizations to enhance their competitiveness and better serve their customers.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
📊

0
Optimizing Structured Data Processing through Robotic Process Automation
Vivek Bhardwaj, Ajit Noonia, Sandeep Chaurasia, Mukesh Kumar, Abdulnaser Rashid, Mohamed Tahar Ben Othman
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has emerged as a game-changing technology in data extraction, revolutionizing the way organizations process and analyze large volumes of documents such as invoices, purchase orders, and payment advices. This study investigates the use of RPA for structured data extraction and evaluates its advantages over manual processes. By comparing human-performed tasks with those executed by RPA software bots, we assess efficiency and accuracy in data extraction from invoices, focusing on the effectiveness of the RPA system. Through four distinct scenarios involving varying numbers of invoices, we measure efficiency in terms of time and effort required for task completion, as well as accuracy by comparing error rates between manual and RPA processes. Our findings highlight the significant efficiency gains achieved by RPA, with bots completing tasks in significantly less time compared to manual efforts across all cases. Moreover, the RPA system consistently achieves perfect accuracy, mitigating the risk of errors and enhancing process reliability. These results underscore the transformative potential of RPA in optimizing operational efficiency, reducing human labor costs, and improving overall business performance.
Read more8/28/2024
➖

0
SmartFlow: Robotic Process Automation using LLMs
Arushi Jain, Shubham Paliwal, Monika Sharma, Lovekesh Vig, Gautam Shroff
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) systems face challenges in handling complex processes and diverse screen layouts that require advanced human-like decision-making capabilities. These systems typically rely on pixel-level encoding through drag-and-drop or automation frameworks such as Selenium to create navigation workflows, rather than visual understanding of screen elements. In this context, we present SmartFlow, an AI-based RPA system that uses pre-trained large language models (LLMs) coupled with deep-learning based image understanding. Our system can adapt to new scenarios, including changes in the user interface and variations in input data, without the need for human intervention. SmartFlow uses computer vision and natural language processing to perceive visible elements on the graphical user interface (GUI) and convert them into a textual representation. This information is then utilized by LLMs to generate a sequence of actions that are executed by a scripting engine to complete an assigned task. To assess the effectiveness of SmartFlow, we have developed a dataset that includes a set of generic enterprise applications with diverse layouts, which we are releasing for research use. Our evaluations on this dataset demonstrate that SmartFlow exhibits robustness across different layouts and applications. SmartFlow can automate a wide range of business processes such as form filling, customer service, invoice processing, and back-office operations. SmartFlow can thus assist organizations in enhancing productivity by automating an even larger fraction of screen-based workflows. The demo-video and dataset are available at https://smartflow-4c5a0a.webflow.io/.
Read more5/22/2024
👨🏫

0
Unveiling Latent Topics in Robotic Process Automation -- an Approach based on Latent Dirichlet Allocation Smart Review
Petr Prucha, Peter Madzik, Lukas Falat, Hajo A. Reijers
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a software technology that in recent years has gained a lot of attention and popularity. By now, research on RPA has spread into multiple research streams. This study aims to create a science map of RPA and its aspects by revealing latent topics related to RPA, their research interest, impact, and time development. We provide a systematic framework that is helpful to develop further research into this technology. By using an unsupervised machine learning method based on Latent Dirichlet Allocation, we were able to analyse over 2000 paper abstracts. Among these, we found 100 distinct study topics, 15 of which have been included in the science map we provide.
Read more4/10/2024
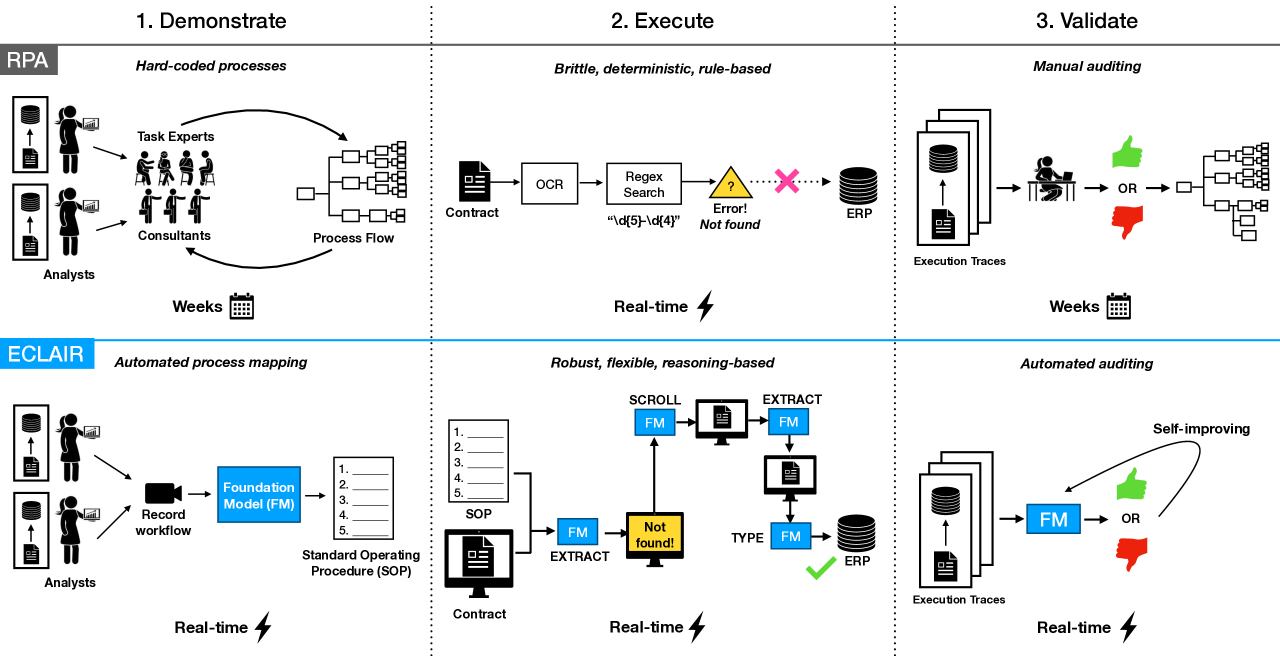

0
Automating the Enterprise with Foundation Models
Michael Wornow, Avanika Narayan, Krista Opsahl-Ong, Quinn McIntyre, Nigam H. Shah, Christopher Re
Automating enterprise workflows could unlock $4 trillion/year in productivity gains. Despite being of interest to the data management community for decades, the ultimate vision of end-to-end workflow automation has remained elusive. Current solutions rely on process mining and robotic process automation (RPA), in which a bot is hard-coded to follow a set of predefined rules for completing a workflow. Through case studies of a hospital and large B2B enterprise, we find that the adoption of RPA has been inhibited by high set-up costs (12-18 months), unreliable execution (60% initial accuracy), and burdensome maintenance (requiring multiple FTEs). Multimodal foundation models (FMs) such as GPT-4 offer a promising new approach for end-to-end workflow automation given their generalized reasoning and planning abilities. To study these capabilities we propose ECLAIR, a system to automate enterprise workflows with minimal human supervision. We conduct initial experiments showing that multimodal FMs can address the limitations of traditional RPA with (1) near-human-level understanding of workflows (93% accuracy on a workflow understanding task) and (2) instant set-up with minimal technical barrier (based solely on a natural language description of a workflow, ECLAIR achieves end-to-end completion rates of 40%). We identify human-AI collaboration, validation, and self-improvement as open challenges, and suggest ways they can be solved with data management techniques. Code is available at: https://github.com/HazyResearch/eclair-agents
Read more5/8/2024