The overlooked need for Ethics in Complexity Science: Why it matters

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- The paper discusses the overlooked need for ethics in complexity science.
- It argues that the field of complexity science, which studies complex systems, must incorporate ethical considerations to address the societal impacts of its findings.
- The paper highlights the importance of integrating ethics into complexity science research and decision-making processes.
Plain English Explanation
Complexity science is a field that studies how complex systems, like ecosystems or economies, behave and interact. This research can have significant impacts on society, but often the ethical implications are not given enough attention. The paper suggests that complexity science must incorporate ethical considerations to ensure its findings are used responsibly and for the benefit of all.
For example, research on complex social systems could uncover patterns of inequality or discrimination. Without an ethical framework, this knowledge could be misused to further marginalize vulnerable populations. By integrating ethics into the research process, complexity scientists can identify and mitigate potential harms, and ensure their work promotes social justice and the common good.
Similarly, insights from complexity science could be applied to artificial intelligence and other technologies with far-reaching societal impacts. An ethical approach would help ensure these technologies are developed and deployed in ways that are fair, inclusive, and beneficial to all.
Overall, the paper argues that by bridging the gap between the principles and practices of ethics, complexity science can unlock its full potential to address complex challenges and improve the human condition.
Technical Explanation
The paper makes the case for the critical need to integrate ethics into the field of complexity science. Complexity science is the study of complex systems, which exhibit properties like nonlinearity, emergence, and self-organization. The authors argue that the insights and applications of complexity science can have significant societal impacts, but these ethical implications are often overlooked.
The paper outlines several examples where complexity science research could benefit from an ethical framework. For instance, studies of social systems may uncover patterns of inequality or discrimination, but without ethical considerations, this knowledge could be misused to further marginalize vulnerable populations. Similarly, complexity-informed approaches to artificial intelligence and other technologies must grapple with issues of fairness, transparency, and accountability.
The authors emphasize that by integrating ethics into complexity science, researchers and decision-makers can identify and mitigate potential harms, and ensure that the field's findings are used to promote social justice and the common good. This would involve developing ethical frameworks, guidelines, and decision-making processes that are tailored to the unique challenges of complex systems.
Critical Analysis
The paper makes a compelling argument for the importance of incorporating ethics into complexity science research and practices. The authors provide relevant examples that highlight the potential societal impacts of complexity science findings, and the critical need to address these ethical considerations.
One potential limitation of the paper is that it does not delve deeply into the specific ethical frameworks or methodologies that could be applied to complexity science. The authors acknowledge this, suggesting that further research is needed to develop ethical approaches that are suited to the unique characteristics of complex systems.
Additionally, the paper could have explored in more depth the practical challenges and barriers to integrating ethics into complexity science, such as institutional cultures, resource constraints, or disciplinary silos. Understanding and addressing these challenges would be crucial for successfully implementing the authors' recommendations.
Overall, the paper makes a strong case for the overlooked need for ethics in complexity science, and encourages readers to think critically about the societal implications of this important field of study.
Conclusion
This paper highlights the critical importance of integrating ethical considerations into the field of complexity science. By acknowledging the societal impacts of complexity science research and findings, the authors argue that the field must develop ethical frameworks and decision-making processes to ensure its work promotes social justice, inclusivity, and the common good.
The examples provided in the paper illustrate how complexity science insights, if applied without ethical oversight, could potentially be misused or lead to unintended harms. Incorporating ethics into complexity science research and practices would help mitigate these risks and unlock the field's full potential to address complex challenges and improve the human condition.
Overall, the paper makes a compelling case for the overlooked need for ethics in complexity science, and encourages researchers, policymakers, and the public to engage in critical discussions about the societal implications of this important field of study.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
The overlooked need for Ethics in Complexity Science: Why it matters
Olumide Adisa, Enio Alterman Blay, Yasaman Asgari, Gabriele Di Bona, Samantha Dies, Ana Maria Jaramillo, Paulo H. Resende, Ana Maria de Sousa Leitao
Complexity science, despite its broad scope and potential impact, has not kept pace with fields like artificial intelligence, biotechnology and social sciences in addressing ethical concerns. The field lacks a comprehensive ethical framework, leaving us, as a community, vulnerable to ethical challenges and dilemmas. Other areas have gone through similar experiences and created, with discussions and working groups, their guides, policies and recommendations. Therefore, here we highlight the critical absence of formal guidelines, dedicated ethical committees, and widespread discussions on ethics within the complexity science community. Drawing on insights from the disciplines mentioned earlier, we propose a roadmap to enhance ethical awareness and action. Our recommendations include (i) initiating supportive mechanisms to develop ethical guidelines specific to complex systems research, (ii) creating open-access resources, and (iii) fostering inclusive dialogues to ensure that complexity science can responsibly tackle societal challenges and achieve a more inclusive environment. By initiating this dialogue, we aim to encourage a necessary shift in how ethics is integrated into complexity research, positioning the field to address contemporary challenges more effectively.
Read more9/4/2024
🏅

0
On the role of ethics and sustainability in business innovation
Maria Fay, Frederik F. Flother
For organizations to survive and flourish in the long term, innovation and novelty must be continually introduced, which is particularly true in today's rapidly changing world. This raises a variety of ethical and sustainability considerations that seldom receive the attention they deserve. Existing innovation adoption frameworks often focus on technological, organizational, environmental, and social factors impacting adoption. In this chapter, we explore the ethical and sustainability angles, particularly as they relate to emerging technologies, artificial intelligence (AI) being a prominent example. We consider how to facilitate the development and cultivation of innovation cultures in organizations, including budding startups as well as established enterprises, through approaches such as systems thinking.
Read more4/12/2024
➖

0
Balancing Innovation and Ethics in AI-Driven Software Development
Mohammad Baqar
This paper critically examines the ethical implications of integrating AI tools like GitHub Copilot and ChatGPT into the software development process. It explores issues such as code ownership, bias, accountability, privacy, and the potential impact on the job market. While these AI tools offer significant benefits in terms of productivity and efficiency, they also introduce complex ethical challenges. The paper argues that addressing these challenges is essential to ensuring that AI's integration into software development is both responsible and beneficial to society
Read more8/21/2024

0
Towards an Ethical and Inclusive Implementation of Artificial Intelligence in Organizations: A Multidimensional Framework
Ernesto Giralt Hern'andez
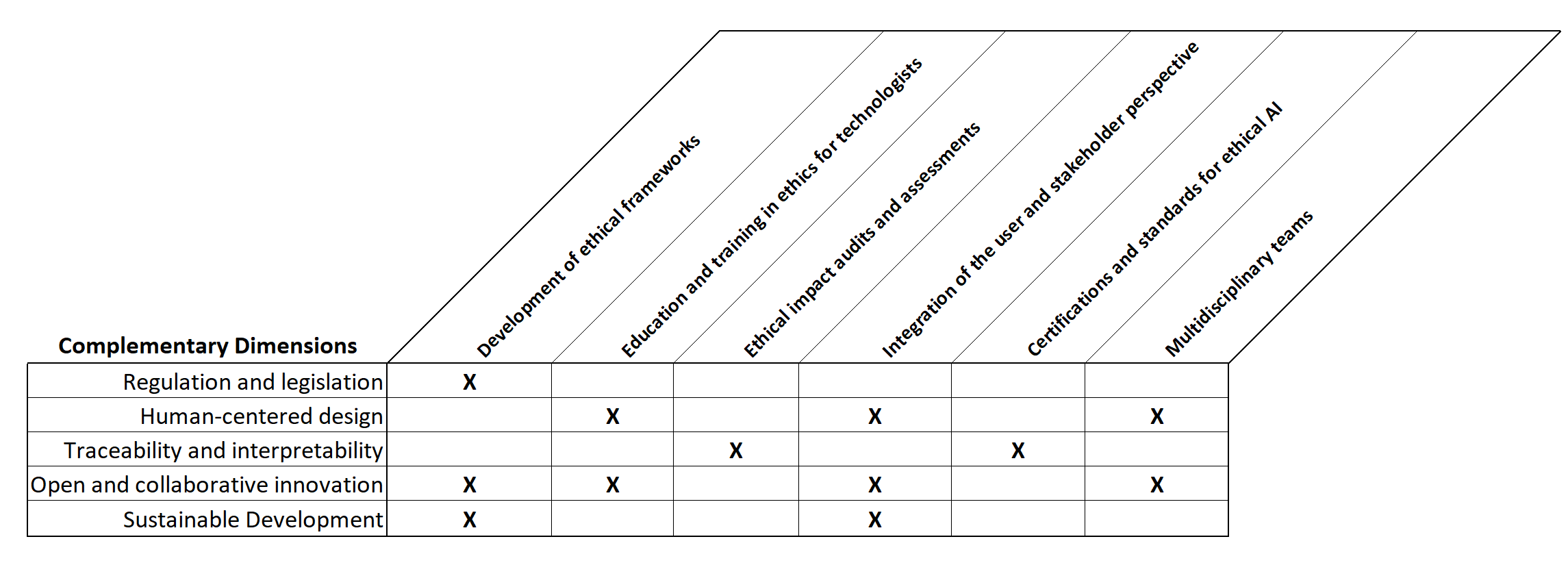
This article analyzes the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on contemporary society and the importance of adopting an ethical approach to its development and implementation within organizations. It examines the technocritical perspective of some philosophers and researchers, who warn of the risks of excessive technologization that could undermine human autonomy. However, the article also acknowledges the active role that various actors, such as governments, academics, and civil society, can play in shaping the development of AI aligned with human and social values. A multidimensional approach is proposed that combines ethics with regulation, innovation, and education. It highlights the importance of developing detailed ethical frameworks, incorporating ethics into the training of professionals, conducting ethical impact audits, and encouraging the participation of stakeholders in the design of AI. In addition, four fundamental pillars are presented for the ethical implementation of AI in organizations: 1) Integrated values, 2) Trust and transparency, 3) Empowering human growth, and 4) Identifying strategic factors. These pillars encompass aspects such as alignment with the company's ethical identity, governance and accountability, human-centered design, continuous training, and adaptability to technological and market changes. The conclusion emphasizes that ethics must be the cornerstone of any organization's strategy that seeks to incorporate AI, establishing a solid framework that ensures that technology is developed and used in a way that respects and promotes human values.
Read more5/6/2024