On the Potential of an Independent Avatar to Augment Metaverse Social Networks

0

Sign in to get full access
Overview
- This paper explores the potential of an independent avatar to enhance user socialization time in the metaverse.
- The researchers investigate the impact of an autonomous avatar on user engagement and social interactions within a virtual environment.
- The study examines various factors that may influence the avatar's ability to augment socialization, such as its level of autonomy and the user's perception of the avatar.
Plain English Explanation
The metaverse is a rapidly evolving digital space where people can interact, collaborate, and explore virtual worlds. In this context, the researchers wanted to understand how an independent avatar – a digital representation of a person that can act and behave autonomously – could potentially enhance the social experience for users.
Imagine you're in a virtual meeting or event, and your avatar can initiate conversations, respond to others, and even suggest activities or topics to discuss. This autonomous behavior could help you feel more engaged and connected, leading to longer and more meaningful interactions with other users.
The researchers looked at different aspects of the avatar's design and functionality, such as how much control the user has over the avatar's actions, and how realistic or lifelike the avatar appears. They wanted to see how these factors might influence the user's willingness to spend time socializing in the virtual environment.
By understanding the potential benefits of an independent avatar, the researchers hope to inform the design and development of more immersive and engaging metaverse experiences, where users feel empowered to connect and collaborate in meaningful ways.
Technical Explanation
The paper examines the potential of an independent avatar to augment user socialization time in the metaverse. The researchers propose a conceptual model that considers the autonomy of the avatar, the user's perception of the avatar, and the resulting impact on socialization time.
The study explores the relationship between the avatar's level of autonomy and the user's socialization time. Avatars with higher levels of autonomy, such as the ability to initiate conversations or suggest activities, may be more likely to engage users and encourage longer social interactions.
Additionally, the researchers investigate how the user's perception of the avatar, in terms of its realism, lifelikeness, and embodiment, can influence the socialization time. Avatars that are perceived as more realistic and relatable may foster a stronger sense of connection and engagement, leading to increased socialization.
The paper presents a theoretical framework that outlines the key variables and their potential relationships. This model can serve as a foundation for future empirical studies to test the hypotheses and explore the practical implications of independent avatars in the metaverse.
Critical Analysis
The paper presents a thoughtful and well-structured conceptual model for understanding the potential of independent avatars to augment user socialization time in the metaverse. The researchers have identified relevant factors, such as avatar autonomy and user perception, that warrant further investigation.
However, the paper is primarily theoretical, and the proposed model has not yet been empirically tested. Future research should focus on validating the model through experimental studies or observational data from real-world metaverse environments. This would help to confirm the hypothesized relationships and provide more tangible insights into the practical implementation and benefits of independent avatars.
Additionally, the paper could benefit from a more comprehensive discussion of potential limitations and areas for further research. For example, the researchers could explore the ethical implications of highly autonomous avatars, such as concerns around privacy, data privacy, and the potential for misuse or manipulation.
Overall, the paper provides a solid conceptual foundation for understanding the role of independent avatars in enhancing user socialization in the metaverse. Further empirical research and a more detailed examination of potential challenges and limitations would strengthen the insights and contribute to the ongoing development of more engaging and immersive virtual experiences.
Conclusion
This paper presents a conceptual model for exploring the potential of independent avatars to augment user socialization time in the metaverse. The researchers hypothesize that avatars with higher levels of autonomy and more realistic/lifelike representations can foster stronger user engagement and lead to longer social interactions within virtual environments.
The proposed framework offers a valuable starting point for future research and development in this area. By better understanding the factors that influence user socialization in the metaverse, researchers and designers can work to create more immersive and engaging virtual experiences that facilitate meaningful connections and collaboration among users.
As the metaverse continues to evolve, the integration of autonomous and personalized avatars may play a crucial role in enhancing the overall user experience and fostering a greater sense of presence and social connection within these virtual worlds.
This summary was produced with help from an AI and may contain inaccuracies - check out the links to read the original source documents!
Related Papers


0
On the Potential of an Independent Avatar to Augment Metaverse Social Networks
Theofanis P. Raptis, Chiara Boldrini, Marco Conti, Andrea Passarella
We present a computational modelling approach which targets capturing the specifics on how to virtually augment a Metaverse user's available social time capacity via using an independent and autonomous version of her digital representation in the Metaverse. We motivate why this is a fundamental building block to model large-scale social networks in the Metaverse, and emerging properties herein. We envision a Metaverse-focused extension of the traditional avatar concept: An avatar can be as well programmed to operate independently when its user is not controlling it directly, thus turning it into an agent-based digital human representation. This way, we highlight how such an independent avatar could help its user to better navigate their social relationships and optimize their socializing time in the Metaverse by (partly) offloading some interactions to the avatar. We model the setting and identify the characteristic variables by using selected concepts from social sciences: ego networks, social presence, and social cues. Then, we formulate the problem of maximizing the user's non-avatar-mediated spare time as a linear optimization. Finally, we analyze the feasible region of the problem and we present some initial insights on the spare time that can be achieved for different parameter values of the avatar-mediated interactions.
Read more5/10/2024
📶

0
Privacy-preserving Pseudonym Schemes for Personalized 3D Avatars in Mobile Social Metaverses
Cheng Su, Xiaofeng Luo, Zhenmou Liu, Jiawen Kang, Min Hao, Zehui Xiong, Zhaohui Yang, Chongwen Huang
The emergence of mobile social metaverses, a novel paradigm bridging physical and virtual realms, has led to the widespread adoption of avatars as digital representations for Social Metaverse Users (SMUs) within virtual spaces. Equipped with immersive devices, SMUs leverage Edge Servers (ESs) to deploy their avatars and engage with other SMUs in virtual spaces. To enhance immersion, SMUs incline to opt for 3D avatars for social interactions. However, existing 3D avatars are typically generated through scanning the real faces of SMUs, which can raise concerns regarding information privacy and security, such as profile identity leakages. To tackle this, we introduce a new framework for personalized 3D avatar construction, leveraging a two-layer network model that provides SMUs with the option to customize their personal avatars for privacy preservation. Specifically, our approach introduces avatar pseudonyms to jointly safeguard the profile and digital identity privacy of the generated avatars. Then, we design a novel metric named Privacy of Personalized Avatars (PoPA), to evaluate effectiveness of the avatar pseudonyms. To optimize pseudonym resource, we model the pseudonym distribution process as a Stackelberg game and employ Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) to learn equilibrium strategies under incomplete information. Simulation results validate the efficacy and feasibility of our proposed schemes for mobile social metaverses.
Read more6/18/2024
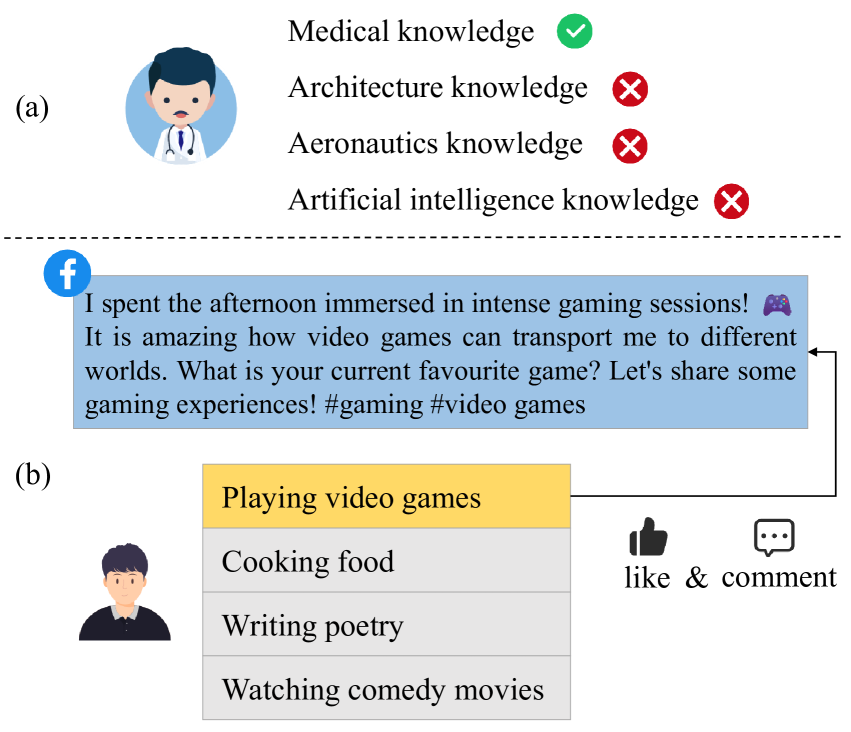

0
Knowledge Boundary and Persona Dynamic Shape A Better Social Media Agent
Junkai Zhou, Liang Pang, Ya Jing, Jia Gu, Huawei Shen, Xueqi Cheng
Constructing personalized and anthropomorphic agents holds significant importance in the simulation of social networks. However, there are still two key problems in existing works: the agent possesses world knowledge that does not belong to its personas, and it cannot eliminate the interference of diverse persona information on current actions, which reduces the personalization and anthropomorphism of the agent. To solve the above problems, we construct the social media agent based on personalized knowledge and dynamic persona information. For personalized knowledge, we add external knowledge sources and match them with the persona information of agents, thereby giving the agent personalized world knowledge. For dynamic persona information, we use current action information to internally retrieve the persona information of the agent, thereby reducing the interference of diverse persona information on the current action. To make the agent suitable for social media, we design five basic modules for it: persona, planning, action, memory and reflection. To provide an interaction and verification environment for the agent, we build a social media simulation sandbox. In the experimental verification, automatic and human evaluations demonstrated the effectiveness of the agent we constructed.
Read more4/3/2024


0
Perception in Pixels: Understanding Avatar Representation in Video-Mediated Collaborative Interactions
Pitch Sinlapanuntakul, Mark Zachry
Despite the abundance of research concerning virtual reality (VR) avatars, the impact of screen-based or augmented reality (AR) avatars for real-world applications remain relatively unexplored. Notably, there is a lack of research examining video-mediated collaborative interaction experiences using AR avatars for goal-directed group activities. This study bridges this gap with a mixed-methods, quasi-experimental user study that investigates video-based small-group interactions when employing AR avatars as opposed to traditional video for user representation. We found that the use of avatars positively influenced self-esteem and video-based collaboration satisfaction. In addition, our group interview findings highlight experiences and perceptions regarding the dynamic use of avatars in video-mediated collaborative interactions, including benefits, challenges, and factors that would influence a decision to use avatars. This study contributes an empirical understanding of avatar representation in mediating video-based collaborative interactions, implications and perceptions surrounding the adoption of AR avatars, and a comprehensive comparison of key characteristics between user representations.
Read more5/8/2024