QoE-Aware and Secure UAV-Aided Rate-Splitting Multiple Access Based Communications
2405.14524

0
0
🏅
Abstract
In this work, we address the issue of quality of experience (QoE) in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) aided multiuser rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) networks under secrecy constraints. The problem is formulated as maximization of sum mean opinion scores (MOSs) of the users. The problem is decomposed into two subproblems, beamforming and rate allocation and UAV trajectory subproblem. For, beamforming and rate allocation subproblem, we use the epigraph method, property of polynomials, and the norm-bounded error of channels, we linearize the objective function. Then, applying second-order conic (SOC) and first Taylor expansion, we convexify the remaining nonconvex constraints. For the highly nonconvex UAV trajectory, we unroll the constraints and we apply first Taylor expansion on the unrolled constraints. The simulation results demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed framework.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This paper addresses the issue of quality of experience (QoE) in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) aided multiuser rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) networks under secrecy constraints.
- The problem is formulated as maximizing the sum of mean opinion scores (MOSs) of the users.
- The problem is decomposed into two subproblems: beamforming and rate allocation, and UAV trajectory optimization.
Plain English Explanation
In this research, the authors explore how to improve the quality of experience (QoE) for users in a wireless network that uses UAVs (drones) to help deliver the signal. The network uses a technique called rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA), which allows multiple users to share the same wireless channel.
The key challenge is that the users need to be able to communicate securely, without their messages being intercepted. The researchers formulate this as a mathematical optimization problem, where the goal is to maximize the overall "satisfaction" of the users, as measured by their mean opinion scores (MOSs).
The problem is broken down into two parts. First, they need to figure out the best way to transmit the signals using beamforming (shaping the wireless signal) and allocating the data rates to each user. Then, they need to optimize the flight path of the UAV to improve the network performance.
The researchers use a variety of mathematical techniques, including linearizing the objective function, convexifying the constraints, and unrolling the UAV trajectory constraints. The goal is to find an efficient solution to this complex optimization problem.
Technical Explanation
The researchers formulate the problem as maximizing the sum of the mean opinion scores (MOSs) of the users in the UAV-aided RSMA network under secrecy constraints. They decompose the problem into two subproblems: beamforming and rate allocation, and UAV trajectory optimization.
For the beamforming and rate allocation subproblem, the researchers use the epigraph method, the properties of polynomials, and the norm-bounded error of channels to linearize the objective function. They then apply second-order conic (SOC) programming and first-order Taylor expansion to convexify the remaining nonconvex constraints.
For the highly nonconvex UAV trajectory subproblem, the researchers unroll the constraints and apply first-order Taylor expansion on the unrolled constraints.
The simulation results demonstrate the efficiency of the proposed framework in improving the QoE of the users while ensuring secure communications, compared to other resource management approaches and secure UAV communications.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a comprehensive solution to the QoE optimization problem in UAV-aided RSMA networks under secrecy constraints. The researchers have made significant efforts to address the challenges of nonconvexity and complexity in the problem formulation.
However, the paper does not consider the impact of imperfect channel state information (CSI) on the system performance. In practical scenarios, the CSI may be subject to estimation errors, which could affect the effectiveness of the proposed beamforming and rate allocation strategies.
Additionally, the paper focuses on maximizing the sum of MOSs, which may not always align with the individual user's preferences or fairness considerations. It could be interesting to explore alternative optimization objectives, such as proportional fairness or max-min fairness, to ensure a more equitable distribution of QoE among the users.
Further research could also investigate the scalability of the proposed solution as the number of users or the size of the network increases. The computational complexity of the optimization problem may become a limiting factor in larger-scale deployments.
Conclusion
This paper presents a novel framework for optimizing the quality of experience (QoE) in UAV-aided multiuser rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) networks under secrecy constraints. The researchers have developed a two-stage optimization approach, addressing the beamforming and rate allocation as well as the UAV trajectory optimization subproblems.
The proposed solution leverages advanced mathematical techniques to handle the nonconvexity and complexity of the problem. The simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the framework in improving the overall user satisfaction while ensuring secure communications.
This research contributes to the growing field of UAV-enabled wireless communications and rate-splitting multiple access techniques, paving the way for more efficient and secure wireless networks in the future.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Multi-UAV Multi-RIS QoS-Aware Aerial Communication Systems using DRL and PSO
Marwan Dhuheir, Aiman Erbad, Ala Al-Fuqaha, Mohsen Guizani

0
0
Recently, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) have attracted the attention of researchers in academia and industry for providing wireless services to ground users in diverse scenarios like festivals, large sporting events, natural and man-made disasters due to their advantages in terms of versatility and maneuverability. However, the limited resources of UAVs (e.g., energy budget and different service requirements) can pose challenges for adopting UAVs for such applications. Our system model considers a UAV swarm that navigates an area, providing wireless communication to ground users with RIS support to improve the coverage of the UAVs. In this work, we introduce an optimization model with the aim of maximizing the throughput and UAVs coverage through optimal path planning of UAVs and multi-RIS phase configurations. The formulated optimization is challenging to solve using standard linear programming techniques, limiting its applicability in real-time decision-making. Therefore, we introduce a two-step solution using deep reinforcement learning and particle swarm optimization. We conduct extensive simulations and compare our approach to two competitive solutions presented in the recent literature. Our simulation results demonstrate that our adopted approach is 20 % better than the brute-force approach and 30% better than the baseline solution in terms of QoS.
6/26/2024
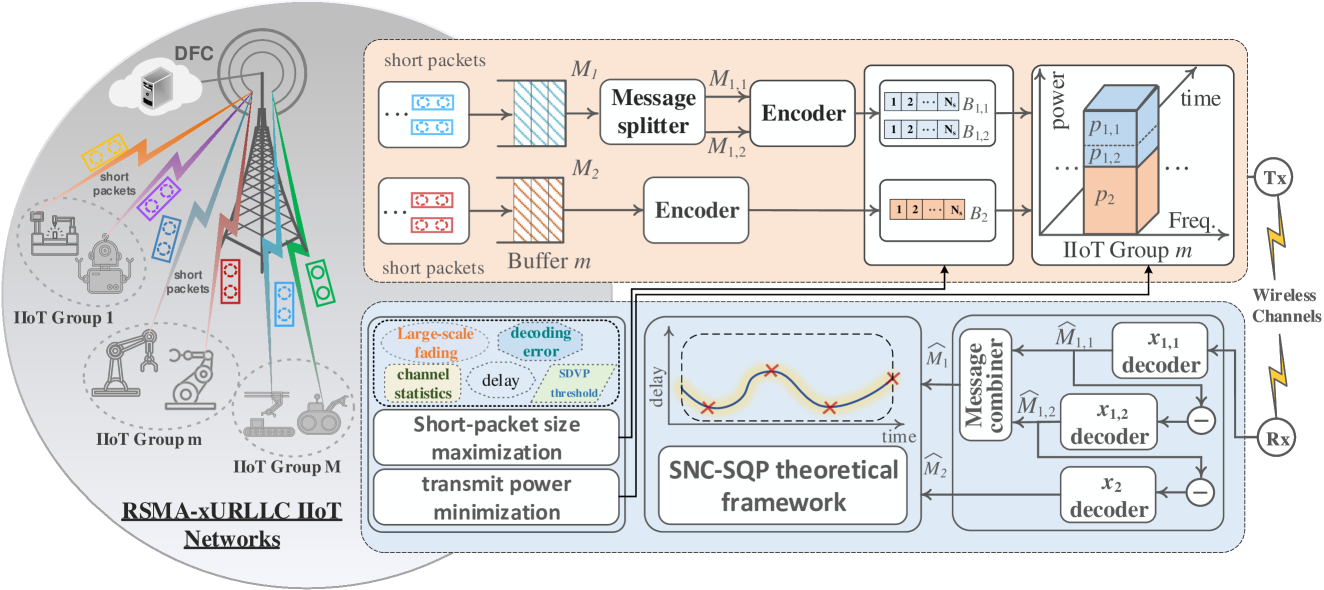
Performance Optimization in RSMA-assisted Uplink xURLLC IIoT Networks with Statistical QoS Provisioning
Yuang Chen, Hancheng Lu, Chang Wu, Langtian Qin, Xiaobo Guo

0
0
Industry 5.0 and beyond networks have driven the emergence of numerous mission-critical applications, prompting contemplation of the neXt-generation ultra-reliable low-latency communication (xURLLC). To guarantee low-latency requirements, xURLLC heavily relies on short-blocklength packets with sporadic arrival traffic. As a disruptive multi-access technique, rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) has emerged as a promising avenue to enhance quality of service (QoS) and flexibly manage interference for next-generation communication networks. In this paper, we investigate an innovative RSMA-assisted uplink xURLLC industrial internet-of-things (IIoT) (RSMA-xURLLC-IIoT) network. To unveil reliable insights into the statistical QoS provisioning (SQP) for our proposed network with sporadic arrival traffic, we leverage stochastic network calculus (SNC) to develop a dependable theoretical framework. Building upon this theoretical framework, we formulate the SQP-driven short-packet size maximization problem and the SQP-driven transmit power minimization problem, aiming to guarantee the SQP performance to latency, decoding, and reliability while maximizing the short-packet size and minimizing the transmit power, respectively. By exploiting Monte-Carlo methods, we have thoroughly validated the dependability of the developed theoretical framework. Moreover, through extensive comparison analysis with state-of-the-art multi-access techniques, including non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and orthogonal multiple access (OMA), we have demonstrated the superior performance gains achieved by the proposed RSMA-xURLLC-IIoT networks.
5/28/2024
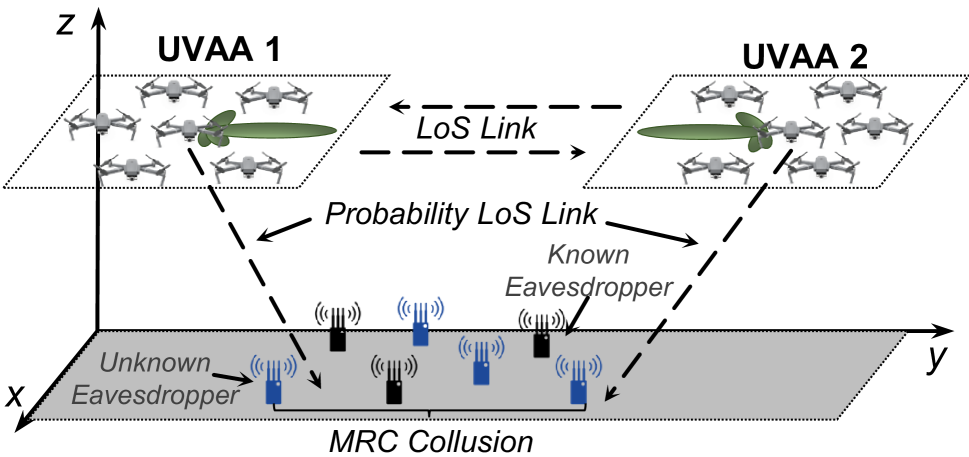
Two-Way Aerial Secure Communications via Distributed Collaborative Beamforming under Eavesdropper Collusion
Jiahui Li, Geng Sun, Qingqing Wu, Shuang Liang, Pengfei Wang, Dusit Niyato

0
0
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)-enabled aerial communication provides a flexible, reliable, and cost-effective solution for a range of wireless applications. However, due to the high line-of-sight (LoS) probability, aerial communications between UAVs are vulnerable to eavesdropping attacks, particularly when multiple eavesdroppers collude. In this work, we aim to introduce distributed collaborative beamforming (DCB) into UAV swarms and handle the eavesdropper collusion by controlling the corresponding signal distributions. Specifically, we consider a two-way DCB-enabled aerial communication between two UAV swarms and construct these swarms as two UAV virtual antenna arrays. Then, we minimize the two-way known secrecy capacity and the maximum sidelobe level to avoid information leakage from the known and unknown eavesdroppers, respectively. Simultaneously, we also minimize the energy consumption of UAVs for constructing virtual antenna arrays. Due to the conflicting relationships between secure performance and energy efficiency, we consider these objectives as a multi-objective optimization problem. Following this, we propose an enhanced multi-objective swarm intelligence algorithm via the characterized properties of the problem. Simulation results show that our proposed algorithm can obtain a set of informative solutions and outperform other state-of-the-art baseline algorithms. Experimental tests demonstrate that our method can be deployed in limited computing power platforms of UAVs and is beneficial for saving computational resources.
4/12/2024

Radio Resource Management Design for RSMA: Optimization of Beamforming, User Admission, and Discrete/Continuous Rates with Imperfect SIC
L. F. Abanto-Leon, A. Krishnamoorthy, A. Garcia-Saavedra, G. H. Sim, R. Schober, M. Hollick

0
0
This paper investigates the radio resource management (RRM) design for multiuser rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA), accounting for various characteristics of practical wireless systems, such as the use of discrete rates, the inability to serve all users, and the imperfect successive interference cancellation (SIC). Specifically, failure to consider these characteristics in RRM design may lead to inefficient use of radio resources. Therefore, we formulate the RRM of RSMA as optimization problems to maximize respectively the weighted sum rate (WSR) and weighted energy efficiency (WEE), and jointly optimize the beamforming, user admission, discrete/continuous rates, accounting for imperfect SIC, which result in nonconvex mixed-integer nonlinear programs that are challenging to solve. Despite the difficulty of the optimization problems, we develop algorithms that can find high-quality solutions. We show via simulations that carefully accounting for the aforementioned characteristics, can lead to significant gains. Precisely, by considering that transmission rates are discrete, the transmit power can be utilized more intelligently, allocating just enough power to guarantee a given discrete rate. Additionally, we reveal that user admission plays a crucial role in RSMA, enabling additional gains compared to random admission by facilitating the servicing of selected users with mutually beneficial channel characteristics. Furthermore, provisioning for possibly imperfect SIC makes RSMA more robust and reliable.
5/1/2024