PatentGPT: A Large Language Model for Intellectual Property
2404.18255

0
0
Abstract
In recent years, large language models(LLMs) have attracted significant attention due to their exceptional performance across a multitude of natural language process tasks, and have been widely applied in various fields. However, the application of large language models in the Intellectual Property (IP) domain is challenging due to the strong need for specialized knowledge, privacy protection, processing of extremely long text in this field. In this technical report, we present for the first time a low-cost, standardized procedure for training IP-oriented LLMs, meeting the unique requirements of the IP domain. Using this standard process, we have trained the PatentGPT series models based on open-source pretrained models. By evaluating them on the open-source IP-oriented benchmark MOZIP, our domain-specific LLMs outperforms GPT-4, indicating the effectiveness of the proposed training procedure and the expertise of the PatentGPT models in the IP domain. Remarkably, our model surpassed GPT-4 on the 2019 China Patent Agent Qualification Examination, scoring 65 and matching human expert levels. Additionally, the PatentGPT model, which utilizes the SMoE architecture, achieves performance comparable to that of GPT-4 in the IP domain and demonstrates a better cost-performance ratio on long-text tasks, potentially serving as an alternative to GPT-4 within the IP domain.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper introduces PatentGPT, a large language model specifically designed for intellectual property applications.
- The model is trained on a vast corpus of patent data to help with tasks such as prior art search, patent generation, and patent analysis.
- Key innovations include a novel pretraining strategy and specialized fine-tuning approaches tailored to intellectual property use cases.
Plain English Explanation
PatentGPT is a powerful AI system that has been trained on a huge amount of patent data. This allows it to understand the unique language and concepts used in patents, and to assist with various intellectual property tasks.
For example, PatentGPT could help researchers quickly find relevant prior art when working on a new invention. It could also generate draft patent applications, or analyze existing patents to surface key insights. The goal is to make intellectual property workflows more efficient and productive.
The researchers developed some innovative techniques to train PatentGPT. This includes a specialized pretraining strategy that exposes the model to a diverse corpus of patent data. They also fine-tuned the model for specific IP-related tasks to optimize its performance.
Overall, PatentGPT represents an exciting application of large language models to the domain of intellectual property. By leveraging advanced AI, the hope is to empower inventors, lawyers, and others working in this important field.
Technical Explanation
The key innovations in this work include the pretraining strategy and the specialized fine-tuning approaches used to adapt the model for intellectual property tasks.
For pretraining, the researchers assembled a diverse corpus of patent data, including full-text documents, abstracts, claims, and metadata. This allowed PatentGPT to learn the unique language patterns and concepts prevalent in patents.
They also experimented with different pretraining objectives, such as next-sentence prediction and masked language modeling, to further enhance the model's understanding of patent structure and content.
To specialize PatentGPT for IP applications, the researchers fine-tuned the model on tasks like prior art search, patent generation, and patent classification. This involved curating task-specific datasets and designing appropriate fine-tuning strategies.
Through extensive experimentation, the researchers demonstrate PatentGPT's strong performance on these IP-related benchmarks, outperforming various baselines. They also showcase the model's versatility by applying it to real-world use cases like patent analysis and invention ideation.
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge several limitations and avenues for future work. For example, PatentGPT's training data is primarily in English, so extending it to other languages is an important next step.
Additionally, while the model performs well on various IP tasks, there may be concerns around potential misuse, such as generating deceptive patent applications. Careful monitoring and responsible development practices will be crucial.
Further research is also needed to better understand the model's reasoning process and the factors that influence its performance. Incorporating more domain-specific knowledge and reasoning capabilities could also enhance PatentGPT's utility for intellectual property professionals.
Conclusion
PatentGPT represents an exciting advancement in the application of large language models to the field of intellectual property. By leveraging specialized pretraining and fine-tuning strategies, the researchers have created a powerful tool that can assist with a variety of IP-related tasks.
As AI continues to evolve, innovations like PatentGPT have the potential to significantly streamline and enhance intellectual property workflows, benefiting inventors, patent professionals, and ultimately, the broader innovation ecosystem.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers
💬
LawGPT: A Chinese Legal Knowledge-Enhanced Large Language Model
Zhi Zhou, Jiang-Xin Shi, Peng-Xiao Song, Xiao-Wen Yang, Yi-Xuan Jin, Lan-Zhe Guo, Yu-Feng Li

0
0
Large language models (LLMs), including both proprietary and open-source models, have showcased remarkable capabilities in addressing a wide range of downstream tasks. Nonetheless, when it comes to practical Chinese legal tasks, these models fail to meet the actual requirements. Proprietary models do not ensure data privacy for sensitive legal cases, while open-source models demonstrate unsatisfactory performance due to their lack of legal knowledge. To address this problem, we introduce LawGPT, the first open-source model specifically designed for Chinese legal applications. LawGPT comprises two key components: legal-oriented pre-training and legal supervised fine-tuning. Specifically, we employ large-scale Chinese legal documents for legal-oriented pre-training to incorporate legal domain knowledge. To further improve the model's performance on downstream legal tasks, we create a knowledge-driven instruction dataset for legal supervised fine-tuning. Our experimental results demonstrate that LawGPT outperforms the open-source LLaMA 7B model. Our code and resources are publicly available at https://github.com/pengxiao-song/LaWGPT and have received 5.7K stars on GitHub.
6/10/2024

PharmGPT: Domain-Specific Large Language Models for Bio-Pharmaceutical and Chemistry
Linqing Chen, Weilei Wang, Zilong Bai, Peng Xu, Yan Fang, Jie Fang, Wentao Wu, Lizhi Zhou, Ruiji Zhang, Yubin Xia, Chaobo Xu, Ran Hu, Licong Xu, Qijun Cai, Haoran Hua, Jing Sun, Jin Liu, Tian Qiu, Haowen Liu, Meng Hu, Xiuwen Li, Fei Gao, Yufu Wang, Lin Tie, Chaochao Wang, Jianping Lu, Cheng Sun, Yixin Wang, Shengjie Yang, Yuancheng Li, Lu Jin, Lisha Zhang, Fu Bian, Changyang Tu

0
0
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized Natural Language Processing (NLP) by by minimizing the need for complex feature engineering. However, the application of LLMs in specialized domains like biopharmaceuticals and chemistry remains largely unexplored. These fields are characterized by intricate terminologies, specialized knowledge, and a high demand for precision areas where general purpose LLMs often fall short. In this study, we introduce PharmGPT, a suite of multilingual LLMs with 13 billion and 70 billion parameters, specifically trained on a comprehensive corpus of hundreds of billions of tokens tailored to the Bio-Pharmaceutical and Chemical sectors. Our evaluation shows that PharmGPT matches or surpasses existing general models on key benchmarks, such as NAPLEX, demonstrating its exceptional capability in domain-specific tasks. This advancement establishes a new benchmark for LLMs in the Bio-Pharmaceutical and Chemical fields, addressing the existing gap in specialized language modeling. Furthermore, this suggests a promising path for enhanced research and development in these specialized areas, paving the way for more precise and effective applications of NLP in specialized domains.
6/27/2024
Large Language Model Informed Patent Image Retrieval
Hao-Cheng Lo, Jung-Mei Chu, Jieh Hsiang, Chun-Chieh Cho

0
0
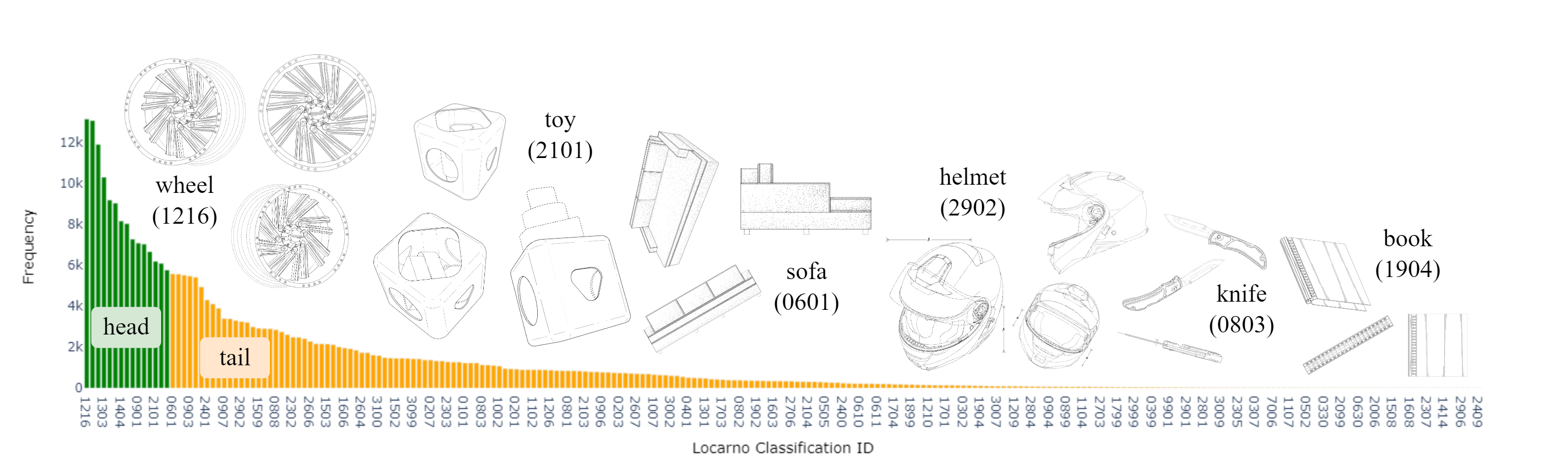
In patent prosecution, image-based retrieval systems for identifying similarities between current patent images and prior art are pivotal to ensure the novelty and non-obviousness of patent applications. Despite their growing popularity in recent years, existing attempts, while effective at recognizing images within the same patent, fail to deliver practical value due to their limited generalizability in retrieving relevant prior art. Moreover, this task inherently involves the challenges posed by the abstract visual features of patent images, the skewed distribution of image classifications, and the semantic information of image descriptions. Therefore, we propose a language-informed, distribution-aware multimodal approach to patent image feature learning, which enriches the semantic understanding of patent image by integrating Large Language Models and improves the performance of underrepresented classes with our proposed distribution-aware contrastive losses. Extensive experiments on DeepPatent2 dataset show that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art or comparable performance in image-based patent retrieval with mAP +53.3%, Recall@10 +41.8%, and MRR@10 +51.9%. Furthermore, through an in-depth user analysis, we explore our model in aiding patent professionals in their image retrieval efforts, highlighting the model's real-world applicability and effectiveness.
5/1/2024
Demonstration of DB-GPT: Next Generation Data Interaction System Empowered by Large Language Models
Siqiao Xue, Danrui Qi, Caigao Jiang, Wenhui Shi, Fangyin Cheng, Keting Chen, Hongjun Yang, Zhiping Zhang, Jianshan He, Hongyang Zhang, Ganglin Wei, Wang Zhao, Fan Zhou, Hong Yi, Shaodong Liu, Hongjun Yang, Faqiang Chen

0
0
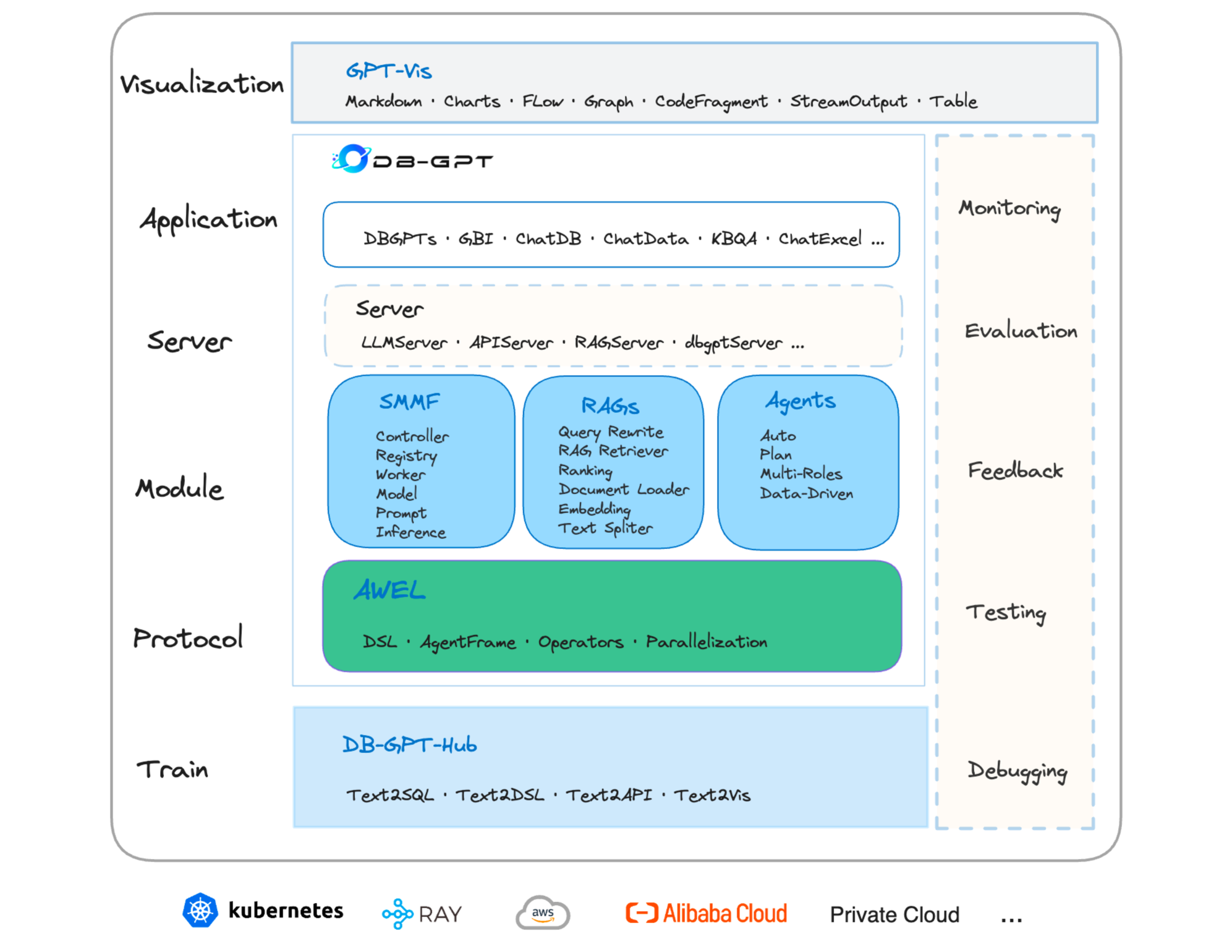
The recent breakthroughs in large language models (LLMs) are positioned to transition many areas of software. The technologies of interacting with data particularly have an important entanglement with LLMs as efficient and intuitive data interactions are paramount. In this paper, we present DB-GPT, a revolutionary and product-ready Python library that integrates LLMs into traditional data interaction tasks to enhance user experience and accessibility. DB-GPT is designed to understand data interaction tasks described by natural language and provide context-aware responses powered by LLMs, making it an indispensable tool for users ranging from novice to expert. Its system design supports deployment across local, distributed, and cloud environments. Beyond handling basic data interaction tasks like Text-to-SQL with LLMs, it can handle complex tasks like generative data analysis through a Multi-Agents framework and the Agentic Workflow Expression Language (AWEL). The Service-oriented Multi-model Management Framework (SMMF) ensures data privacy and security, enabling users to employ DB-GPT with private LLMs. Additionally, DB-GPT offers a series of product-ready features designed to enable users to integrate DB-GPT within their product environments easily. The code of DB-GPT is available at Github(https://github.com/eosphoros-ai/DB-GPT) which already has over 10.7k stars. Please install DB-GPT for your own usage with the instructions(https://github.com/eosphoros-ai/DB-GPT#install) and watch a 5-minute introduction video on Youtube(https://youtu.be/n_8RI1ENyl4) to further investigate DB-GPT.
4/26/2024