Planning of Truck Platooning for Road-Network Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem
2404.13512

0
0
Abstract
Truck platooning, a linking technology of trucks on the highway, has gained enormous attention in recent years due to its benefits in energy and operation cost savings. However, most existing studies on truck platooning limit their focus on scenarios in which each truck can serve only one customer demand and is thus with a specified origin-destination pair, so only routing and time schedules are considered. Nevertheless, in real-world logistics, each truck may need to serve multiple customers located at different places, and the operator has to determine not only the routing and time schedules of each truck but also the set of customers allocated to each truck and their sequence to visit. This is well known as a capacitated vehicle routing problem with time windows (CVRPTW), and considering the application of truck platooning in such a problem entails new modeling frameworks and tailored solution algorithms. In light of this, this study makes the first attempt to optimize the truck platooning plan for a road-network CVRPTW to minimize the total operation cost, including vehicles' fixed dispatch cost and energy cost, while fulfilling all delivery demands within their time window constraints. Specifically, the operation plan will dictate the number of trucks to be dispatched, the set of customers, and the routing and time schedules for each truck. In addition, the modeling framework is constructed based on a road network instead of a traditional customer node graph to better resemble and facilitate the platooning operation. A 3-stage algorithm embedded with a route-then-schedule scheme, dynamic programming, and modified insertion heuristic, is developed to solve the proposed model in a timely manner. Numerical experiments are conducted to validate the modeling framework, demonstrate the performance of the proposed solution algorithm, and quantify the benefit of truck platooning.
Create account to get full access
Overview
- This research paper focuses on planning truck platooning operations for the Road-Network Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (RCVRP).
- Truck platooning involves coordinating a group of trucks to travel in close proximity, improving fuel efficiency and traffic flow.
- The RCVRP is a complex logistics optimization problem that aims to find the most efficient routes for a fleet of vehicles to serve a set of customer demands.
- The researchers propose a novel optimization framework that integrates truck platooning into the RCVRP, considering factors like road network constraints and vehicle capacity limits.
Plain English Explanation
The paper tackles the challenge of planning truck platooning operations for a specific type of logistics problem called the Road-Network Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (RCVRP). Truck platooning is a technology that allows a group of trucks to travel closely together, which can improve fuel efficiency and traffic flow.
The RCVRP is a complex optimization problem that aims to find the most efficient routes for a fleet of vehicles to deliver goods to customers, while considering factors like the road network and the capacity of the vehicles. The researchers developed a new optimization framework that integrates truck platooning into the RCVRP, taking into account the constraints of the road network and the limits on how much each vehicle can carry.
By combining truck platooning with the RCVRP, the researchers hope to improve the overall efficiency of logistics operations, potentially leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact. This research could have important implications for the future of transportation and logistics.
Technical Explanation
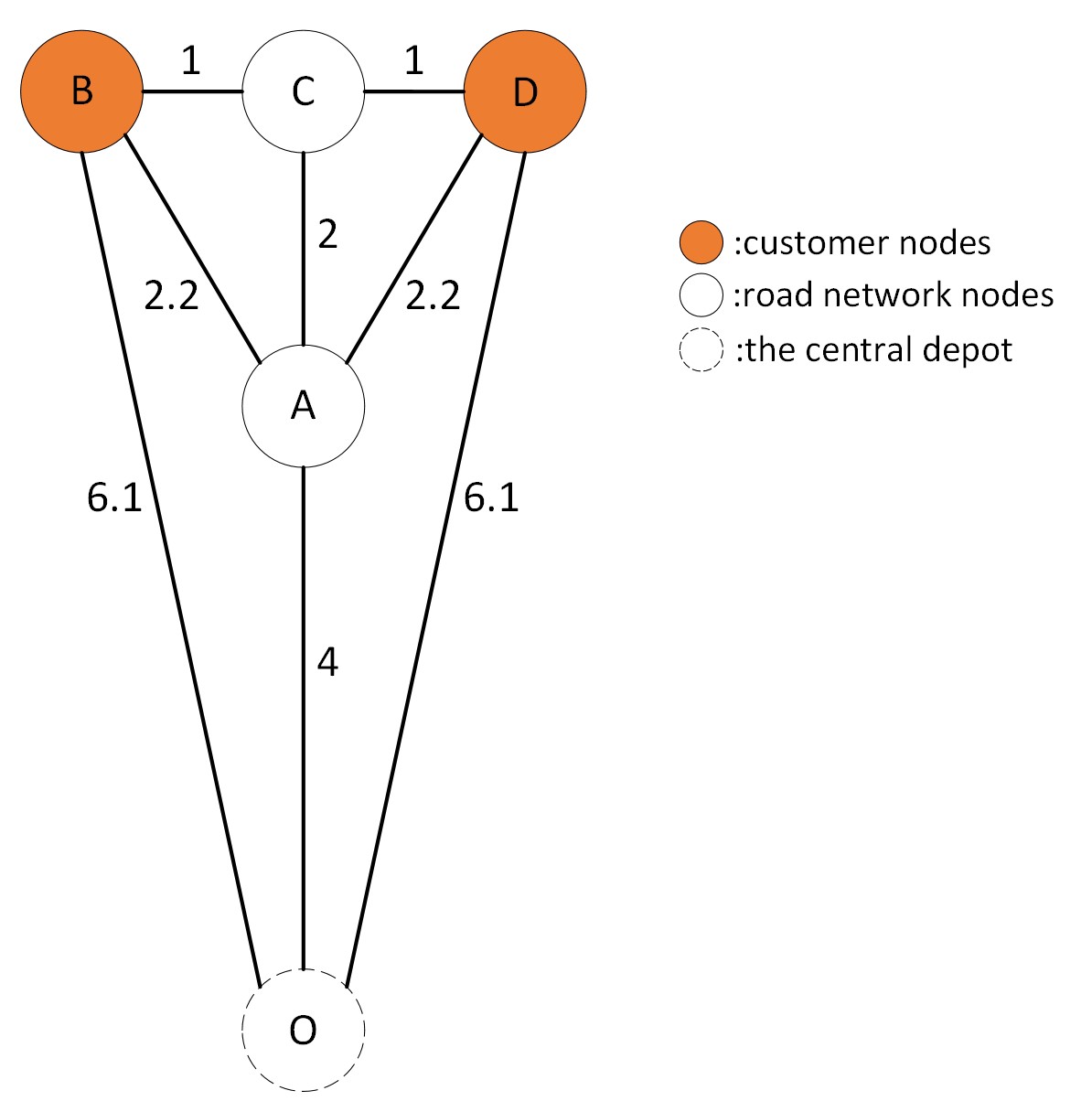
The researchers formulate the Road-Network Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem with Truck Platooning (RCVRP-TP) as a mixed-integer linear programming problem. They consider a road network with a set of nodes (customer locations) and a set of edges (road segments) with associated travel times and capacities.
The objective is to determine the optimal routes for a fleet of vehicles to serve all customer demands while minimizing the total travel time and the number of vehicles used. The key decision variables include the assignment of customers to vehicles, the sequence of visits for each vehicle, and the formation of truck platoons.
The researchers develop a novel optimization framework that integrates truck platooning into the RCVRP. Their approach considers factors such as the maximum platoon size, the impact of platooning on travel times, and the constraints of the road network. They also incorporate vehicle capacity limits and ensure that customer demands are satisfied.
The researchers evaluate their proposed approach using realistic case studies and compare it to traditional RCVRP solutions without platooning. Their results demonstrate the potential benefits of integrating truck platooning, including reduced travel times and fuel consumption.
Critical Analysis
The researchers acknowledge several limitations and areas for further research. For instance, they assume perfect coordination and communication between the trucks in a platoon, which may not always be realistic in practice. Additionally, the impact of factors like traffic congestion and weather conditions on platooning operations is not explicitly considered.
Furthermore, the researchers focus on the strategic planning aspect of truck platooning, but the operational and control challenges, such as dynamic platoon formation and dissolution, are not addressed in depth.
Future research could explore more realistic scenarios, including the integration of other transportation modes (e.g., drones, autonomous vehicles) and the incorporation of stochastic elements (e.g., uncertain travel times, customer demands) into the optimization framework.
Conclusion
This research paper presents a novel optimization framework for planning truck platooning operations within the context of the Road-Network Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem. By integrating truck platooning into the RCVRP, the researchers aim to improve the overall efficiency of logistics operations, potentially leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
The proposed approach demonstrates the potential benefits of combining advanced transportation technologies, such as truck platooning, with complex logistics optimization problems. As the field of transportation and logistics continues to evolve, this research highlights the importance of exploring innovative solutions that can enhance the sustainability and resilience of supply chain networks.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers

Optimization-based Learning for Dynamic Load Planning in Trucking Service Networks
Ritesh Ojha, Wenbo Chen, Hanyu Zhang, Reem Khir, Alan Erera, Pascal Van Hentenryck

0
0
The load planning problem is a critical challenge in service network design for parcel carriers: it decides how many trailers to assign for dispatch over time between pairs of terminals. Another key challenge is to determine a flow plan, which specifies how parcel volumes are assigned to planned loads. This paper considers the Outbound Load Planning Problem (OLPP) that considers flow and load planning challenges jointly in order to adjust loads and flows as the demand forecast changes over time before the day of operations in a terminal. The paper aims at developing a decision-support tool to inform planners making these decisions at terminals across the network. The paper formulates the OLPP as a mixed-integer programming model and shows that it admits a large number of symmetries in a network where each commodity can be routed through primary and alternate terminals. As a result, an optimization solver may return fundamentally different solutions to closely related problems, confusing planners and reducing trust in optimization. To remedy this limitation, this paper proposes a lexicographical optimization approach that eliminates those symmetries by generating optimal solutions staying close to a reference plan. Moreover, this paper designs an optimization proxy that addresses the computational challenges of the optimization model. The optimization proxy combines a machine-learning model and a repair procedure to find near-optimal solutions that satisfy real-time constraints imposed by planners in the loop. An extensive computational study on industrial instances shows that the optimization proxy is orders of magnitude faster for generating solutions that are consistent with each other. The proposed approach also demonstrates the benefits of the OLPP for load consolidation and the significant savings obtained from combining machine learning and optimization.
4/30/2024
🏅
Using Reinforcement Learning for the Three-Dimensional Loading Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem
Stefan Schoepf, Stephen Mak, Julian Senoner, Liming Xu, Netland Torbjorn, Alexandra Brintrup

0
0
Heavy goods vehicles are vital backbones of the supply chain delivery system but also contribute significantly to carbon emissions with only 60% loading efficiency in the United Kingdom. Collaborative vehicle routing has been proposed as a solution to increase efficiency, but challenges remain to make this a possibility. One key challenge is the efficient computation of viable solutions for co-loading and routing. Current operations research methods suffer from non-linear scaling with increasing problem size and are therefore bound to limited geographic areas to compute results in time for day-to-day operations. This only allows for local optima in routing and leaves global optimisation potential untouched. We develop a reinforcement learning model to solve the three-dimensional loading capacitated vehicle routing problem in approximately linear time. While this problem has been studied extensively in operations research, no publications on solving it with reinforcement learning exist. We demonstrate the favourable scaling of our reinforcement learning model and benchmark our routing performance against state-of-the-art methods. The model performs within an average gap of 3.83% to 8.10% compared to established methods. Our model not only represents a promising first step towards large-scale logistics optimisation with reinforcement learning but also lays the foundation for this research stream. GitHub: https://github.com/if-loops/3L-CVRP
6/12/2024
📈
Dyna-Style Learning with A Macroscopic Model for Vehicle Platooning in Mixed-Autonomy Traffic
Yichuan Zou, Li Jin, Xi Xiong

0
0
Platooning of connected and autonomous vehicles (CAVs) plays a vital role in modernizing highways, ushering in enhanced efficiency and safety. This paper explores the significance of platooning in smart highways, employing a coupled partial differential equation (PDE) and ordinary differential equation (ODE) model to elucidate the complex interaction between bulk traffic flow and CAV platoons. Our study focuses on developing a Dyna-style planning and learning framework tailored for platoon control, with a specific goal of reducing fuel consumption. By harnessing the coupled PDE-ODE model, we improve data efficiency in Dyna-style learning through virtual experiences. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of our macroscopic model in modeling platoons within mixed-autonomy settings, demonstrating a notable $10.11%$ reduction in vehicular fuel consumption compared to conventional approaches.
5/6/2024
VRPD-DT: Vehicle Routing Problem with Drones Under Dynamically Changing Traffic Conditions
Navid Imran, Myounggyu Won

0
0
The vehicle routing problem with drones (VRP-D) is to determine the optimal routes of trucks and drones such that the total operational cost is minimized in a scenario where the trucks work in tandem with the drones to deliver parcels to customers. While various heuristic algorithms have been developed to address the problem, existing solutions are built based on simplistic cost models, overlooking the temporal dynamics of the costs, which fluctuate depending on the dynamically changing traffic conditions. In this paper, we present a novel problem called the vehicle routing problem with drones under dynamically changing traffic conditions (VRPD-DT) to address the limitation of existing VRP-D solutions. We design a novel cost model that factors in the actual travel distance and projected travel time, computed using a machine learning-driven travel time prediction algorithm. A variable neighborhood descent (VND) algorithm is developed to find the optimal truck-drone routes under the dynamics of traffic conditions through incorporation of the travel time prediction model. A simulation study was performed to evaluate the performance compared with a state-of-the-art VRP-D heuristic solution. The results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms the state-of-the-art algorithm in various delivery scenarios.
4/16/2024