Performance Optimization in RSMA-assisted Uplink xURLLC IIoT Networks with Statistical QoS Provisioning

0
Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores performance optimization in uplink next-generation ultra-reliable and low-latency communications (xURLLC) industrial internet-of-things (IIoT) networks using rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) and statistical quality-of-service (QoS) provisioning.
- The researchers aim to improve the reliability and efficiency of IIoT communication systems by leveraging RSMA and stochastic network calculus techniques.
Plain English Explanation
In this paper, the researchers are looking at ways to improve the performance and reliability of communication networks used in industrial internet-of-things (IIoT) applications. IIoT systems often require very fast and highly reliable communication to support critical applications like factory automation or remote control of machinery.
The researchers focus on using a technique called rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) to optimize the communication in the uplink, which is the connection from the IIoT devices back to the network infrastructure. RSMA allows multiple IIoT devices to share the same communication channel by splitting up the data transmission in a smart way.
To ensure the communication meets the strict reliability and latency requirements of IIoT, the researchers also apply statistical quality-of-service (QoS) techniques. This allows them to provide hard guarantees on the communication performance, even with the dynamic nature of IIoT networks.
By combining RSMA and statistical QoS, the researchers aim to create a more efficient and reliable IIoT communication system that can support the demanding requirements of industrial applications.
Technical Explanation
The paper investigates performance optimization in RSMA-assisted uplink xURLLC IIoT networks with statistical QoS provisioning. The researchers propose a framework that leverages RSMA and stochastic network calculus to enhance the reliability and efficiency of IIoT communication systems.
The key technical elements include:
- RSMA: A multiple access technique that splits the users' data streams and superimposes them, allowing for improved spectral efficiency and better support for low-latency applications.
- Stochastic network calculus: A mathematical framework used to provide statistical QoS guarantees, accounting for the inherent randomness in IIoT network traffic.
- Optimization problem: The researchers formulate an optimization problem to maximize the system's throughput while meeting stringent latency and reliability requirements.
- Algorithm design: They develop a low-complexity algorithm to solve the optimization problem and efficiently allocate resources in the RSMA-assisted IIoT network.
The proposed approach is evaluated through simulations, demonstrating its ability to outperform conventional multiple access schemes in terms of throughput, latency, and reliability for xURLLC IIoT applications.
Critical Analysis
The paper provides a comprehensive and technically sound approach to optimizing the performance of RSMA-assisted uplink xURLLC IIoT networks. The use of stochastic network calculus to provide statistical QoS guarantees is a notable strength, as it accounts for the dynamic nature of IIoT traffic patterns.
However, the paper does not discuss the potential practical challenges of implementing the proposed framework in real-world IIoT deployments. For example, the computational complexity of the optimization algorithm and its scalability to large-scale IIoT networks could be explored further. Additionally, the impact of factors like hardware limitations, energy consumption, and implementation costs on the feasibility of the approach are not addressed.
While the simulation results demonstrate the potential benefits of the proposed framework, it would be valuable to see experimental validation or case studies involving actual IIoT deployments to better understand the real-world applicability and limitations of the approach.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel framework for performance optimization in RSMA-assisted uplink xURLLC IIoT networks, leveraging statistical QoS provisioning. The key contributions include the integration of RSMA and stochastic network calculus to enhance the reliability and efficiency of IIoT communication systems.
The proposed approach shows promising results in simulation, outperforming conventional multiple access schemes in terms of throughput, latency, and reliability. However, further research is needed to address the practical challenges of implementing the framework in real-world IIoT deployments and to evaluate its scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Overall, the work represents a valuable contribution to the field of IIoT communication optimization, and the insights gained could potentially be applied to other demanding communication scenarios requiring ultra-reliable and low-latency performance.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
Performance Optimization in RSMA-assisted Uplink xURLLC IIoT Networks with Statistical QoS Provisioning
Yuang Chen, Hancheng Lu, Chang Wu, Langtian Qin, Xiaobo Guo
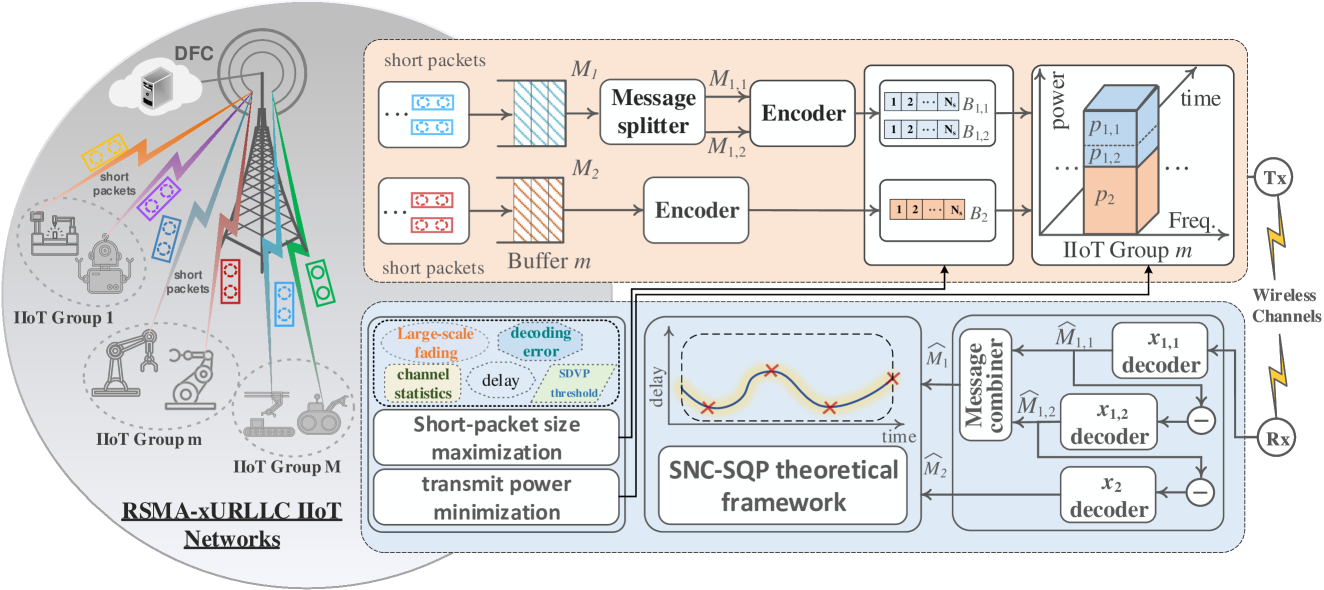
Industry 5.0 and beyond networks have driven the emergence of numerous mission-critical applications, prompting contemplation of the neXt-generation ultra-reliable low-latency communication (xURLLC). To guarantee low-latency requirements, xURLLC heavily relies on short-blocklength packets with sporadic arrival traffic. As a disruptive multi-access technique, rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) has emerged as a promising avenue to enhance quality of service (QoS) and flexibly manage interference for next-generation communication networks. In this paper, we investigate an innovative RSMA-assisted uplink xURLLC industrial internet-of-things (IIoT) (RSMA-xURLLC-IIoT) network. To unveil reliable insights into the statistical QoS provisioning (SQP) for our proposed network with sporadic arrival traffic, we leverage stochastic network calculus (SNC) to develop a dependable theoretical framework. Building upon this theoretical framework, we formulate the SQP-driven short-packet size maximization problem and the SQP-driven transmit power minimization problem, aiming to guarantee the SQP performance to latency, decoding, and reliability while maximizing the short-packet size and minimizing the transmit power, respectively. By exploiting Monte-Carlo methods, we have thoroughly validated the dependability of the developed theoretical framework. Moreover, through extensive comparison analysis with state-of-the-art multi-access techniques, including non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and orthogonal multiple access (OMA), we have demonstrated the superior performance gains achieved by the proposed RSMA-xURLLC-IIoT networks.
Read more5/28/2024
🏅

0
QoE-Aware and Secure UAV-Aided Rate-Splitting Multiple Access Based Communications
Abuzar B. M. Adam, Xiaoyu Wan, Mohammed Saleh Ali Muthanna
In this work, we address the issue of quality of experience (QoE) in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) aided multiuser rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) networks under secrecy constraints. The problem is formulated as maximization of sum mean opinion scores (MOSs) of the users. The problem is decomposed into two subproblems, beamforming and rate allocation and UAV trajectory subproblem. For, beamforming and rate allocation subproblem, we use the epigraph method, property of polynomials, and the norm-bounded error of channels, we linearize the objective function. Then, applying second-order conic (SOC) and first Taylor expansion, we convexify the remaining nonconvex constraints. For the highly nonconvex UAV trajectory, we unroll the constraints and we apply first Taylor expansion on the unrolled constraints. The simulation results demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed framework.
Read more5/24/2024


0
Towards Resilient 6G O-RAN: An Energy-Efficient URLLC Resource Allocation Framework
Rana M. Sohaib, Syed Tariq Shah, Poonam Yadav
The demands of ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) in ``NextG cellular networks necessitate innovative approaches for efficient resource utilisation. The current literature on 6G O-RAN primarily addresses improved mobile broadband (eMBB) performance or URLLC latency optimisation individually, often neglecting the intricate balance required to optimise both simultaneously under practical constraints. This paper addresses this gap by proposing a DRL-based resource allocation framework integrated with meta-learning to manage eMBB and URLLC services adaptively. Our approach efficiently allocates heterogeneous network resources, aiming to maximise energy efficiency (EE) while minimising URLLC latency, even under varying environmental conditions. We highlight the critical importance of accurately estimating the traffic distribution flow in the multi-connectivity (MC) scenario, as its uncertainty can significantly degrade EE. The proposed framework demonstrates superior adaptability across different path loss models, outperforming traditional methods and paving the way for more resilient and efficient 6G networks.
Read more9/10/2024


0
Resource Management in RIS-Assisted Rate Splitting Multiple Access for Next Generation (xG) Wireless Communications: Models, State-of-the-Art, and Future Directions
Ibrahim Aboumahmoud, Ekram Hossain, Amine Mezghani
Next generation wireless networks require more stringent performance levels. New technologies such as Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) and rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) are candidates for meeting some of the performance requirements, including higher user rates at reduced costs. RSMA provides a new way of mixing the messages of multiple users, and the RIS provides a controllable wireless environment. This paper provides a comprehensive survey on the various aspects of the synergy between reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) and rate splitting multiple access (RSMA) for next-generation (xG) wireless communications systems. In particular, the paper studies more than 60 articles considering over 20 different system models where the RIS-aided RSMA system shows performance advantage (in terms of sum-rate or outage probability) over traditional RSMA models. These models include reflective RIS, simultaneously transmitting and reflecting surfaces (STAR-RIS), as well as transmissive surfaces. The state-of-the-art resource management methods for RIS-assisted RSMA communications employ traditional optimization techniques and/or machine learning techniques. We outline major research challenges and multiple future research directions.
Read more4/11/2024